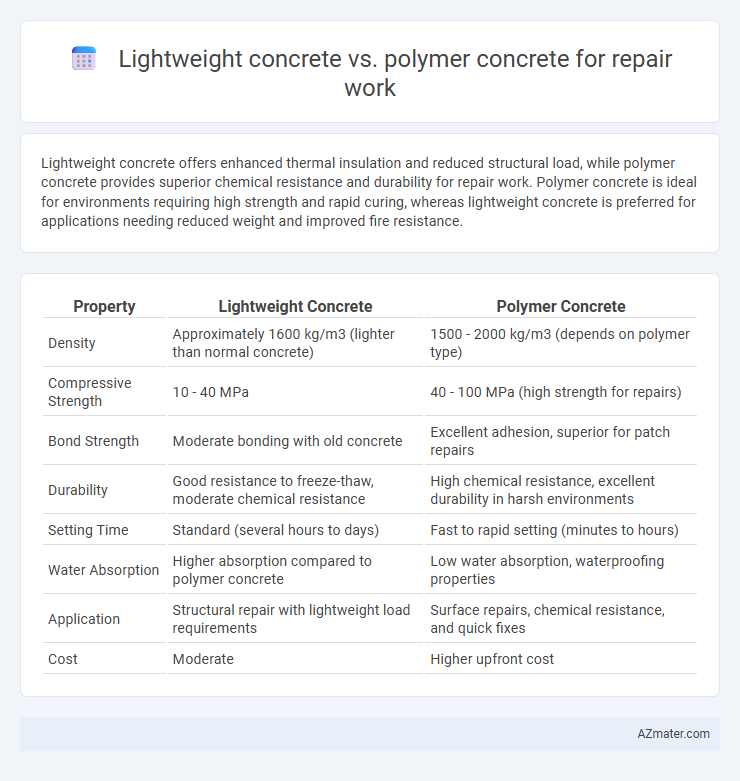
Lightweight concrete offers enhanced thermal insulation and reduced structural load, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability for repair work. Polymer concrete is ideal for environments requiring high strength and rapid curing, whereas lightweight concrete is preferred for applications needing reduced weight and improved fire resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lightweight Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Approximately 1600 kg/m3 (lighter than normal concrete) | 1500 - 2000 kg/m3 (depends on polymer type) |
| Compressive Strength | 10 - 40 MPa | 40 - 100 MPa (high strength for repairs) |
| Bond Strength | Moderate bonding with old concrete | Excellent adhesion, superior for patch repairs |
| Durability | Good resistance to freeze-thaw, moderate chemical resistance | High chemical resistance, excellent durability in harsh environments |
| Setting Time | Standard (several hours to days) | Fast to rapid setting (minutes to hours) |
| Water Absorption | Higher absorption compared to polymer concrete | Low water absorption, waterproofing properties |
| Application | Structural repair with lightweight load requirements | Surface repairs, chemical resistance, and quick fixes |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher upfront cost |
Introduction to Concrete Repair Materials
Lightweight concrete features lower density and enhanced thermal insulation properties, making it suitable for structural repairs requiring reduced load. Polymer concrete incorporates polymers as binders, offering superior chemical resistance and rapid curing for durable surface restoration. Both materials deliver distinct advantages in concrete repair, with selection dependent on specific project requirements such as load capacity and environmental exposure.
Overview of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density achieved through the use of lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay or shale, offers excellent thermal insulation and reduced structural load, making it ideal for repair work in buildings requiring weight-sensitive applications. Its porosity enhances durability and fire resistance, contributing to extended service life in distressed structures. Compared to polymer concrete, lightweight concrete provides cost-effective solutions with good compressive strength and ease of application in patching and structural repairs.
Overview of Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete is a composite material consisting of polymer binder and aggregates, offering superior chemical resistance, high compressive strength, and excellent durability compared to traditional lightweight concrete. It is ideal for repair work in harsh environments due to its rapid curing time and strong adhesion to existing concrete surfaces. Polymer concrete's enhanced mechanical properties make it suitable for structural repairs where longevity and resistance to corrosion or abrasion are critical.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Lightweight concrete offers lower density and improved thermal insulation, making it ideal for reducing structural load during repair work. Polymer concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance, higher compressive strength, and enhanced bonding capabilities, which provide durability in aggressive environments. Both materials vary significantly in shrinkage behavior and curing times, influencing their suitability based on specific repair conditions and performance requirements.
Strength and Durability Factors
Lightweight concrete offers moderate compressive strength and enhanced thermal insulation, making it suitable for non-structural repair work that requires reduced load. Polymer concrete demonstrates superior strength and chemical resistance due to its resin binder, providing exceptional durability in harsh environmental conditions and heavy load applications. For repair projects prioritizing long-term durability and high strength, polymer concrete outperforms lightweight concrete by maintaining structural integrity and resisting degradation over time.
Bonding Performance and Adhesion
Lightweight concrete offers moderate bonding performance due to its porous structure, which enhances mechanical interlocking but may require surface treatment to improve adhesion in repair work. Polymer concrete exhibits superior adhesion because its resin matrix chemically bonds with existing substrates, providing enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors. The choice between lightweight and polymer concrete hinges on the specific repair requirements, with polymer concrete favored for high-bond strength applications and lightweight concrete selected for repairs needing reduced structural load.
Installation Process and Workability
Lightweight concrete offers ease of installation due to its reduced density and enhanced workability, allowing for faster application and better handling during repair work. Polymer concrete, composed of polymer resins and aggregates, provides superior bonding and chemical resistance but requires precise mixing ratios and curing conditions, which can complicate the installation process. The choice between these materials depends on project-specific requirements such as structural load, environmental exposure, and desired repair longevity.
Cost Analysis: Lightweight vs Polymer Concrete
Lightweight concrete generally offers a lower initial material cost compared to polymer concrete, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale repair projects. Polymer concrete, while more expensive upfront due to specialized resins, often provides superior durability and chemical resistance that can reduce long-term maintenance expenses and repair frequency. Cost analysis should balance the immediate savings of lightweight concrete with the potential lifecycle cost benefits of polymer concrete in aggressive or high-stress environments.
Ideal Applications and Limitations
Lightweight concrete is ideal for repair work involving structural elements requiring reduced dead load, such as bridge decks and precast panels, due to its good thermal insulation and fire resistance properties. Polymer concrete is best suited for repairs in environments exposed to aggressive chemicals, moisture, and heavy traffic, owing to its superior chemical resistance, low permeability, and high mechanical strength. Limitations include lightweight concrete's lower compressive strength compared to traditional concrete, making it unsuitable for high-load applications, while polymer concrete can be cost-prohibitive and requires specialized curing conditions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Repair Work
Lightweight concrete offers advantages in ease of handling and reduced structural load, making it suitable for non-structural repairs and applications requiring thermal insulation. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance, high strength, and excellent adhesion, ideal for structural repairs exposed to harsh environments. Selecting the right material depends on the specific repair conditions, load requirements, and environmental factors to ensure durability and performance.
Infographic: Lightweight concrete vs Polymer concrete for Repair work
 azmater.com
azmater.com