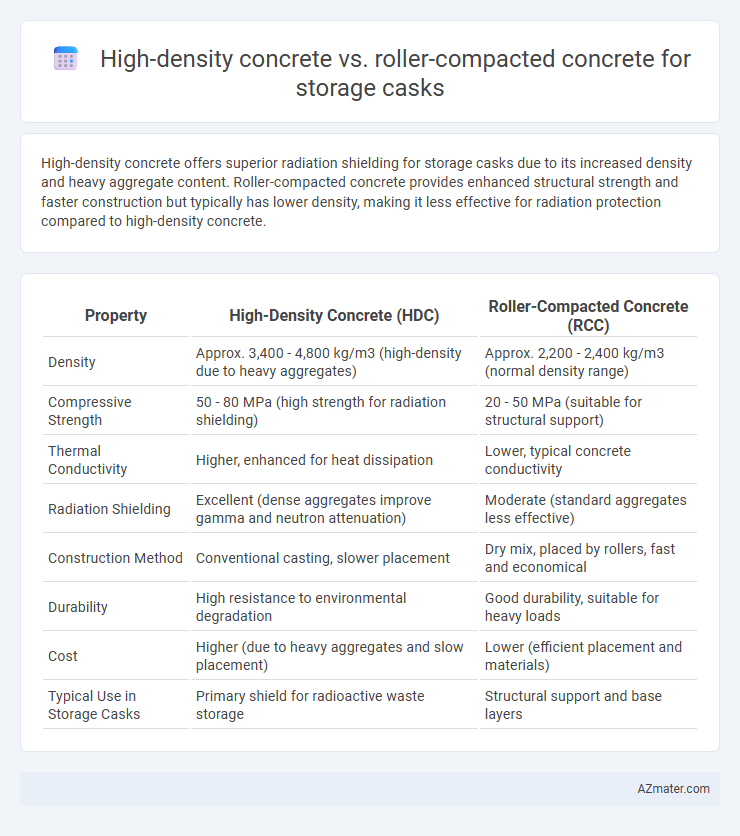
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding for storage casks due to its increased density and heavy aggregate content. Roller-compacted concrete provides enhanced structural strength and faster construction but typically has lower density, making it less effective for radiation protection compared to high-density concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete (HDC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Approx. 3,400 - 4,800 kg/m3 (high-density due to heavy aggregates) | Approx. 2,200 - 2,400 kg/m3 (normal density range) |
| Compressive Strength | 50 - 80 MPa (high strength for radiation shielding) | 20 - 50 MPa (suitable for structural support) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher, enhanced for heat dissipation | Lower, typical concrete conductivity |
| Radiation Shielding | Excellent (dense aggregates improve gamma and neutron attenuation) | Moderate (standard aggregates less effective) |
| Construction Method | Conventional casting, slower placement | Dry mix, placed by rollers, fast and economical |
| Durability | High resistance to environmental degradation | Good durability, suitable for heavy loads |
| Cost | Higher (due to heavy aggregates and slow placement) | Lower (efficient placement and materials) |
| Typical Use in Storage Casks | Primary shield for radioactive waste storage | Structural support and base layers |
Introduction to Storage Cask Materials
Storage cask materials for radioactive waste management primarily involve high-density concrete and roller-compacted concrete, each offering distinct structural and shielding properties. High-density concrete is favored for its superior radiation attenuation due to the inclusion of heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, ensuring enhanced protection. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid placement and cost efficiency with adequate shielding, achieved through a drier mix compacted by rollers, making it suitable for large-scale containment structures.
Overview of High-Density Concrete
High-density concrete (HDC) offers enhanced shielding properties due to its increased density achieved by incorporating heavy aggregates such as barite or magnetite, making it ideal for storage casks in nuclear applications. This material provides superior radiation attenuation compared to conventional roller-compacted concrete (RCC), which typically uses standard aggregates and focuses on rapid placement and cost efficiency. The increased density and shielding effectiveness of HDC make it essential for protecting against gamma and neutron radiation in nuclear waste containment.
Understanding Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers a dense, low-porosity structure ideal for storage casks, providing enhanced durability and radiation shielding comparable to that of high-density concrete. Its placement method using heavy rollers achieves uniform compaction and accelerated construction timelines, reducing costs without compromising structural integrity. RCC's optimized mixture of coarse aggregates and minimal cement paste enhances compressive strength, making it a cost-effective alternative for secure cask containment.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
High-density concrete exhibits superior compressive strength and enhanced gamma radiation shielding, making it ideal for storage cask applications requiring maximum durability and protection. Roller-compacted concrete, while offering excellent compressive strength and rapid construction benefits, typically presents lower density and slightly reduced shielding capacity compared to traditional high-density mixes. The mechanical performance of high-density concrete includes increased modulus of elasticity and lower permeability, which are critical for the long-term integrity and safety of nuclear waste storage casks.
Radiation Shielding Capabilities
High-density concrete, composed of heavyweight aggregates like barite or magnetite, offers superior radiation shielding for storage casks due to its higher atomic number and density, effectively attenuating gamma rays and neutrons. Roller-compacted concrete, while cost-effective and mechanically robust, typically uses conventional aggregates resulting in lower density and reduced shielding efficiency. The enhanced radiation attenuation properties of high-density concrete make it the preferred material for storage casks requiring stringent radiation protection.
Durability and Longevity
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding and enhanced durability for storage casks, with increased resistance to environmental degradation and structural stress. Roller-compacted concrete provides cost-effective construction with rapid placement but may require additional additives or curing techniques to achieve comparable long-term durability. Studies indicate high-density concrete maintains integrity longer under harsh storage conditions, making it preferable for prolonged waste containment.
Construction Methods and Speed
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding for storage casks but requires traditional casting methods, which involve longer curing times and intricate formwork, slowing the overall construction process. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) enables faster construction with its dry-mix consistency, allowing for rapid placement using paving equipment and minimal formwork, significantly reducing curing duration. The choice between high-density concrete and RCC directly impacts project timelines, with RCC favored for expedited construction while high-density concrete ensures optimal safety performance.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
High-density concrete offers superior radiation shielding and durability for storage casks but involves higher material and production costs compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC), which provides a cost-effective alternative with faster placement and reduced labor expenses. RCC's efficient construction process lowers overall project timelines and labor costs, making it advantageous for large-volume applications despite slightly lower density and shielding performance. Cost efficiency analysis favors RCC in projects prioritizing budget and speed, while high-density concrete remains optimal for critical shielding requirements demanding maximum protection.
Environmental Impacts
High-density concrete (HDC) offers superior radiation shielding for storage casks but often involves higher cement content, leading to increased CO2 emissions during production. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) uses less cement and employs energy-efficient compaction methods, significantly reducing its carbon footprint while maintaining adequate strength and durability for cask storage. Lifecycle assessments indicate RCC's lower environmental impact compared to HDC, making it a more sustainable choice for large-scale storage cask construction.
Application Suitability for Storage Casks
High-density concrete offers enhanced radiation shielding properties essential for nuclear storage casks, providing superior protection against gamma and neutron radiation. Roller-compacted concrete, while cost-effective and rapid to place, typically lacks the specific density and uniformity necessary for optimal radiation attenuation in storage cask applications. Therefore, high-density concrete is preferred for storage casks requiring rigorous containment and shielding performance.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Storage cask
 azmater.com
azmater.com