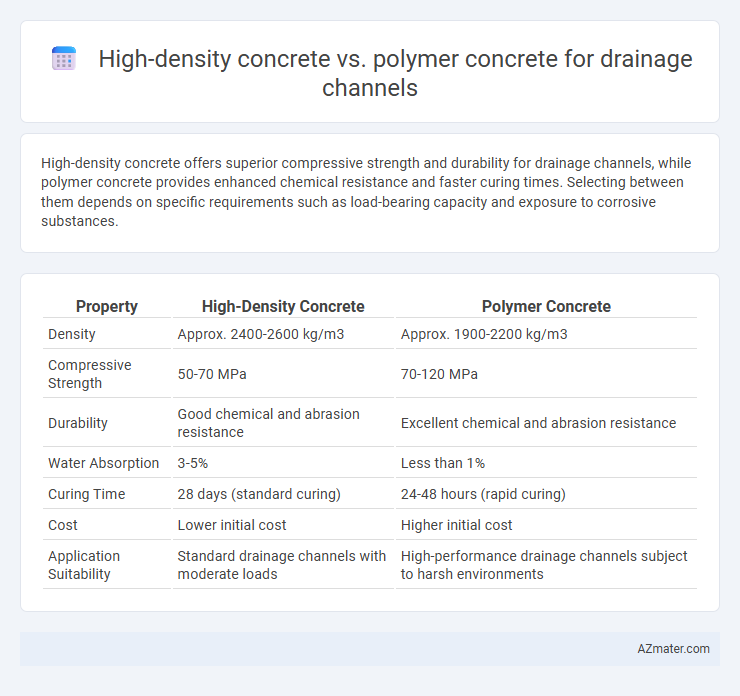
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability for drainage channels, while polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and faster curing times. Selecting between them depends on specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity and exposure to corrosive substances.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Approx. 2400-2600 kg/m3 | Approx. 1900-2200 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 50-70 MPa | 70-120 MPa |
| Durability | Good chemical and abrasion resistance | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Water Absorption | 3-5% | Less than 1% |
| Curing Time | 28 days (standard curing) | 24-48 hours (rapid curing) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Application Suitability | Standard drainage channels with moderate loads | High-performance drainage channels subject to harsh environments |
Overview of Drainage Channel Materials
High-density concrete offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for drainage channels subjected to heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. Polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and rapid curing times, which are beneficial for channels exposed to corrosive substances and requiring quick installation. Selecting the appropriate material depends on specific project demands such as load capacity, chemical exposure, and installation speed.
What is High-Density Concrete?
High-density concrete is a specialized construction material characterized by its increased mass per unit volume, typically achieved by incorporating heavy aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite. This type of concrete offers enhanced radiation shielding and improved structural durability, making it suitable for drainage channels requiring high load-bearing capacity and resistance to environmental stressors. When compared to polymer concrete, high-density concrete provides greater weight and impact resistance but may have lower chemical resistance and longer curing times.
What is Polymer Concrete?
Polymer concrete is a composite material consisting of a mixture of aggregates bound together by a polymer resin, typically epoxy or polyester, which provides superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Unlike high-density concrete that relies on heavy aggregates for density and strength, polymer concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive environments and better adhesion to channel components, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to corrosive substances. Its fast curing time and resistance to freeze-thaw cycles reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of drainage infrastructure.
Key Properties of High-Density Concrete
High-density concrete is characterized by its high compressive strength, enhanced radiation shielding, and superior durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty drainage channels subjected to aggressive environmental conditions. It typically incorporates heavyweight aggregates such as barite or magnetite, resulting in increased density and improved structural integrity compared to polymer concrete. Its resistance to chemical attack and wear ensures long-term performance in water management systems where load-bearing capacity and durability are critical.
Key Properties of Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability compared to high-density concrete, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to aggressive environments. Its high tensile and flexural strength combined with low permeability minimizes water infiltration and corrosion risks. Additionally, polymer concrete exhibits excellent bonding characteristics and faster curing times, ensuring longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in drainage applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength typically ranging from 40 to 60 MPa, making it ideal for heavy load-bearing drainage channels exposed to traffic stress. Polymer concrete exhibits enhanced chemical resistance and exceptional durability against aggressive waterborne chemicals, extending service life in corrosive environments. While high-density concrete provides robust mechanical strength, polymer concrete excels in resisting environmental degradation, ensuring greater longevity in drainage applications subjected to harsh chemical exposure.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
High-density concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its dense matrix and low porosity, effectively withstanding aggressive wastewater and acidic environments in drainage channels. Polymer concrete offers enhanced corrosion resistance by utilizing resins like epoxy and polyester, which prevent water ingress and chemical attack better than traditional cementitious materials. Both materials are suitable for drainage applications, with polymer concrete providing longer service life against chemical degradation, while high-density concrete offers cost-effective durability in moderately aggressive conditions.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy load drainage channels, but it requires longer curing times and specialized equipment during installation. Polymer concrete accelerates installation with faster curing and easier handling due to its lightweight properties, yet may need more frequent inspections to address potential chemical resistance issues in aggressive environments. Maintenance of high-density concrete channels typically involves less frequent repairs due to its resilience, whereas polymer concrete requires proactive upkeep to prevent surface deterioration and maintain structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle
High-density concrete offers lower initial material costs compared to polymer concrete, which involves higher expenses due to specialized resins and additives. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over the drainage channel's lifecycle. Evaluating total cost of ownership, polymer concrete can be more economical in corrosive environments despite its upfront price, while high-density concrete suits applications with less aggressive conditions and budget constraints.
Best Applications for Each Material
High-density concrete excels in drainage channel applications requiring superior load-bearing capacity, radiation shielding, and high durability under heavy traffic or industrial environments. Polymer concrete is best suited for drainage channels exposed to aggressive chemicals, corrosive environments, and areas needing rapid installation with minimal curing time. Selecting high-density concrete supports long-term structural integrity, while polymer concrete optimizes resistance to chemical attack and flexibility in maintenance.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drainage channel
 azmater.com
azmater.com