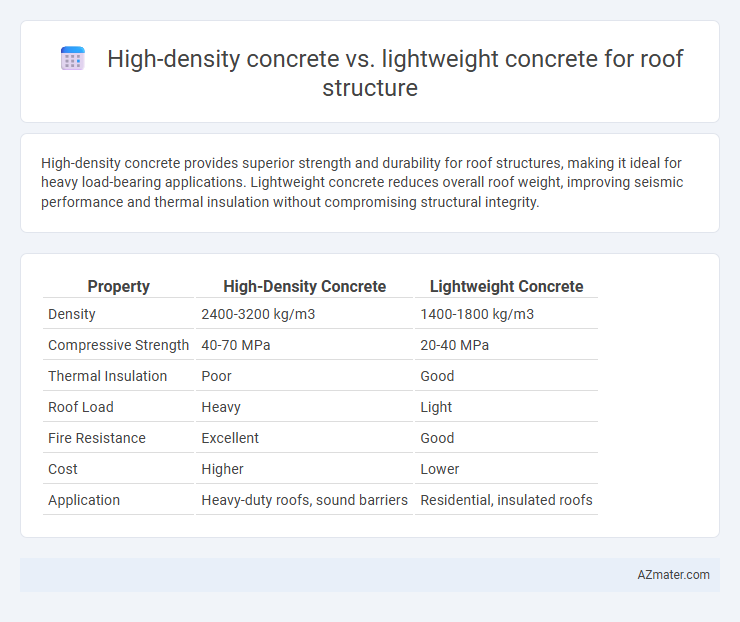
High-density concrete provides superior strength and durability for roof structures, making it ideal for heavy load-bearing applications. Lightweight concrete reduces overall roof weight, improving seismic performance and thermal insulation without compromising structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2400-3200 kg/m3 | 1400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 40-70 MPa | 20-40 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Poor | Good |
| Roof Load | Heavy | Light |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application | Heavy-duty roofs, sound barriers | Residential, insulated roofs |
Introduction to Roof Structure Concrete Types
High-density concrete offers superior strength and radiation shielding, making it ideal for roof structures requiring robustness and durability. Lightweight concrete reduces dead load on the roof, improving seismic performance and thermal insulation. Choosing between high-density and lightweight concrete depends on structural load requirements, environmental factors, and insulation needs.
What is High-Density Concrete?
High-density concrete is a specialized type of concrete made with heavy aggregates such as barite, magnetite, or hematite, resulting in a density typically above 3,600 kg/m3. This type of concrete offers superior radiation shielding, higher compressive strength, and enhanced durability compared to normal and lightweight concrete, making it suitable for roof structures requiring enhanced load-bearing capacity and protection. Unlike lightweight concrete, which prioritizes reduced weight for ease of handling and thermal insulation, high-density concrete is used where mass and strength are critical factors to resist mechanical stress and environmental hazards.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete characterized by its lower density, typically ranging from 1600 to 2000 kg/m3, achieved by incorporating lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice. It offers advantages in roof structures including reduced dead load, enhanced thermal insulation, and improved seismic performance compared to high-density concrete, which usually has a density above 2400 kg/m3 due to conventional aggregates like gravel or crushed stone. Using lightweight concrete in roofing reduces structural demands on foundations and framing while maintaining adequate strength and durability for long-term performance.
Key Properties Comparison
High-density concrete offers superior compressive strength and enhanced radiation shielding, making it ideal for roofs requiring heavy load support and durability. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load due to its lower density, improves thermal insulation, and minimizes seismic forces, benefiting energy-efficient roof designs. Porosity and water absorption rates differ significantly, with lightweight concrete exhibiting higher porosity, which may affect durability and waterproofing in roof applications.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
High-density concrete exhibits superior structural strength and load-bearing capacity compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for roof structures requiring enhanced durability and resistance to heavy loads. The increased density, typically ranging from 2400 to 2500 kg/m3, contributes to higher compressive strength and improved impact resistance. Lightweight concrete, with densities between 1600 and 1800 kg/m3, reduces dead load on the roof but may compromise strength, making it suitable for applications prioritizing weight savings over maximum load capacity.
Thermal Insulation Performance
High-density concrete exhibits lower thermal insulation capabilities due to its dense aggregate composition, resulting in higher heat transfer rates. Lightweight concrete, composed of porous aggregates like expanded clay or pumice, provides superior thermal insulation by trapping air within its structure, significantly reducing heat conduction. This advantage makes lightweight concrete a preferred material for roof structures in climates demanding energy efficiency and temperature regulation.
Acoustic Performance for Roof Structures
High-density concrete offers superior acoustic insulation for roof structures due to its higher mass, effectively reducing airborne sound transmission and external noise intrusion. Lightweight concrete, while providing benefits in structural weight reduction and thermal insulation, generally exhibits lower soundproofing capabilities because of its porous nature and reduced density. Roof designs prioritizing acoustic performance typically favor high-density concrete to achieve optimal noise control in residential and commercial buildings.
Construction and Installation Challenges
High-density concrete poses construction challenges for roof structures due to its significant weight, requiring robust support systems and careful handling to prevent structural overload and enhance safety during installation. Lightweight concrete offers easier handling and faster installation times, but demands meticulous mixing and proper curing to ensure adequate strength and durability against environmental factors. Both materials require specialized equipment and skilled labor to address their unique properties and optimize long-term performance in roofing applications.
Cost Analysis: High-Density vs Lightweight Concrete
High-density concrete typically costs 20-30% more than lightweight concrete due to the use of heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, which increase material expenses. Lightweight concrete offers savings in transportation and structural support costs by reducing dead load, potentially lowering overall project expenditure by up to 15%. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on balancing material price against benefits in structural efficiency and long-term durability for roof applications.
Best Applications and Recommendations
High-density concrete, characterized by its superior compressive strength and enhanced radiation shielding properties, is best suited for roof structures requiring increased load-bearing capacity and durability in industrial or nuclear facilities. Lightweight concrete, offering excellent thermal insulation and reduced dead load, is ideal for residential and commercial roofs where energy efficiency and ease of installation are priorities. For optimal performance, select high-density concrete for heavy-duty applications demanding structural robustness, and lightweight concrete for projects focused on weight savings and thermal performance.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Roof structure
 azmater.com
azmater.com