Green concrete uses industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag to reduce carbon emissions and improve sustainability, making it ideal for eco-friendly flooring. Polymer concrete incorporates synthetic resins for enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and faster curing times, offering superior performance in high-traffic or corrosive environments.
Table of Comparison
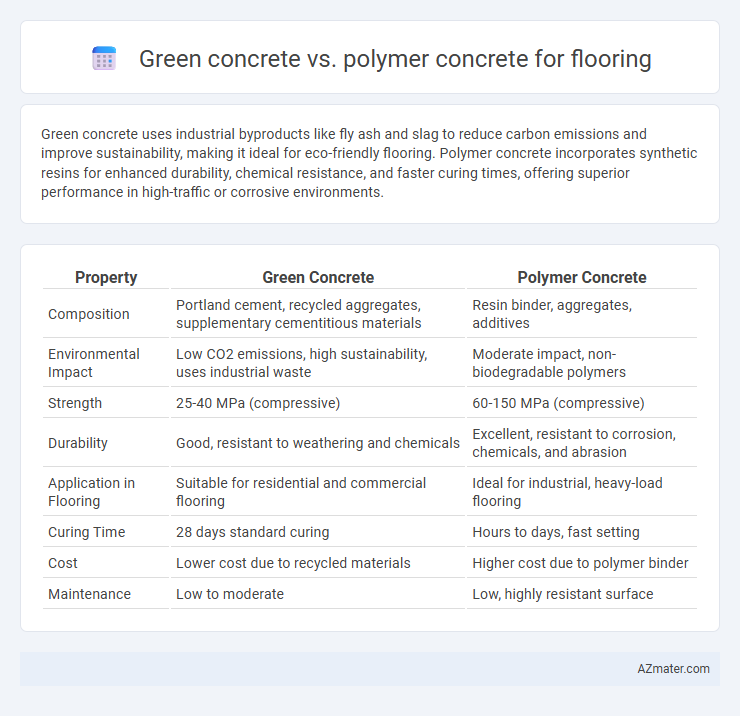
| Property | Green Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Portland cement, recycled aggregates, supplementary cementitious materials | Resin binder, aggregates, additives |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 emissions, high sustainability, uses industrial waste | Moderate impact, non-biodegradable polymers |
| Strength | 25-40 MPa (compressive) | 60-150 MPa (compressive) |
| Durability | Good, resistant to weathering and chemicals | Excellent, resistant to corrosion, chemicals, and abrasion |
| Application in Flooring | Suitable for residential and commercial flooring | Ideal for industrial, heavy-load flooring |
| Curing Time | 28 days standard curing | Hours to days, fast setting |
| Cost | Lower cost due to recycled materials | Higher cost due to polymer binder |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate | Low, highly resistant surface |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Polymer Concrete
Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash and slag to reduce environmental impact, offering sustainable alternatives with lower carbon emissions and improved durability. Polymer concrete utilizes synthetic resins as binders instead of traditional cement, providing superior chemical resistance and rapid curing properties ideal for specialized flooring applications. Both materials present advanced solutions in construction, with green concrete emphasizing eco-friendliness and polymer concrete focusing on enhanced mechanical and chemical performance.
Composition and Material Differences
Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates to reduce cement content and enhance sustainability, while polymer concrete uses synthetic resins such as epoxy or polyester as binders instead of traditional cement. The composition of green concrete emphasizes eco-friendly materials with lower carbon footprints, whereas polymer concrete relies on polymers that offer superior chemical resistance and faster curing times. These material differences affect durability, environmental impact, and application suitability for flooring in industrial and commercial settings.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Green concrete significantly reduces carbon footprint by incorporating industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, minimizing cement usage and lowering CO2 emissions during production. Polymer concrete, composed of synthetic resins and aggregates, offers durability but relies on petrochemical resources, resulting in higher embodied energy and limited biodegradability. From an environmental impact perspective, green concrete presents a more sustainable flooring option due to its eco-friendly materials and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Durability and Lifespan
Green concrete exhibits superior durability due to its use of recycled materials and supplementary cementitious compounds, resulting in enhanced resistance to cracking and environmental stress. Polymer concrete offers exceptional lifespan benefits through its chemical resistance and low permeability, making it ideal for harsh industrial flooring applications. Both materials provide long-term performance, but polymer concrete typically surpasses green concrete in lifespan under aggressive chemical exposure.
Installation Process and Ease
Green concrete offers a straightforward installation process similar to traditional concrete, requiring standard mixing, pouring, and curing techniques, which makes it user-friendly for flooring applications. Polymer concrete, composed of resin binders and aggregates, requires precise mixing and sometimes specialized equipment for proper curing and bonding, potentially complicating the installation process. Flooring projects favor green concrete for its ease of use and adaptability, while polymer concrete demands more expertise to achieve optimal surface durability and adhesion.
Performance in Flooring Applications
Green concrete demonstrates excellent durability and environmental benefits in flooring applications, offering high compressive strength and resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure. Polymer concrete outperforms in rapid curing time, superior tensile strength, and enhanced flexibility, making it ideal for industrial floors subjected to heavy loads and dynamic stresses. Both materials provide excellent surface finish, but polymer concrete delivers better crack resistance and adhesion, essential for long-lasting, high-performance flooring solutions.
Maintenance Requirements
Green concrete flooring requires minimal maintenance due to its enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors, reducing the frequency of repairs and cleaning. Polymer concrete flooring exhibits superior chemical and abrasion resistance, which lowers maintenance needs and extends lifespan compared to traditional concrete. Both options offer sustainable solutions, but polymer concrete generally demands less upkeep in industrial or high-traffic areas.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Green concrete typically offers lower initial material costs due to the use of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, making it a budget-friendly option for sustainable flooring projects. Polymer concrete, while more expensive upfront because of costly resins and additives, provides superior durability and chemical resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Cost analysis favors green concrete for projects with strict budget constraints, whereas polymer concrete proves more affordable over time in high-performance flooring applications requiring enhanced longevity.
Suitability for Different Flooring Environments
Green concrete offers exceptional suitability for eco-friendly flooring environments, providing high durability and resource-efficient composition ideal for residential and commercial spaces seeking sustainability. Polymer concrete excels in industrial flooring settings due to its superior chemical resistance, rapid curing time, and high mechanical strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty and high-traffic applications. Both materials cater to specific flooring needs, with green concrete favored for environmentally conscious projects and polymer concrete preferred in environments requiring robust performance against harsh chemicals and wear.
Future Trends in Sustainable Flooring Materials
Green concrete utilizes recycled industrial waste and natural materials to reduce carbon emissions, making it a highly sustainable option for flooring with improved thermal insulation properties. Polymer concrete incorporates synthetic resins and aggregates, offering enhanced chemical resistance and durability while enabling customization for specific industrial applications. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach combining bio-based polymers and eco-friendly binders to optimize mechanical performance and environmental impact in sustainable flooring solutions.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Polymer concrete for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com