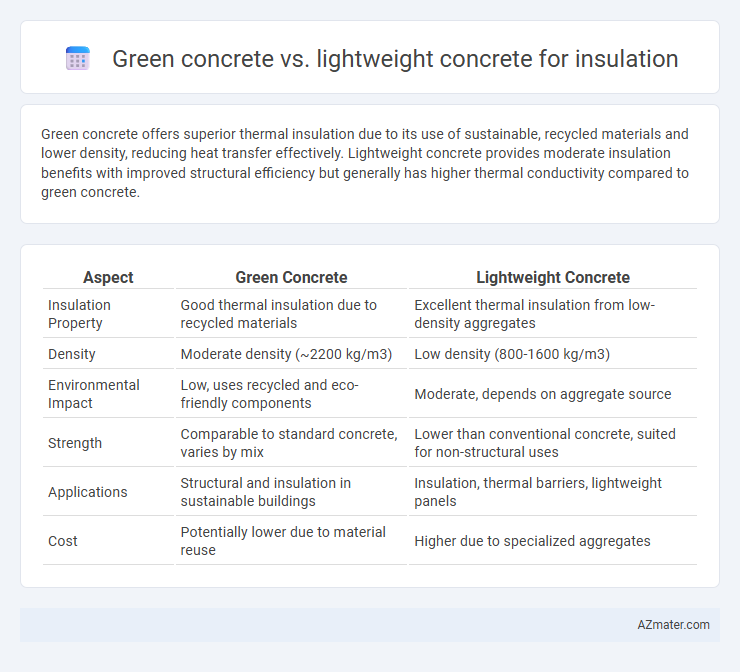
Green concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its use of sustainable, recycled materials and lower density, reducing heat transfer effectively. Lightweight concrete provides moderate insulation benefits with improved structural efficiency but generally has higher thermal conductivity compared to green concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Green Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Property | Good thermal insulation due to recycled materials | Excellent thermal insulation from low-density aggregates |
| Density | Moderate density (~2200 kg/m3) | Low density (800-1600 kg/m3) |
| Environmental Impact | Low, uses recycled and eco-friendly components | Moderate, depends on aggregate source |
| Strength | Comparable to standard concrete, varies by mix | Lower than conventional concrete, suited for non-structural uses |
| Applications | Structural and insulation in sustainable buildings | Insulation, thermal barriers, lightweight panels |
| Cost | Potentially lower due to material reuse | Higher due to specialized aggregates |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Green concrete utilizes industrial byproducts such as fly ash or slag to reduce environmental impact while providing effective thermal insulation. Lightweight concrete incorporates natural or synthetic aggregates like expanded clay or polystyrene beads, significantly lowering density and enhancing insulating properties. Both materials contribute to energy-efficient building solutions but differ in composition and insulation performance.
Composition and Material Differences
Green concrete incorporates industrial waste materials such as fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, reducing environmental impact while maintaining structural strength. Lightweight concrete uses lightweight aggregates like expanded clay, shale, or pumice to achieve lower density and improved thermal insulation. The key difference lies in green concrete's sustainable mix design versus lightweight concrete's emphasis on porous aggregates for enhanced insulation performance.
Environmental Benefits: Green Concrete vs Lightweight Concrete
Green concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products such as fly ash and slag, enhancing sustainability compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, while providing improved thermal insulation due to its lower density and air-entrained structure, often relies on traditional cement production which has a higher environmental footprint. Utilizing green concrete promotes eco-friendly construction practices by minimizing natural resource depletion and reducing waste, offering superior environmental benefits over lightweight concrete in insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers moderate thermal insulation with a typical thermal conductivity ranging from 0.4 to 0.7 W/m*K. Lightweight concrete, composed of expanded clay, shale, or pumice aggregates, demonstrates superior thermal insulation properties due to its lower density and higher porosity, often achieving thermal conductivity values below 0.3 W/m*K. Consequently, lightweight concrete is more effective for reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in building envelopes compared to conventional green concrete mixes.
Structural Strength and Durability
Green concrete, made with recycled materials and industrial by-products, offers enhanced durability and environmental benefits while maintaining comparable structural strength to traditional concrete. Lightweight concrete, incorporating materials like expanded clay or foam, significantly improves insulation properties but generally exhibits lower compressive strength and durability compared to green concrete. For applications requiring optimal insulation without compromising load-bearing capacity, green concrete provides a balanced solution with superior long-term performance and sustainability.
Application Areas in Construction
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, excels in sustainable building projects requiring thermal mass and environmental efficiency, commonly used in foundations, pavements, and large structural elements. Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density and superior insulation properties, is ideal for non-load-bearing walls, roof insulation, and precast panels where thermal insulation and weight reduction are critical. Both materials support energy-efficient construction but target different application areas based on structural needs and insulation performance.
Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Green concrete, utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, offers long-term cost savings through enhanced durability and reduced carbon emissions, despite potentially higher initial material costs compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete, made with expanded shale or clay aggregates, provides effective thermal insulation with lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent maintenance and repairs, impacting overall economic viability. Both materials influence construction costs and environmental impact differently, necessitating a detailed cost-benefit analysis to determine the best option for insulation in specific projects.
Installation and Workability
Green concrete offers improved workability due to its use of recycled materials and supplementary cementitious substances, which enhance flow and reduce water demand during installation. Lightweight concrete, characterized by reduced density through expanded clay or shale aggregates, provides easier handling and faster placement, especially beneficial for insulation purposes in building envelopes. Both types facilitate efficient installation, but green concrete's sustainability advantage complements the superior thermal insulation properties and ease of use found in lightweight concrete.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Green concrete, made with recycled materials and industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, offers superior energy efficiency through enhanced thermal mass and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional mixes. Lightweight concrete improves insulation properties by incorporating air-filled aggregates such as expanded clay or shale, significantly reducing heat transfer and lowering energy consumption in buildings. Both materials contribute to sustainability; green concrete minimizes resource depletion and carbon emissions, while lightweight concrete reduces structural loads, enabling more efficient use of resources and longer building lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Insulation Needs
Green concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its eco-friendly materials like fly ash and recycled aggregates, effectively reducing heat transfer in buildings. Lightweight concrete, made from expanded clay or shale, provides excellent insulation through its porous structure, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing structural load. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing insulation performance, environmental impact, and structural requirements specific to the construction project.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com