Foam concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for non-structural applications, while ready-mix concrete provides high strength and durability suited for structural components in general construction. Foam concrete reduces overall project weight and improves energy efficiency, whereas ready-mix concrete ensures faster construction times and consistent quality.
Table of Comparison
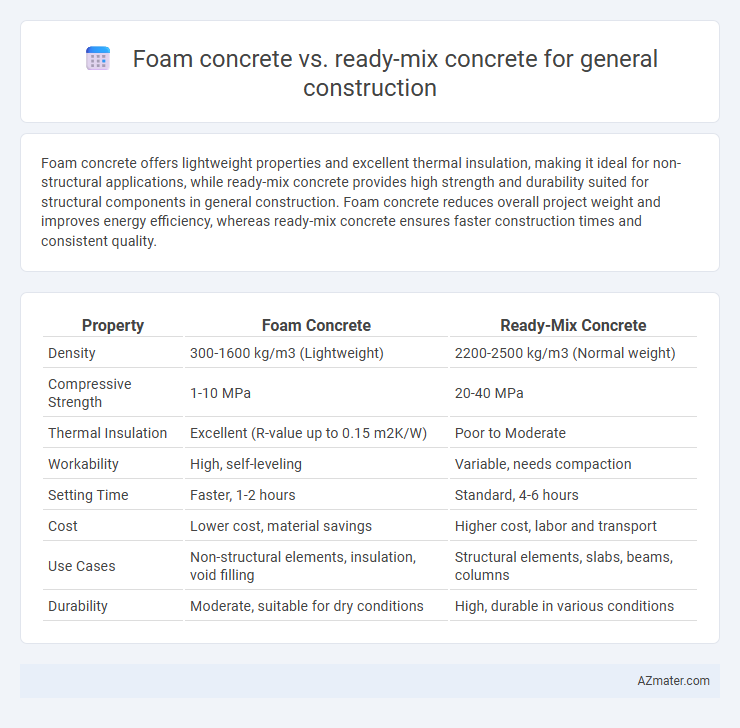
| Property | Foam Concrete | Ready-Mix Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (Normal weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-10 MPa | 20-40 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent (R-value up to 0.15 m2K/W) | Poor to Moderate |
| Workability | High, self-leveling | Variable, needs compaction |
| Setting Time | Faster, 1-2 hours | Standard, 4-6 hours |
| Cost | Lower cost, material savings | Higher cost, labor and transport |
| Use Cases | Non-structural elements, insulation, void filling | Structural elements, slabs, beams, columns |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for dry conditions | High, durable in various conditions |
Introduction: Foam Concrete vs Ready-Mix Concrete
Foam concrete offers lightweight and thermal insulation properties with a reduced density, making it suitable for non-structural applications and areas requiring energy efficiency. Ready-mix concrete provides high compressive strength and durability, ideal for structural components and large-scale construction projects. Choosing between foam concrete and ready-mix concrete depends on project requirements such as load-bearing capacity, thermal performance, and construction speed.
Composition and Material Differences
Foam concrete is composed of cement, water, fine aggregates, and a foaming agent that introduces air bubbles to reduce density, resulting in lightweight material with thermal insulation and soundproofing properties. Ready-mix concrete consists of cement, water, coarse and fine aggregates, and admixtures, providing high strength and durability for structural applications. The key material difference lies in foam concrete's aerated structure versus the dense, aggregate-rich mix of ready-mix concrete, affecting performance and suitability in general construction projects.
Structural Properties and Strength
Foam concrete exhibits lower density and compressive strength compared to ready-mix concrete, making it ideal for non-load-bearing applications and thermal insulation in general construction. Ready-mix concrete offers superior structural properties with high compressive strength and durability, suitable for load-bearing elements such as columns, beams, and foundations. The choice between foam concrete and ready-mix concrete depends on the specific strength requirements and functional roles within the construction project.
Weight and Density Comparison
Foam concrete typically has a density ranging from 400 to 1600 kg/m3, making it significantly lighter than ready-mix concrete, which usually weighs between 2200 to 2500 kg/m3. This lower density of foam concrete reduces structural load and improves thermal insulation, ideal for non-load-bearing applications and energy-efficient buildings. In contrast, ready-mix concrete's higher density provides superior compressive strength, making it suitable for structural elements that require durability and load-bearing capacity.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation
Foam concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in general construction. Its lightweight composition also provides excellent acoustic insulation by dampening sound transmission compared to traditional ready-mix concrete. While ready-mix concrete delivers higher compressive strength, foam concrete's insulation properties make it a preferred choice for projects prioritizing temperature control and noise reduction.
Workability and Ease of Application
Foam concrete offers superior workability due to its lightweight and flowable nature, making it ideal for filling voids and complex shapes in general construction projects. Ready-mix concrete provides consistent quality and ease of application with rapid placement, suitable for structural elements requiring high strength. The choice between foam and ready-mix concrete depends on project requirements, with foam concrete excelling in insulation and lightweight applications, while ready-mix concrete delivers durability and load-bearing capacity.
Cost Considerations in Construction
Foam concrete offers significant cost savings in general construction due to its lightweight nature, reducing transportation and labor expenses compared to traditional ready-mix concrete. The lower material density of foam concrete also minimizes the need for heavy structural support, further decreasing overall project costs. However, ready-mix concrete provides superior compressive strength and faster curing times, which can lead to reduced construction timelines and potentially lower labor costs on high-load bearing projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam concrete significantly reduces environmental impact by incorporating recycled materials and requiring less cement, which lowers carbon dioxide emissions compared to ready-mix concrete. Its lightweight nature improves energy efficiency in buildings by enhancing thermal insulation, contributing to sustainable construction practices. Ready-mix concrete, while versatile and high-strength, often involves higher resource consumption and carbon footprint, making foam concrete a more eco-friendly alternative for green building projects.
Common Applications in General Construction
Foam concrete is widely used in non-structural applications such as void filling, roof insulation, and lightweight partitions due to its excellent thermal insulation and low density. Ready-mix concrete is preferred for structural elements like foundations, beams, and slabs, offering high strength and durability with consistent quality. Both materials serve distinct purposes in general construction, with foam concrete optimizing thermal properties and ready-mix concrete providing structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Concrete: Key Factors
Foam concrete offers lightweight properties, excellent thermal insulation, and reduced dead load, making it ideal for non-structural applications, while ready-mix concrete provides high compressive strength and durability suitable for load-bearing structures. Key factors for choosing between foam concrete and ready-mix concrete include project load requirements, thermal performance needs, curing time, and cost-efficiency. Evaluating site accessibility and environmental impact also influences the decision, as foam concrete reduces waste and energy consumption, whereas ready-mix concrete ensures consistent quality and faster construction timelines.
Infographic: Foam concrete vs Ready-mix concrete for General construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com