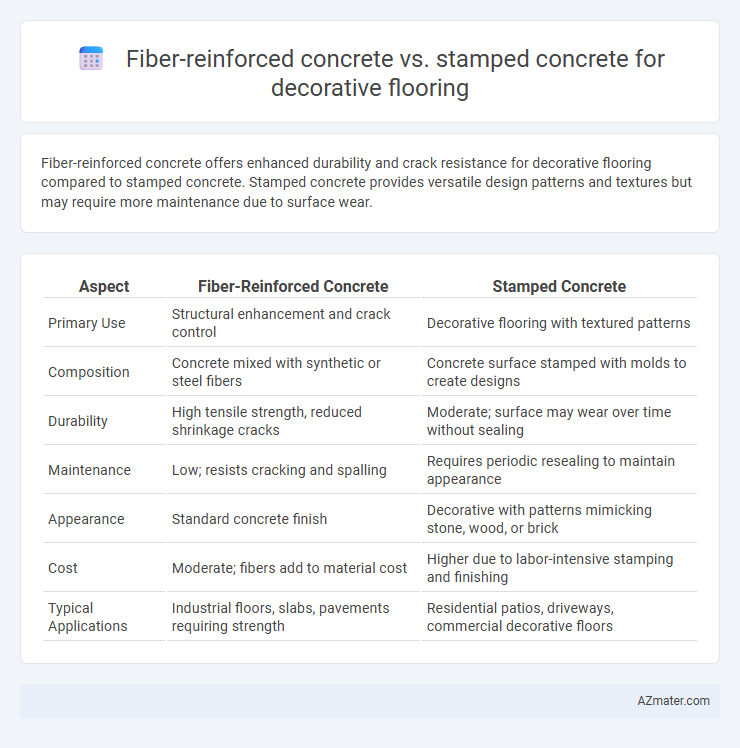
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced durability and crack resistance for decorative flooring compared to stamped concrete. Stamped concrete provides versatile design patterns and textures but may require more maintenance due to surface wear.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete | Stamped Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Structural enhancement and crack control | Decorative flooring with textured patterns |
| Composition | Concrete mixed with synthetic or steel fibers | Concrete surface stamped with molds to create designs |
| Durability | High tensile strength, reduced shrinkage cracks | Moderate; surface may wear over time without sealing |
| Maintenance | Low; resists cracking and spalling | Requires periodic resealing to maintain appearance |
| Appearance | Standard concrete finish | Decorative with patterns mimicking stone, wood, or brick |
| Cost | Moderate; fibers add to material cost | Higher due to labor-intensive stamping and finishing |
| Typical Applications | Industrial floors, slabs, pavements requiring strength | Residential patios, driveways, commercial decorative floors |
Introduction to Decorative Flooring Options
Decorative flooring options such as fiber-reinforced concrete and stamped concrete offer unique benefits for enhancing surface durability and aesthetic appeal. Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to increase tensile strength and reduce cracking, making it ideal for high-traffic areas requiring robust performance. Stamped concrete, on the other hand, utilizes molds and color stains to replicate natural materials like stone or brick, providing customizable design options with a textured, decorative finish.
What is Fiber-Reinforced Concrete?
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) incorporates discrete fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials to enhance the material's tensile strength, durability, and crack resistance, making it ideal for decorative flooring applications requiring long-term performance. Unlike stamped concrete, which primarily relies on surface patterns and color to achieve aesthetic appeal, FRC offers improved structural integrity while maintaining the customization benefits of concrete finishes. The reinforcing fibers distribute stress within the concrete matrix, reducing shrinkage cracks and increasing toughness in high-traffic decorative floors.
Understanding Stamped Concrete Techniques
Stamped concrete involves creating textured patterns and designs on freshly poured concrete using specialized molds and stamps, offering a highly customizable decorative flooring option. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances structural integrity by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers, improving durability and crack resistance, but does not inherently provide decorative textures. Mastery of stamped concrete techniques requires precise timing to imprint patterns before the concrete sets, use of release agents for color variation, and skillful application of stains or dyes to achieve realistic stone, brick, or wood effects.
Aesthetic Appeal: Comparing Decorative Potential
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers a smooth, uniform surface that can be enhanced with pigments, stains, and exposed aggregate for subtle texture variations, providing a modern and durable aesthetic appeal. Stamped concrete excels in mimicking natural materials such as stone, brick, and wood, delivering intricate patterns and vibrant colors that create highly realistic and customizable decorative flooring designs. The decorative potential of stamped concrete generally surpasses fiber-reinforced concrete due to its ability to replicate diverse textures and detailed motifs, making it a preferred choice for visually striking surfaces.
Strength and Durability Assessment
Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly enhances tensile strength and crack resistance by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers, making it ideal for high-traffic decorative flooring applications requiring superior durability. In comparison, stamped concrete provides aesthetic versatility with surface patterns and textures but relies on traditional concrete's strength, necessitating proper sealing to prevent wear and damage over time. For long-lasting decorative flooring, fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior structural integrity and reduced maintenance compared to stamped concrete.
Installation Process: Steps and Challenges
Fiber-reinforced concrete installation for decorative flooring involves mixing synthetic or steel fibers into the concrete before pouring, which enhances structural integrity and reduces cracking during curing. Stamped concrete requires precise timing for stamping patterns onto freshly poured slabs to achieve desired textures, demanding skilled labor and careful moisture control to avoid imperfections. Both methods face challenges like ensuring proper curing conditions to prevent surface defects and require expertise to balance aesthetics with durability.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced durability and crack resistance, reducing long-term maintenance needs compared to standard stamped concrete, which may require periodic sealing and repair to maintain its aesthetic appeal. Stamped concrete provides versatile decorative patterns and textures but is more susceptible to surface wear and fading over time, necessitating regular upkeep. Fiber-reinforced concrete's improved structural integrity extends the lifespan of decorative flooring, making it a cost-effective solution for high-traffic areas.
Cost Comparison: Materials and Labor
Fiber-reinforced concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized fibers such as steel or synthetic additives, but it often reduces labor expenses by minimizing cracking and repair needs. Stamped concrete materials, including colorants and stamping tools, can be moderately priced, yet labor costs tend to be higher because of the detailed stamping and finishing processes required for decorative patterns. Overall, fiber-reinforced concrete offers long-term savings in maintenance despite a higher upfront material investment, whereas stamped concrete demands more extensive skilled labor, increasing total project cost.
Best Use Cases for Each Flooring Type
Fiber-reinforced concrete excels in high-traffic commercial areas and industrial settings due to its enhanced tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability. Stamped concrete is ideal for residential patios, walkways, and decorative driveways where aesthetic appeal and customizable patterns mimic natural stone or brick surfaces. Selecting fiber-reinforced concrete supports structural integrity in demanding environments, while stamped concrete provides versatile design options for visually striking decorative flooring.
Choosing the Right Decorative Concrete for Your Project
Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances decorative flooring by improving structural strength, crack resistance, and durability, making it ideal for high-traffic areas requiring long-lasting performance. Stamped concrete offers diverse patterns and textures, closely mimicking natural materials like stone or brick, providing aesthetic versatility for patios, walkways, and decorative driveways. Choosing the right decorative concrete depends on balancing functional requirements such as load-bearing capacity and maintenance with design preferences and budget constraints to achieve optimal project outcomes.
Infographic: Fiber-reinforced concrete vs Stamped concrete for Decorative flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com