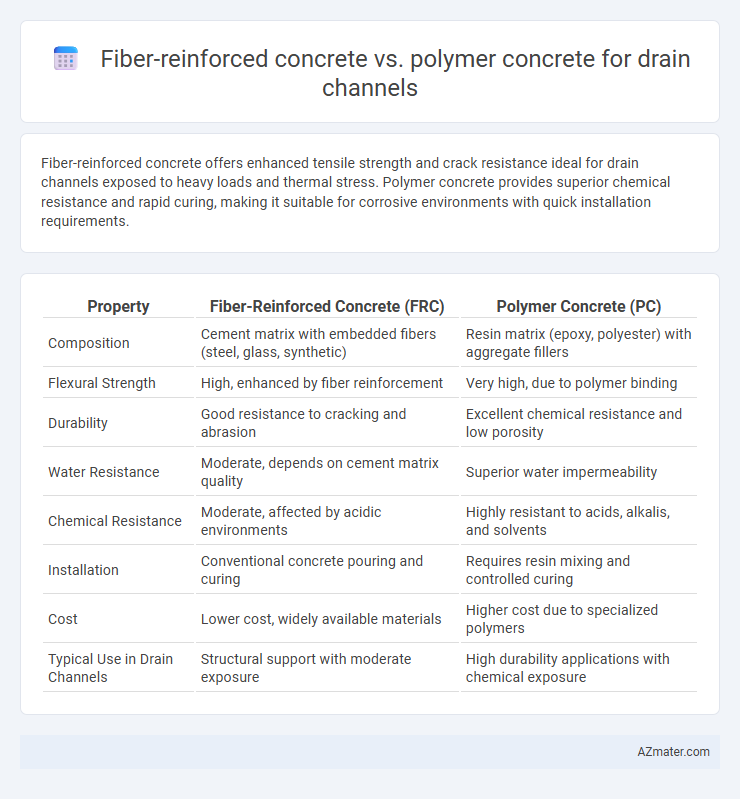
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance ideal for drain channels exposed to heavy loads and thermal stress. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and rapid curing, making it suitable for corrosive environments with quick installation requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) | Polymer Concrete (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Cement matrix with embedded fibers (steel, glass, synthetic) | Resin matrix (epoxy, polyester) with aggregate fillers |
| Flexural Strength | High, enhanced by fiber reinforcement | Very high, due to polymer binding |
| Durability | Good resistance to cracking and abrasion | Excellent chemical resistance and low porosity |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, depends on cement matrix quality | Superior water impermeability |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, affected by acidic environments | Highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Installation | Conventional concrete pouring and curing | Requires resin mixing and controlled curing |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available materials | Higher cost due to specialized polymers |
| Typical Use in Drain Channels | Structural support with moderate exposure | High durability applications with chemical exposure |
Introduction to Advanced Drain Channel Materials
Fiber-reinforced concrete incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to enhance tensile strength and crack resistance, making it highly durable for drain channel applications exposed to heavy loads and environmental stress. Polymer concrete utilizes resin binders combined with aggregates, offering superior chemical resistance and rapid curing times, ideal for drainage systems in corrosive environments. Both materials represent advancements over traditional concrete, delivering improved longevity and performance tailored to specific infrastructure needs.
Overview of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances traditional concrete by incorporating synthetic or steel fibers, significantly improving tensile strength, impact resistance, and crack control, making it ideal for drain channel applications exposed to heavy loads and environmental stresses. FRC offers superior durability and reduced permeability compared to polymer concrete, providing extended service life in harsh conditions such as freeze-thaw cycles and chemical exposure. Its cost-effectiveness and ease of placement also contribute to widespread use in infrastructure projects requiring reliable and long-lasting drainage solutions.
Key Features of Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and rapid curing compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, making it ideal for drain channels exposed to harsh environmental conditions and aggressive wastewater. Its high compressive strength and excellent adhesion ensure durability and minimize maintenance requirements in infrastructure applications. The lightweight nature of polymer concrete also facilitates easier handling and installation without compromising structural integrity.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Fiber-reinforced concrete exhibits higher tensile strength and crack resistance compared to polymer concrete, making it ideal for drain channels subjected to dynamic loads and thermal expansion. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and impermeability, enhancing durability in corrosive environments typical of drainage systems exposed to industrial waste. Both materials provide excellent durability, but selection depends on specific site conditions: fiber-reinforced concrete excels in structural resilience, while polymer concrete excels in chemical and environmental resistance.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced chemical resistance due to the incorporation of fibers that reduce crack propagation, minimizing exposure to aggressive substances commonly found in drain channels. Polymer concrete exhibits superior corrosion resistance as its resin matrix effectively seals against acidic and alkaline chemicals, preventing deterioration in harsh environments. Both materials provide durability, but polymer concrete is often preferred in highly corrosive drain channel applications due to its exceptional resistance to chemical attack.
Installation and Workability Considerations
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior flexibility and reduced cracking during curing, enhancing installation ease in drain channel applications with complex shapes. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing times, minimizing downtime but often requires precise mixing conditions for optimal workability. Both materials demand careful handling; fiber-reinforced concrete benefits from adjustable fiber content for tailored workability, whereas polymer concrete requires controlled environmental conditions to ensure proper adhesion and strength development.
Cost Analysis: Fiber-Reinforced vs Polymer Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers a cost-effective solution for drain channels due to its lower material expenses and easier handling compared to polymer concrete, which typically involves higher initial costs from synthetic resins and specialized curing processes. Maintenance costs for fiber-reinforced concrete remain minimal, thanks to its enhanced durability and crack resistance, while polymer concrete's superior chemical resistance can justify its higher price in corrosive environments. Overall, fiber-reinforced concrete presents better budget efficiency for standard drain channel applications, whereas polymer concrete suits scenarios demanding extreme chemical or abrasion resistance despite increased investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) offers enhanced durability and crack resistance, reducing maintenance frequency and material consumption, which lowers its environmental footprint in drain channel applications. Polymer concrete, composed of resins and aggregates, provides chemical resistance and rapid curing but relies on petrochemical-based polymers, raising concerns about non-renewable resource use and recyclability. Sustainable drain channel construction favors FRC due to its incorporation of industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, which reduce carbon emissions and promote circular economy practices.
Typical Applications in Drainage Systems
Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability and crack resistance, making it ideal for drain channels exposed to heavy traffic and dynamic loading. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and rapid curing, suited for industrial drainage systems handling aggressive wastewater and corrosive environments. Both materials improve drainage system longevity, with fiber-reinforced concrete favored for structural resilience and polymer concrete preferred in chemically harsh settings.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Drain Channel
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers superior tensile strength and crack resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty drain channels exposed to dynamic loads and harsh environmental conditions. Polymer concrete excels in chemical resistance and rapid curing, suitable for drain channels in corrosive environments or where quick installation is critical. Selecting the best material depends on project-specific factors such as load requirements, exposure to chemicals, installation time, and cost efficiency.
Infographic: Fiber-reinforced concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drain channel
 azmater.com
azmater.com