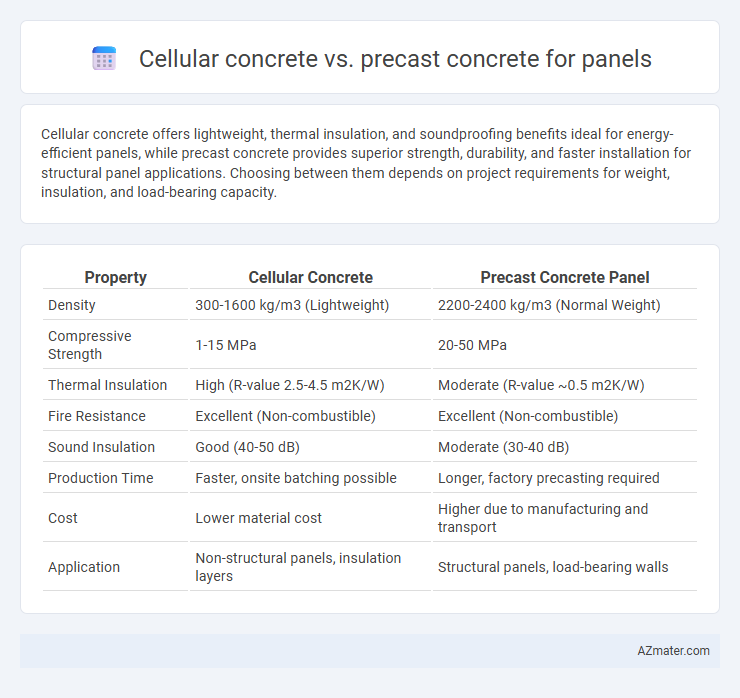
Cellular concrete offers lightweight, thermal insulation, and soundproofing benefits ideal for energy-efficient panels, while precast concrete provides superior strength, durability, and faster installation for structural panel applications. Choosing between them depends on project requirements for weight, insulation, and load-bearing capacity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Precast Concrete Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 2200-2400 kg/m3 (Normal Weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-15 MPa | 20-50 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | High (R-value 2.5-4.5 m2K/W) | Moderate (R-value ~0.5 m2K/W) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent (Non-combustible) | Excellent (Non-combustible) |
| Sound Insulation | Good (40-50 dB) | Moderate (30-40 dB) |
| Production Time | Faster, onsite batching possible | Longer, factory precasting required |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Higher due to manufacturing and transport |
| Application | Non-structural panels, insulation layers | Structural panels, load-bearing walls |
Introduction to Cellular Concrete and Precast Concrete Panels
Cellular concrete, a lightweight material composed of cement, water, and foaming agents, offers excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance properties ideal for panel construction. Precast concrete panels, manufactured off-site in controlled environments, provide high strength, durability, and fast installation advantages in building projects. Both materials serve distinct structural and insulation needs, with cellular concrete panels emphasizing energy efficiency and precast panels focusing on load-bearing capacity and precision.
Composition and Material Properties
Cellular concrete is characterized by a lightweight, aerated cementitious mixture containing numerous air bubbles, which reduces density and enhances thermal insulation properties. Precast concrete panels are composed of traditional concrete with aggregates like gravel and sand, reinforced with steel for higher compressive strength and durability. While cellular concrete offers superior insulating and fire-resistant qualities, precast concrete provides greater structural load-bearing capacity and uniformity in controlled manufacturing environments.
Manufacturing Processes: Cellular vs Precast Panels
Cellular concrete panels are manufactured using a process that incorporates air or gas bubbles into the wet concrete mix, resulting in a lightweight, insulating material that cures through a foaming reaction and sets quickly in molds. Precast concrete panels are produced in controlled factory environments by pouring dense concrete mixtures into reusable molds, allowing for precise shaping, reinforcement integration, and extended curing times to achieve higher strength and durability. The cellular concrete manufacturing emphasizes speed and thermal efficiency, while precast concrete focuses on structural integrity and dimensional accuracy in panel production.
Structural Strength and Load-bearing Capabilities
Cellular concrete offers lower density and reduced compressive strength compared to precast concrete, making it less suitable for high load-bearing applications in structural panels. Precast concrete provides superior structural strength and enhanced load-bearing capabilities due to its dense composition and controlled manufacturing process. For projects requiring robust durability and high load resistance, precast concrete panels are the preferred choice over cellular concrete panels.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Cellular concrete panels provide superior thermal insulation due to their porous structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to denser precast concrete panels. Acoustic insulation in cellular concrete is enhanced by air pockets that absorb sound waves, resulting in better noise reduction than precast concrete, which typically has higher density and reflects sound. For applications requiring energy efficiency and noise control, cellular concrete panels offer a more effective solution than traditional precast concrete.
Installation Time and On-Site Requirements
Cellular concrete panels offer significantly reduced installation time due to their lightweight nature, which simplifies handling and reduces the need for heavy lifting equipment on-site. In contrast, precast concrete panels require more substantial crane equipment and precise alignment, increasing both installation time and labor demands. The on-site requirements for cellular concrete are minimal, often allowing for faster project turnover and lower overall labor costs compared to the rigid foundation and larger workforce needed for precast panel installation.
Cost Comparison: Cellular Concrete vs Precast Concrete
Cellular concrete offers significant cost savings in panel construction due to its lightweight nature, which reduces transportation and handling expenses compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete panels involve higher upfront costs related to formwork, curing, and skilled labor, whereas cellular concrete can be cast in situ with less specialized equipment. Over time, cellular concrete panels provide improved thermal insulation, potentially lowering operational energy costs and enhancing overall project affordability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete offers superior sustainability through its lightweight structure, reducing material consumption and energy use during transportation and installation compared to precast concrete panels. Its enhanced thermal insulation properties contribute to lower energy costs for heating and cooling, significantly reducing the building's carbon footprint. Precast concrete, while durable, involves higher embodied energy due to intensive manufacturing and transportation processes, resulting in a greater environmental impact over its lifecycle.
Typical Applications in Construction Projects
Cellular concrete is ideal for lightweight wall panels, insulation layers, and void filling in construction projects, offering superior thermal and sound insulation properties. Precast concrete panels are commonly utilized for structural walls, facade cladding, and flooring systems due to their high strength and durability. Both materials serve distinct roles, with cellular concrete emphasizing energy efficiency and precast concrete focusing on load-bearing capacity and rapid installation.
Choosing the Right Panel Solution: Key Considerations
Cellular concrete panels offer enhanced thermal insulation and lightweight characteristics, making them ideal for energy-efficient building designs, while precast concrete panels provide superior compressive strength and faster installation for structural applications. Key considerations include project load requirements, thermal performance goals, installation speed, and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating factors such as fire resistance, durability, and environmental impact will help determine the optimal panel solution for specific construction needs.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Precast concrete for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com