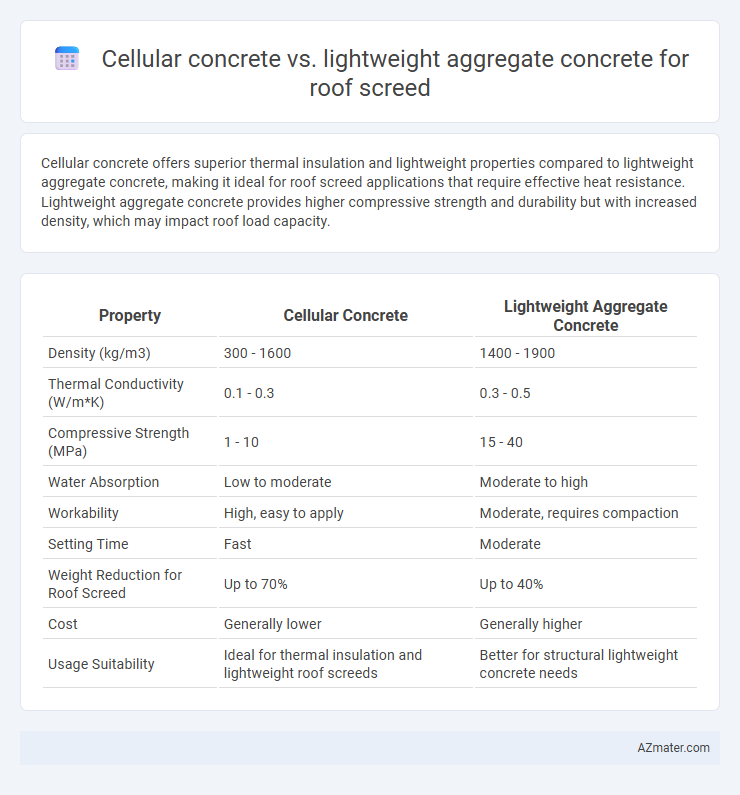
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight properties compared to lightweight aggregate concrete, making it ideal for roof screed applications that require effective heat resistance. Lightweight aggregate concrete provides higher compressive strength and durability but with increased density, which may impact roof load capacity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Lightweight Aggregate Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density (kg/m3) | 300 - 1600 | 1400 - 1900 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.1 - 0.3 | 0.3 - 0.5 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) | 1 - 10 | 15 - 40 |
| Water Absorption | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Workability | High, easy to apply | Moderate, requires compaction |
| Setting Time | Fast | Moderate |
| Weight Reduction for Roof Screed | Up to 70% | Up to 40% |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Usage Suitability | Ideal for thermal insulation and lightweight roof screeds | Better for structural lightweight concrete needs |
Introduction to Roof Screed Materials
Cellular concrete and lightweight aggregate concrete serve as essential roof screed materials with distinct properties impacting drainage, insulation, and load-bearing capacity. Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its air-filled cellular structure, reducing thermal bridging and enhancing energy efficiency. Lightweight aggregate concrete provides greater compressive strength and durability, making it suitable for structural support in roofing applications where mechanical loads are a concern.
What is Cellular Concrete?
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, low-density material composed of cement, water, fine aggregates, and pre-formed foam, offering excellent thermal insulation and sound absorption properties ideal for roof screed applications. Its uniform cellular structure reduces dead load on roofs while maintaining sufficient compressive strength, making it advantageous compared to traditional lightweight aggregate concrete. This type of concrete provides superior workability, faster curing times, and enhanced fire resistance, contributing to overall durability and energy efficiency in roofing systems.
What is Lightweight Aggregate Concrete?
Lightweight Aggregate Concrete (LWAC) is a type of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or slate to reduce density while maintaining structural integrity, making it ideal for roof screeds where weight reduction is critical. LWAC offers improved thermal insulation and fire resistance compared to traditional concrete, enhancing energy efficiency and safety in roofing applications. Its lower dead load decreases stress on building frameworks, thereby optimizing roof design and longevity.
Key Differences in Composition
Cellular concrete contains a mixture of cement, water, and a foaming agent to create air bubbles, resulting in a lightweight, highly insulative material. Lightweight aggregate concrete incorporates expanded natural or synthetic aggregates like expanded clay or shale, providing enhanced structural strength while reducing weight compared to traditional concrete. The key difference lies in cellular concrete's foamed structure for better thermal insulation versus lightweight aggregate concrete's use of solid, porous aggregates for load-bearing applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation for roof screeds due to its high air content and low density, resulting in lower thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.08 to 0.20 W/m*K. In contrast, lightweight aggregate concrete typically exhibits thermal conductivity between 0.30 and 0.50 W/m*K, providing moderate insulation but increased structural strength compared to cellular concrete. Choosing cellular concrete enhances energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for thermal insulation in roofing applications.
Weight and Structural Load Implications
Cellular concrete offers significantly lower density, typically ranging from 400 to 1600 kg/m3, compared to lightweight aggregate concrete, which usually falls between 1600 and 2000 kg/m3, resulting in reduced self-weight and decreased structural load on the roof system. The lower weight of cellular concrete minimizes the demand on supporting structures, enabling more efficient design and potential cost savings on foundation and framing elements. However, lightweight aggregate concrete provides higher compressive strength and durability, making it suitable for roof screeds where enhanced structural performance is required without excessively increasing load.
Installation and Workability Factors
Cellular concrete offers superior workability for roof screed applications due to its lightweight nature and excellent flowability, enabling easy pumping and spreading with minimal labor. In contrast, lightweight aggregate concrete requires more effort in mixing and placing because of the variability in aggregate size and density, which can compromise uniformity in thin screeds. Installation of cellular concrete also benefits from faster setting times and better thermal insulation properties, making it more suitable for efficient roof screed application and long-term performance.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Cellular concrete offers superior durability for roof screeds due to its high resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and exceptional water absorption control, extending structural longevity in harsh weather conditions. Lightweight aggregate concrete, while providing good compressive strength and thermal insulation, may exhibit variable durability based on the quality of aggregates and proper curing techniques. Long-term performance analysis favors cellular concrete in aggressive environments where moisture resistance and crack prevention are critical for roof screed durability.
Cost Considerations and Economic Factors
Cellular concrete offers significant cost savings in roof screed applications due to its lower material density and reduced transportation expenses compared to lightweight aggregate concrete. The ease of pumping and placing cellular concrete also minimizes labor costs and accelerates construction timelines, enhancing overall economic efficiency. Lightweight aggregate concrete, while providing better structural strength, typically incurs higher costs in materials and handling, making cellular concrete a more cost-effective solution for non-load-bearing roof screeds.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete offers superior environmental benefits for roof screed due to its lower density and reduced raw material consumption, significantly decreasing carbon footprint compared to lightweight aggregate concrete. Lightweight aggregate concrete relies on expanded clay or shale, which requires energy-intensive processes, whereas cellular concrete incorporates air bubbles that reduce material use and enhance insulation, promoting energy efficiency in buildings. The sustainable nature of cellular concrete aligns with green building standards by minimizing resource extraction and improving thermal performance, thereby supporting long-term ecological balance.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Lightweight aggregate concrete for Roof screed
 azmater.com
azmater.com