Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced weight compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for lightweight block construction. Its porous structure enhances fire resistance and soundproofing while maintaining adequate compressive strength for building applications.
Table of Comparison
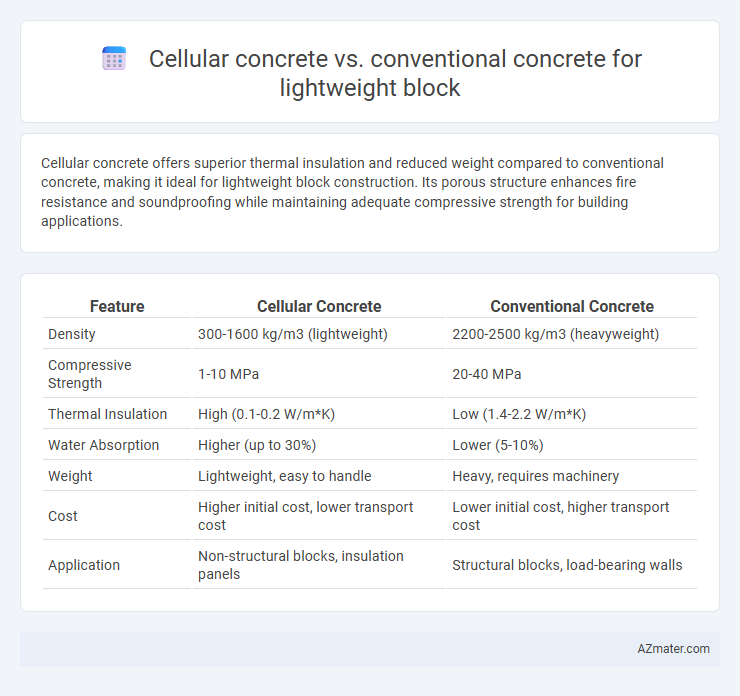
| Feature | Cellular Concrete | Conventional Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 300-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (heavyweight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-10 MPa | 20-40 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | High (0.1-0.2 W/m*K) | Low (1.4-2.2 W/m*K) |
| Water Absorption | Higher (up to 30%) | Lower (5-10%) |
| Weight | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavy, requires machinery |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower transport cost | Lower initial cost, higher transport cost |
| Application | Non-structural blocks, insulation panels | Structural blocks, load-bearing walls |
Introduction to Cellular Concrete and Conventional Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight material composed of cement, water, and air bubbles introduced through a foaming agent, resulting in reduced density and enhanced thermal insulation properties. Conventional concrete is a dense mixture of cement, water, sand, and aggregates, providing high compressive strength but significantly higher weight. Lightweight blocks made from cellular concrete offer superior thermal efficiency and easier handling compared to the heavier, stronger conventional concrete blocks.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Cellular concrete is composed of cement, fine aggregates, water, and a foaming agent that introduces stable air bubbles, resulting in a lightweight material with reduced density compared to conventional concrete. Conventional concrete for lightweight blocks typically uses natural or artificial lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, mixed with cement and water without the addition of foaming agents. The manufacturing process of cellular concrete involves pre-foaming and mixing foam with the concrete slurry, casting into molds, and curing, whereas conventional lightweight concrete is produced by mixing lightweight aggregates with cement and water, followed by standard casting and curing procedures.
Weight and Density Comparison
Cellular concrete typically has a density range of 400 to 1600 kg/m3, significantly lower than conventional concrete, which ranges from 2200 to 2500 kg/m3, making it an ideal choice for lightweight blocks. The reduced weight of cellular concrete, often 30-70% lighter, enhances ease of handling and reduces structural load, contributing to improved seismic performance and cost savings in foundation design. Lightweight blocks made from cellular concrete also provide better thermal insulation due to their porous structure, contrasting with the denser and heavier conventional concrete blocks.
Strength and Structural Performance
Cellular concrete offers lower density and enhanced thermal insulation compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for lightweight blocks in non-load-bearing applications. Conventional concrete exhibits higher compressive strength and superior structural performance, suitable for load-bearing components requiring durability and stability. The choice between cellular and conventional concrete depends on balancing weight reduction with required strength for specific structural demands.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Properties
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for lightweight block applications where energy efficiency is critical. Its acoustic insulation properties outperform conventional concrete by absorbing sound waves within its cellular matrix, enhancing noise reduction in residential and commercial buildings. The lower density of cellular concrete blocks also contributes to improved thermal resistance and sound dampening without compromising structural integrity.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Cellular concrete offers superior fire resistance compared to conventional concrete for lightweight blocks due to its porous structure, which effectively absorbs and dissipates heat. This enhanced thermal insulation reduces the risk of structural failure and improves overall safety during fire exposure. Conventional concrete, while strong, lacks the same level of fireproofing, making cellular concrete a preferred choice for fire-resistant construction applications.
Workability and Ease of Handling
Cellular concrete offers superior workability compared to conventional concrete due to its lightweight and highly flowable mix, allowing for easier pouring and shaping in lightweight block production. Its reduced density enhances ease of handling and transport, minimizing labor effort and improving efficiency on construction sites. In contrast, conventional concrete blocks are denser and heavier, requiring more effort during mixing, placement, and curing, which can slow down the workflow and increase physical strain.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Cellular concrete offers significant cost advantages over conventional concrete for lightweight blocks due to reduced material usage and lower transportation expenses, thanks to its lower density and improved workability. The economic viability of cellular concrete is enhanced by decreased labor costs and faster curing times, leading to shorter project durations and overall budget savings. Despite slightly higher initial material costs, cellular concrete's energy efficiency and improved thermal insulation contribute to long-term operational cost reductions, making it a financially sustainable choice for lightweight block applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete significantly reduces environmental impact compared to conventional concrete due to its lower density and reduced cement content, resulting in decreased carbon emissions during production. Its lightweight properties enhance energy efficiency in transportation and construction, while improved thermal insulation contributes to lower building energy consumption. The use of industrial by-products like fly ash in cellular concrete further supports sustainability by reducing waste and conserving natural resources.
Applications and Suitability for Lightweight Block Construction
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for lightweight block construction in energy-efficient buildings and soundproof partitions. Conventional concrete provides higher compressive strength, suitable for structural elements requiring load-bearing capacity in lightweight block applications. The choice depends on project requirements, balancing insulation benefits of cellular concrete with the mechanical strength of conventional concrete.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Conventional concrete for Lightweight block
 azmater.com
azmater.com