Blast-resistant concrete enhances driveway safety by providing superior impact and explosive load resistance through high-strength aggregates and specialized admixtures. Air-entrained concrete improves durability in driveways by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that reduce freeze-thaw damage and increase resistance to deicing chemicals.
Table of Comparison
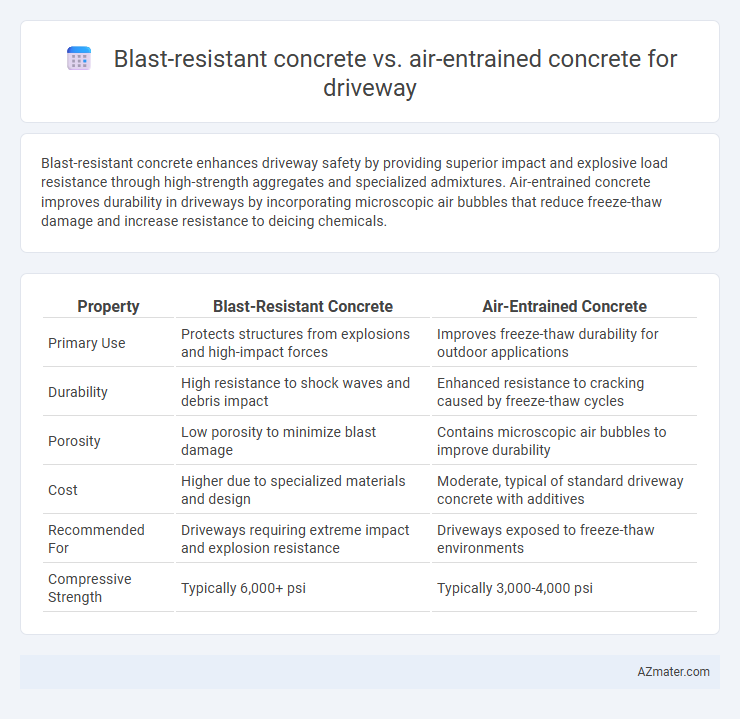
| Property | Blast-Resistant Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Protects structures from explosions and high-impact forces | Improves freeze-thaw durability for outdoor applications |
| Durability | High resistance to shock waves and debris impact | Enhanced resistance to cracking caused by freeze-thaw cycles |
| Porosity | Low porosity to minimize blast damage | Contains microscopic air bubbles to improve durability |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and design | Moderate, typical of standard driveway concrete with additives |
| Recommended For | Driveways requiring extreme impact and explosion resistance | Driveways exposed to freeze-thaw environments |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 6,000+ psi | Typically 3,000-4,000 psi |
Introduction: Importance of Concrete Selection for Driveways
Selecting the appropriate concrete type for driveways directly impacts durability, safety, and maintenance costs. Blast-resistant concrete offers enhanced strength and shock absorption, ideal for high-security or industrial areas, while air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw resistance, crucial for regions with frequent temperature fluctuations. Understanding these specialized properties ensures long-lasting performance and structural integrity under varying environmental and load conditions.
What Is Blast-Resistant Concrete?
Blast-resistant concrete is specially engineered to withstand high-pressure shock waves and impacts from explosions, making it ideal for driveways in high-risk areas or industrial settings. It incorporates high-strength aggregates, fibers, and admixtures to enhance toughness, energy absorption, and crack resistance. Unlike air-entrained concrete, which improves freeze-thaw durability by introducing microscopic air bubbles, blast-resistant concrete prioritizes structural integrity under extreme forces.
What Is Air-Entrained Concrete?
Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve durability by enhancing freeze-thaw resistance, making it ideal for driveways exposed to harsh weather conditions. Blast-resistant concrete, in contrast, is engineered to withstand extreme impact and pressure from explosions but lacks the specific porosity benefits of air-entrained mixes. Using air-entrained concrete for driveways ensures reduced cracking and surface scaling in cold climates, providing longevity and improved structural integrity.
Composition and Structural Properties
Blast-resistant concrete for driveways incorporates high-strength aggregates, steel fibers, and polymer additives to enhance impact absorption and reduce spalling under explosive loads, resulting in superior compressive strength and toughness. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles introduced by air-entraining agents, improving freeze-thaw durability and workability but having lower density and slightly reduced compressive strength compared to blast-resistant mixtures. Structural properties of blast-resistant concrete emphasize high modulus of elasticity and energy dissipation capacity, while air-entrained concrete prioritizes resistance to cracking caused by environmental cycles, making each suitable for distinct driveway performance demands.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Blast-resistant concrete offers superior structural integrity and energy absorption, making it highly effective in mitigating explosive forces and enhancing driveway safety under extreme conditions. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, which prevent cracking and scaling in cold climates but provides limited protection against blasts. Selecting blast-resistant concrete ensures optimal performance against high-impact threats, while air-entrained concrete excels in improving longevity in areas with frequent temperature fluctuations.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Blast-resistant concrete provides superior durability in extreme impact or explosive conditions, maintaining structural integrity without significant spalling or cracking, making it ideal for high-risk environments. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, significantly extending the lifespan of driveways in cold climates through improved durability against water infiltration and surface scaling. While blast-resistant concrete is optimized for impact resistance, air-entrained concrete offers long-term durability in fluctuating weather conditions, with typical lifespan extensions reaching 30 to 50 years depending on environmental exposure.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Blast-resistant concrete typically incurs higher costs due to specialized materials and reinforcement techniques essential for impact and pressure resistance. In contrast, air-entrained concrete is more cost-effective, primarily designed to improve freeze-thaw durability and prevent cracking in driveways exposed to harsh weather. Budget considerations must balance initial investment with long-term performance benefits, where air-entrained concrete offers affordability and durability, while blast-resistant options suit high-risk environments but demand significant upfront expenditure.
Installation Process and Maintenance Requirements
Blast-resistant concrete requires specialized mixing with high-strength aggregates and fibers to enhance impact resistance during installation, often needing skilled labor and longer curing times to achieve structural integrity. Air-entrained concrete involves incorporating microscopic air bubbles through admixtures, which simplifies installation by improving workability and frost resistance, reducing the chance of cracking under freeze-thaw cycles. Maintenance for blast-resistant concrete typically involves inspections for micro-cracks and potential repairs after extreme events, whereas air-entrained concrete demands routine sealing and less frequent repairs due to its superior durability against weathering and deicing salts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Blast-resistant concrete incorporates specialized aggregates and additives to enhance durability against explosions, often resulting in higher embodied energy due to complex manufacturing processes. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, which reduces cracking and extends the driveway's lifespan, promoting sustainability through longevity and reduced repair frequency. From an environmental perspective, air-entrained concrete generally has a lower carbon footprint and better durability in cold climates, making it a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable driveway construction.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Driveway
Blast-resistant concrete offers superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for driveways in high-risk or industrial areas where safety is paramount. Air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, reducing cracking in colder climates and providing a long-lasting, resilient surface. Selecting the right concrete depends on environmental conditions and safety requirements, with blast-resistant concrete preferred for extreme protection and air-entrained concrete favored for climates with frequent freeze-thaw cycles.
Infographic: Blast-resistant concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Driveway
 azmater.com
azmater.com