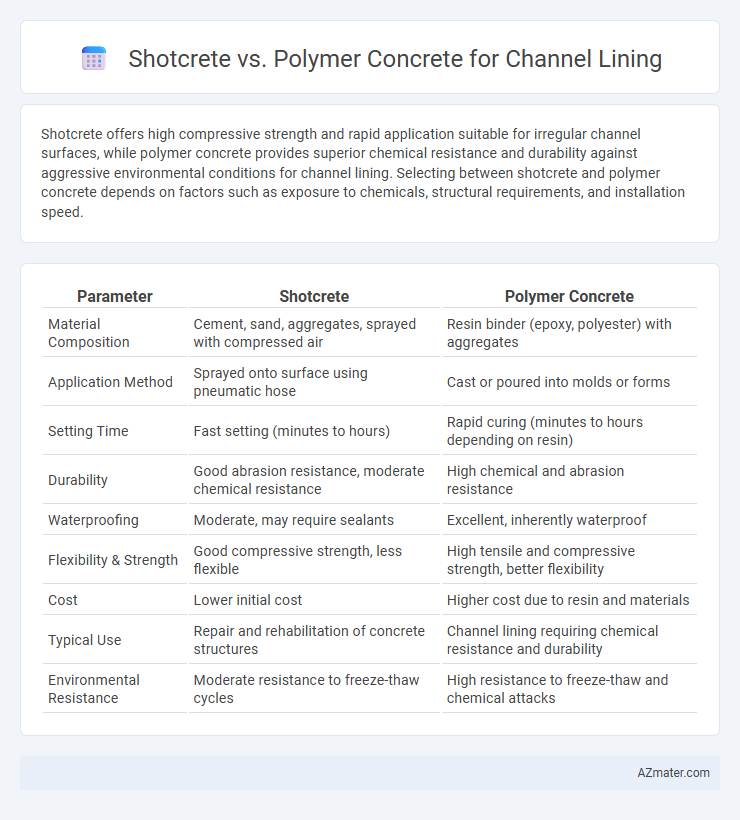
Shotcrete offers high compressive strength and rapid application suitable for irregular channel surfaces, while polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability against aggressive environmental conditions for channel lining. Selecting between shotcrete and polymer concrete depends on factors such as exposure to chemicals, structural requirements, and installation speed.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Shotcrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Cement, sand, aggregates, sprayed with compressed air | Resin binder (epoxy, polyester) with aggregates |
| Application Method | Sprayed onto surface using pneumatic hose | Cast or poured into molds or forms |
| Setting Time | Fast setting (minutes to hours) | Rapid curing (minutes to hours depending on resin) |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, moderate chemical resistance | High chemical and abrasion resistance |
| Waterproofing | Moderate, may require sealants | Excellent, inherently waterproof |
| Flexibility & Strength | Good compressive strength, less flexible | High tensile and compressive strength, better flexibility |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost due to resin and materials |
| Typical Use | Repair and rehabilitation of concrete structures | Channel lining requiring chemical resistance and durability |
| Environmental Resistance | Moderate resistance to freeze-thaw cycles | High resistance to freeze-thaw and chemical attacks |
Introduction to Channel Lining Materials
Shotcrete and polymer concrete are widely utilized channel lining materials due to their durability and adaptability in hydraulic structures. Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete, offers rapid application and excellent adhesion on complex surfaces, enhancing erosion resistance. Polymer concrete incorporates resins as binders, providing superior chemical resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for aggressive environmental conditions.
Overview of Shotcrete Technology
Shotcrete technology involves spraying a mixture of cement, sand, water, and sometimes admixtures at high velocity onto surfaces, providing dense, durable channel lining with excellent adhesion and high compressive strength. This method allows for rapid application and effective reinforcement, forming a continuous, homogeneous layer that resists erosion and minimizes leakage. Shotcrete's adaptability to complex geometries and its ability to be applied without formwork make it a preferred choice for channel lining in water management infrastructure.
Understanding Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete for channel lining offers superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability compared to traditional shotcrete, making it ideal for aggressive environmental conditions. Its composition, which includes polymer binders instead of cement, provides exceptional adhesion and rapid curing properties, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. The versatility of polymer concrete allows for precise application in complex channel geometries where shotcrete may be less effective due to potential segregation or weaker bonding.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Shotcrete offers high compressive strength and excellent adhesion, making it ideal for rapid channel lining in diverse environmental conditions. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability due to its thermosetting polymer binder, suitable for channels exposed to aggressive chemicals or frequent abrasion. Both materials exhibit low permeability, but polymer concrete's flexibility and resistance to thermal cycling often result in longer service life for channel lining applications.
Installation Process: Shotcrete vs Polymer Concrete
Shotcrete installation involves spraying a pneumatically projected concrete mix onto the channel surface, allowing for rapid setting and strong adhesion even on vertical or overhead sections. Polymer concrete, in contrast, requires thorough surface preparation followed by pouring or casting the polymer-infused mixture, which cures chemically to form a durable, corrosion-resistant lining. The shotcrete method generally offers quicker application and immediate structural support, while polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and longer service life after a more controlled curing process.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Shotcrete offers high compressive strength and excellent adhesion, making it suitable for channel lining with moderate durability against weathering and abrasion. Polymer concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance and enhanced durability, providing extended longevity in harsh environments and reducing maintenance needs. Comparative studies indicate polymer concrete outperforms shotcrete in resisting sulfate attack, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion, leading to longer service life in aggressive channel lining conditions.
Cost Considerations and Budget Impact
Shotcrete offers a lower initial cost for channel lining due to reduced material expenses and quicker application times, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects. Polymer concrete, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and chemical resistance, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and repair costs. Careful evaluation of lifecycle costs and project requirements is essential to balance upfront investment against future savings in channel lining applications.
Environmental Resistance and Performance
Shotcrete offers high environmental resistance with excellent durability against water erosion, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for channel linings in harsh outdoor conditions. Polymer concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance and fast curing times, providing enhanced performance in aggressive environments with potential exposure to oils, acids, and salts. Both materials demonstrate strong mechanical strength, but polymer concrete's low permeability and corrosion resistance often result in longer-lasting channel linings under severe environmental stress.
Maintenance and Repair Requirements
Shotcrete requires regular inspection and occasional patching due to potential surface wear and cracking, while polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and durability, resulting in less frequent maintenance and repairs. The polymer concrete's dense, non-porous structure reduces permeability, minimizing damage from exposure to aggressive environmental conditions in channel linings. Maintenance costs for shotcrete can be higher over time due to its susceptibility to spalling and scaling compared to the longer-lasting performance of polymer concrete.
Best Applications and Project Suitability
Shotcrete excels in channel lining projects requiring rapid application and high compressive strength, particularly for curved or complex geometries due to its excellent adherence and moldability. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance and durability against aggressive environmental conditions, making it ideal for channels exposed to corrosive substances or requiring long-term maintenance minimization. Choosing between shotcrete and polymer concrete depends on factors such as exposure conditions, required strength, installation speed, and budget constraints for optimal project suitability.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs Polymer Concrete for Channel Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com