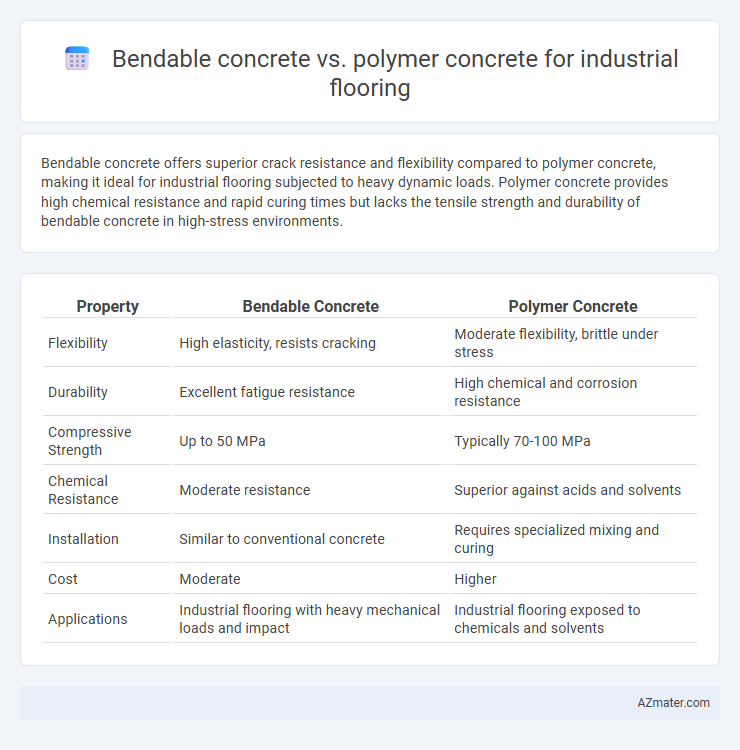
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and flexibility compared to polymer concrete, making it ideal for industrial flooring subjected to heavy dynamic loads. Polymer concrete provides high chemical resistance and rapid curing times but lacks the tensile strength and durability of bendable concrete in high-stress environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bendable Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High elasticity, resists cracking | Moderate flexibility, brittle under stress |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance | High chemical and corrosion resistance |
| Compressive Strength | Up to 50 MPa | Typically 70-100 MPa |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance | Superior against acids and solvents |
| Installation | Similar to conventional concrete | Requires specialized mixing and curing |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Applications | Industrial flooring with heavy mechanical loads and impact | Industrial flooring exposed to chemicals and solvents |
Understanding Bendable Concrete: Composition and Properties
Bendable concrete, also known as ductile concrete, comprises a cementitious matrix reinforced with engineered fibers such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) or steel fibers, enhancing its tensile strain capacity and flexibility. This composite material exhibits superior crack resistance, toughness, and durability compared to traditional concrete, making it ideal for industrial flooring subjected to heavy dynamic loads and thermal stresses. Its unique microstructure enables multiple fine cracks under stress, preventing sudden failure and extending the service life of industrial floors.
Polymer Concrete: Key Features and Advantages
Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance, rapid curing times, and exceptional tensile strength, making it ideal for industrial flooring exposed to harsh chemicals and heavy machinery. Unlike bendable concrete, polymer concrete provides enhanced durability and minimal shrinkage, ensuring long-lasting performance in high-traffic environments. Its excellent adhesion properties and resistance to abrasion reduce maintenance needs and extend the lifespan of industrial floors.
Mechanical Performance Comparison: Strength and Flexibility
Bendable concrete offers superior flexibility with tensile strain capacity up to 0.7%, reducing cracking under mechanical stress, while polymer concrete demonstrates higher compressive strength, often exceeding 80 MPa, ideal for heavy load-bearing floors. The tensile strength of bendable concrete typically ranges between 4 to 7 MPa, providing better impact resistance, whereas polymer concrete's rigidity results in lower tensile strain but greater durability against chemical and abrasion forces. For industrial flooring, the choice depends on whether enhanced flexibility or maximum strength under heavy loads is prioritized.
Durability in Industrial Environments
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and increased tensile strength, making it highly durable under heavy industrial loads and vibrations compared to traditional concrete. Polymer concrete exhibits exceptional chemical resistance and low permeability, ideal for environments exposed to corrosive substances and extreme temperature variations. For industrial flooring, bendable concrete excels in structural longevity, while polymer concrete ensures durability against harsh chemical exposure and moisture infiltration.
Installation Process and Time Efficiency
Bendable concrete, also known as engineered cementitious composite, offers superior crack resistance with a relatively straightforward installation process that requires standard concrete curing times of 7 to 28 days. Polymer concrete involves mixing aggregates with polymer binders, which cure faster, often within 24 to 48 hours, significantly reducing downtime for industrial flooring projects. The faster curing time and chemical resistance of polymer concrete make it ideal for rapid installations, while bendable concrete ensures long-term durability with moderate time efficiency.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Lifecycle Expenses
Bendable concrete offers higher initial investment costs due to its specialized fiber reinforcements and manufacturing process, while polymer concrete typically has moderate upfront expenses linked to resin and aggregate materials. Lifecycle expenses for bendable concrete are lower because of its superior crack resistance and reduced maintenance needs, extending the flooring's durability in industrial environments. Polymer concrete requires more frequent repairs and surface treatments, increasing total cost of ownership despite its lower installation costs.
Resistance to Chemicals and Abrasives
Bendable concrete offers enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, providing superior resistance to cracking under heavy industrial loads, while polymer concrete excels in chemical resistance due to its resin matrix, making it ideal for environments with aggressive chemical exposure. Polymer concrete's composition allows it to withstand a wider range of corrosive chemicals and abrasive materials without degradation, outperforming traditional and bendable concrete in such conditions. Industrial flooring applications demanding high durability against abrasive wear and chemical spills benefit significantly from selecting polymer concrete over bendable concrete.
Maintenance Requirements and Long-term Upkeep
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and flexibility, resulting in reduced maintenance needs and lower long-term repair costs for industrial flooring. Polymer concrete provides enhanced chemical resistance and rapid curing times, but may require more frequent surface treatments to maintain durability in high-impact environments. Both materials extend the lifespan of industrial floors, yet bendable concrete typically demands less upkeep over time due to its inherent flexibility.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bendable concrete offers superior crack resistance and durability, reducing maintenance frequency and lowering resource consumption over the lifespan of industrial flooring, which enhances sustainability. Polymer concrete, composed of resins and aggregates, cures rapidly and resists chemical corrosion, but reliance on synthetic polymers raises concerns about environmental impact and recyclability. Industrial flooring solutions prioritizing sustainability benefit more from bendable concrete due to its longer service life and lower environmental footprint compared to polymer concrete's dependence on petrochemical components.
Best Use Cases: Bendable vs Polymer Concrete for Industrial Flooring
Bendable concrete offers superior tensile strength and crack resistance, making it ideal for industrial flooring subjected to heavy dynamic loads and temperature fluctuations. Polymer concrete excels in chemical resistance and rapid curing, suited for environments exposed to harsh chemicals and requiring fast installation turnaround. Selecting bendable concrete is best for warehouses and manufacturing plants with heavy machinery, whereas polymer concrete suits chemical plants and food processing facilities demanding cleanliness and corrosion resistance.
Infographic: Bendable concrete vs Polymer concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com