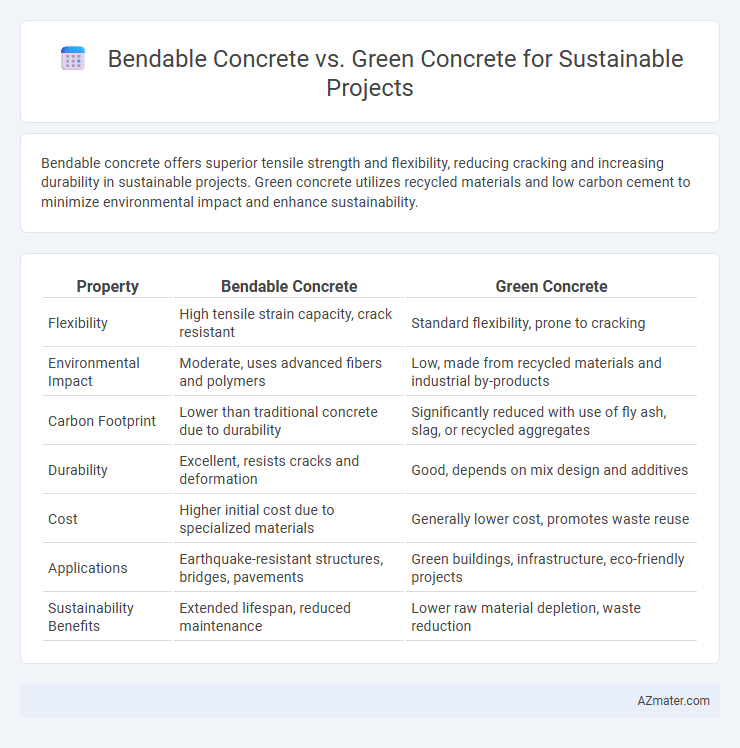
Bendable concrete offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, reducing cracking and increasing durability in sustainable projects. Green concrete utilizes recycled materials and low carbon cement to minimize environmental impact and enhance sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bendable Concrete | Green Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High tensile strain capacity, crack resistant | Standard flexibility, prone to cracking |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, uses advanced fibers and polymers | Low, made from recycled materials and industrial by-products |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower than traditional concrete due to durability | Significantly reduced with use of fly ash, slag, or recycled aggregates |
| Durability | Excellent, resists cracks and deformation | Good, depends on mix design and additives |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to specialized materials | Generally lower cost, promotes waste reuse |
| Applications | Earthquake-resistant structures, bridges, pavements | Green buildings, infrastructure, eco-friendly projects |
| Sustainability Benefits | Extended lifespan, reduced maintenance | Lower raw material depletion, waste reduction |
Introduction to Sustainable Concrete Innovations
Bendable concrete, featuring enhanced tensile strength through fiber reinforcement, offers improved durability and crack resistance, making it ideal for sustainable infrastructure requiring long-lasting performance. Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing carbon emissions and conserving natural resources, thereby promoting eco-friendly construction practices. Both innovations advance sustainable concrete solutions by addressing environmental impact and structural resilience in modern projects.
Understanding Bendable Concrete: Composition and Features
Bendable concrete, also known as engineered cementitious composite (ECC), incorporates short, distributed fibers such as polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) to enhance tensile strength and flexibility, allowing it to withstand significant deformation without cracking. This material's unique microstructure enables strain-hardening behavior, which differs from traditional brittle concrete, making it ideal for sustainable projects that demand durability and reduced maintenance. By improving the structural resilience of infrastructure, bendable concrete contributes to longer service life and lower lifecycle environmental impact compared to standard green concrete variants focused primarily on eco-friendly materials.
What is Green Concrete? Key Ingredients and Benefits
Green concrete is an eco-friendly construction material formulated by incorporating industrial waste products like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, reducing the consumption of cement and natural resources. Key ingredients typically include supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), recycled aggregates, and water-reducing admixtures, which enhance durability and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete. The benefits of green concrete highlight its reduced environmental footprint, improved thermal insulation, and enhanced resistance to chemical attacks, making it ideal for sustainable building projects.
Mechanical Properties: Flexibility vs. Strength
Bendable concrete exhibits superior flexibility and high tensile strain capacity, making it ideal for applications requiring crack resistance and deformation tolerance. Green concrete emphasizes enhanced compressive strength through the use of recycled materials and reduced carbon footprint, supporting structural durability and sustainability. Balancing flexibility in bendable concrete with the robust strength of green concrete offers innovative solutions for sustainable construction projects.
Environmental Impact: Carbon Footprint Comparison
Bendable concrete reduces cracking and extends the lifespan of structures, lowering the demand for repairs and reconstruction, which diminishes the overall carbon footprint compared to traditional concrete. Green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products such as fly ash or slag, significantly reducing CO2 emissions by minimizing cement content. Both materials offer environmental benefits, but green concrete directly addresses carbon emissions during production, making it a critical choice for sustainable projects focused on reducing environmental impact.
Durability and Lifespan in Construction Projects
Bendable concrete features enhanced tensile strength and flexibility, significantly reducing cracking and extending the lifespan of construction projects compared to traditional materials. Green concrete, formulated with recycled materials and industrial byproducts, improves durability by resisting environmental degradation while reducing the carbon footprint. Both types contribute to sustainable construction by offering longer-lasting structural integrity but bendable concrete excels in resilience to dynamic stresses.
Cost Analysis: Production and Long-Term Savings
Bendable concrete, known for its enhanced flexibility and durability, typically incurs higher initial production costs compared to traditional green concrete, which incorporates recycled materials to reduce expenses. Green concrete offers immediate cost benefits through lower raw material usage and energy consumption during production, but bendable concrete's reduced cracking frequency significantly lowers maintenance and repair costs over the structure's lifecycle. Long-term savings favor bendable concrete for sustainable projects requiring resilience, while green concrete suits budget-sensitive initiatives emphasizing environmental impact reduction.
Application Areas: Where Each Concrete Excels
Bendable concrete excels in infrastructure projects requiring high durability and flexibility, such as bridge decks, pavements, and seismic-resistant structures, due to its enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance. Green concrete is ideal for sustainable building construction, including residential, commercial, and industrial projects, as it incorporates recycled materials and reduces carbon footprint while maintaining adequate structural performance. Both types contribute to sustainability, with bendable concrete optimizing longevity and resilience, and green concrete prioritizing environmental impact and resource conservation.
Challenges and Limitations of Bendable and Green Concrete
Bendable concrete faces challenges such as higher production costs, limited large-scale implementation, and durability concerns under extreme environmental conditions. Green concrete often struggles with variability in raw material quality, reduced early strength compared to traditional concrete, and difficulties in large-scale adoption due to supply chain constraints. Both materials require ongoing research to optimize performance and ensure compatibility with existing construction standards for sustainable projects.
Future Trends: Integrating Bendable and Green Concrete for Sustainability
Future trends in sustainable construction emphasize integrating bendable concrete with green concrete to enhance both durability and environmental performance. Bendable concrete's high tensile strain capacity reduces structural damage and extends lifespan, while green concrete's use of recycled materials and lower carbon footprint minimizes environmental impact. Combining these innovations supports resilient infrastructure development aligned with carbon reduction goals and resource efficiency initiatives.
Infographic: Bendable concrete vs Green concrete for Sustainable project
 azmater.com
azmater.com