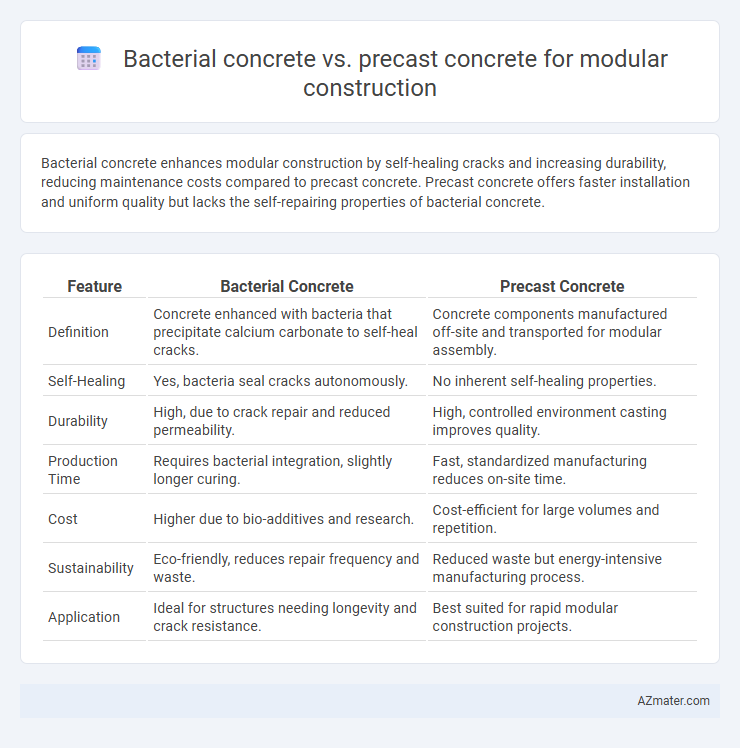
Bacterial concrete enhances modular construction by self-healing cracks and increasing durability, reducing maintenance costs compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete offers faster installation and uniform quality but lacks the self-repairing properties of bacterial concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bacterial Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete enhanced with bacteria that precipitate calcium carbonate to self-heal cracks. | Concrete components manufactured off-site and transported for modular assembly. |
| Self-Healing | Yes, bacteria seal cracks autonomously. | No inherent self-healing properties. |
| Durability | High, due to crack repair and reduced permeability. | High, controlled environment casting improves quality. |
| Production Time | Requires bacterial integration, slightly longer curing. | Fast, standardized manufacturing reduces on-site time. |
| Cost | Higher due to bio-additives and research. | Cost-efficient for large volumes and repetition. |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly, reduces repair frequency and waste. | Reduced waste but energy-intensive manufacturing process. |
| Application | Ideal for structures needing longevity and crack resistance. | Best suited for rapid modular construction projects. |
Introduction to Modular Construction
Modular construction increasingly leverages innovative materials such as bacterial concrete and precast concrete to enhance structural efficiency and sustainability. Bacterial concrete utilizes microorganisms to self-heal cracks, significantly extending the lifespan and durability of modular units in varying environmental conditions. In contrast, precast concrete offers rapid assembly and uniform quality control, making it a favored choice for scalable and repetitive modular construction projects.
Overview of Bacterial Concrete
Bacterial concrete integrates specific bacteria such as Bacillus pasteurii to precipitate calcium carbonate, effectively sealing cracks and enhancing durability, which improves the self-healing properties of modular construction components. This bio-based method reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of concrete structures by autonomously filling microcracks. Compared to precast concrete, bacterial concrete offers superior environmental sustainability through reduced carbon footprint and resource consumption during production.
Fundamentals of Precast Concrete
Precast concrete in modular construction involves casting concrete elements in controlled factory environments, ensuring high quality and uniformity through precise curing and reinforcement techniques. Bacterial concrete enhances durability by incorporating bacteria that precipitate calcium carbonate, healing cracks and improving structural longevity, but it requires integration with standard precast manufacturing processes for optimal results. The fundamental advantage of precast concrete lies in its rapid on-site assembly and consistent strength, making it a reliable backbone for modular construction frameworks.
Material Properties Comparison
Bacterial concrete enhances durability by self-healing micro-cracks through bacterial-induced calcite precipitation, which improves longevity and reduces maintenance needs compared to traditional precast concrete. Precast concrete offers consistent quality and faster construction due to factory-controlled conditions but lacks the self-repairing capability inherent in bacterial concrete. Material properties such as compressive strength are comparable, but bacterial concrete exhibits increased resistance to chemical attacks and environmental degradation, making it advantageous for modular construction demanding long-term resilience.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Bacterial concrete enhances durability by utilizing microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation, which seals microcracks and reduces permeability, resulting in improved resistance to environmental degradation and chemical attack compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete offers controlled manufacturing conditions that ensure consistent quality and strength, but may exhibit standard durability limitations under harsh exposure without additional protective treatments. The self-healing properties of bacterial concrete contribute to extended longevity and reduced maintenance needs in modular construction, making it a promising alternative for sustainable and resilient infrastructure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bacterial concrete enhances sustainability in modular construction by reducing carbon emissions through self-healing properties that extend the lifespan of structures, minimizing repair frequency and material waste. Precast concrete, while offering efficient production and reduced onsite waste, often involves high energy consumption and emissions during manufacturing and transportation stages. Integrating bacterial concrete into modular systems significantly lowers the environmental footprint by promoting durability and resource efficiency compared to traditional precast methods.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term
Bacterial concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to the incorporation of self-healing bacteria and specialized materials, which can reduce long-term maintenance expenses by repairing microcracks autonomously. Precast concrete offers lower upfront costs through mass production and standardized molds, but may result in increased long-term expenses from conventional repairs and weathering. Evaluating the total cost of ownership reveals bacterial concrete's potential for greater lifecycle savings despite its premium initial investment in modular construction.
Construction Speed and Efficiency
Bacterial concrete accelerates modular construction by self-healing micro-cracks, reducing downtime for repairs and enhancing structural integrity, which significantly improves overall speed and efficiency on-site. Precast concrete offers rapid assembly through factory-controlled production, enabling consistent quality and reduced curing time compared to traditional methods. Combining bacterial concrete's durability with precast elements maximizes construction efficiency by minimizing delays and extending structure lifespan.
Applications in Modular Construction
Bacterial concrete enhances modular construction by enabling self-healing properties that extend the lifespan of structural elements, reducing maintenance costs and improving durability in harsh environments. Precast concrete offers rapid assembly with consistent quality and precise dimensions, making it ideal for large-scale modular projects requiring uniformity and speed. Both materials are leveraged in modular construction to optimize structural integrity and construction efficiency, with bacterial concrete favored for longevity and precast concrete prioritized for speed and scalability.
Future Trends and Innovations
Bacterial concrete leverages microbial-induced calcite precipitation to self-heal cracks, significantly enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs in modular construction. Precast concrete benefits from advancements in automation and digital twin technology, enabling faster production cycles and improved quality control for large-scale modular projects. Future trends include integrating bio-based additives in bacterial concrete and AI-driven manufacturing processes in precast concrete to optimize sustainability and structural performance.
Infographic: Bacterial concrete vs Precast concrete for Modular construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com