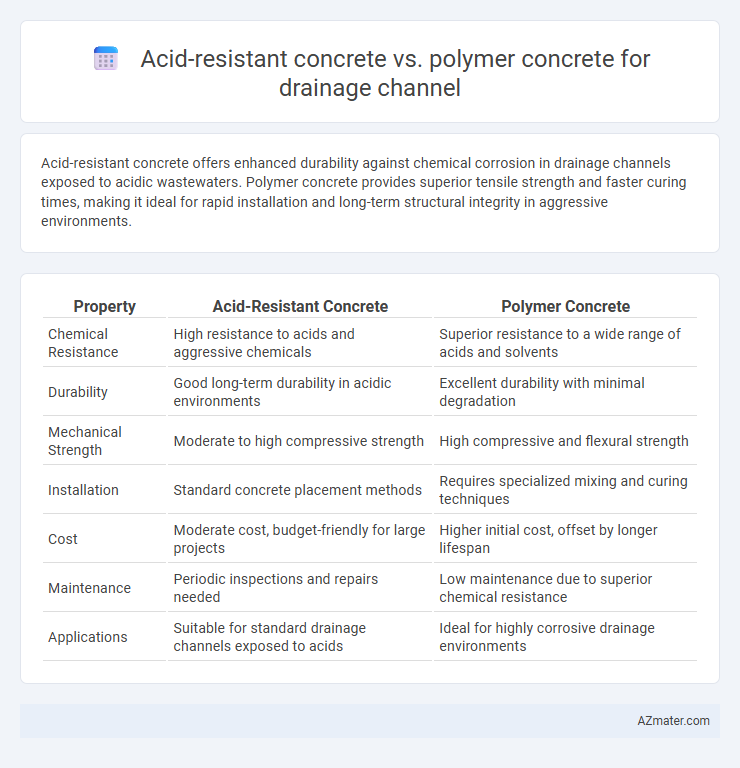
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability against chemical corrosion in drainage channels exposed to acidic wastewaters. Polymer concrete provides superior tensile strength and faster curing times, making it ideal for rapid installation and long-term structural integrity in aggressive environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids and aggressive chemicals | Superior resistance to a wide range of acids and solvents |
| Durability | Good long-term durability in acidic environments | Excellent durability with minimal degradation |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to high compressive strength | High compressive and flexural strength |
| Installation | Standard concrete placement methods | Requires specialized mixing and curing techniques |
| Cost | Moderate cost, budget-friendly for large projects | Higher initial cost, offset by longer lifespan |
| Maintenance | Periodic inspections and repairs needed | Low maintenance due to superior chemical resistance |
| Applications | Suitable for standard drainage channels exposed to acids | Ideal for highly corrosive drainage environments |
Introduction to Acid-Resistant and Polymer Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is engineered with special cement and aggregates to withstand highly corrosive environments, making it ideal for drainage channels exposed to acidic sewage and industrial effluents. Polymer concrete utilizes polymer binders instead of traditional cement, offering superior chemical resistance, rapid curing, and enhanced durability in aggressive environments. Both materials are critical in infrastructure requiring long-term exposure to harsh chemicals, but polymer concrete provides higher tensile strength and decreased permeability compared to acid-resistant concrete.
Importance of Material Selection in Drainage Channels
Material selection for drainage channels is critical to ensure durability and chemical resistance, especially in environments exposed to acidic substances. Acid-resistant concrete offers excellent protection against chemical corrosion due to its specialized cementitious composition, while polymer concrete provides superior mechanical strength and resistance to a wider range of aggressive chemicals through its resin binder matrix. Choosing between acid-resistant concrete and polymer concrete depends on specific site conditions, including exposure to chemicals, load requirements, and maintenance considerations to optimize the lifespan and functionality of drainage systems.
Chemical Resistance: Acid-Resistant vs Polymer Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical resistance against sulfuric and hydrochloric acids commonly found in industrial drainage channels, preventing surface degradation and extending lifespan. Polymer concrete exhibits excellent resistance to a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals, including solvents and alkalis, due to its dense polymer matrix that minimizes permeability. For drainage channels exposed to highly acidic environments, acid-resistant concrete provides more targeted protection, while polymer concrete delivers versatile resistance suitable for mixed chemical exposures.
Mechanical Properties and Durability Comparisons
Acid-resistant concrete offers high compressive strength and moderate tensile strength, making it suitable for heavy load-bearing drainage channels exposed to acidic environments. Polymer concrete exhibits superior tensile strength, enhanced chemical resistance, and improved flexural strength, resulting in excellent durability against aggressive chemicals and thermal cycling. Mechanical properties of polymer concrete contribute to longer service life and reduced maintenance in corrosive drainage applications compared to acid-resistant concrete.
Installation and Construction Techniques
Acid-resistant concrete for drainage channels requires meticulous surface preparation and controlled curing processes to ensure chemical durability, typically involving the use of specialized aggregates and cementitious materials. Polymer concrete installation emphasizes rapid setting and curing times with superior adhesion, allowing for modular or precast segment assembly that minimizes downtime. Construction techniques for polymer concrete often include shot blasting or sandblasting to enhance bonding, whereas acid-resistant concrete demands careful formwork design to prevent permeability and structural weaknesses.
Maintenance Requirements for Each Material
Acid-resistant concrete requires periodic inspection for surface degradation and may need reapplication of protective coatings to maintain its durability against chemical exposure. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance, resulting in lower maintenance frequency and reduced risk of cracks or spalling caused by acid corrosion. Both materials benefit from routine cleaning, but polymer concrete's dense matrix significantly minimizes maintenance efforts in acidic drainage channel environments.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Costs
Acid-resistant concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized cement and aggregate materials designed to withstand corrosive environments in drainage channels. Polymer concrete, while often more expensive upfront, offers reduced lifecycle costs through superior chemical resistance, decreased maintenance, and extended service life in aggressive acid exposure. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals polymer concrete's potential for long-term savings despite initial investment differences.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acid-resistant concrete offers robust chemical resistance, minimizing leaching and reducing environmental contamination in drainage channels exposed to acidic wastewaters. Polymer concrete features superior durability and reduced permeability, lowering maintenance frequency and extending service life, which contributes to sustainability by decreasing resource consumption. Both materials enhance sustainable drainage infrastructure by improving longevity and mitigating harmful environmental effects through tailored chemical resistance properties.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability, effectively resisting corrosion from aggressive acids commonly found in industrial drainage channels. Polymer concrete provides enhanced mechanical strength and excellent resistance to thermal shock and freeze-thaw cycles, making it suitable for extreme temperature variations. Both materials excel in harsh environments, but polymer concrete demonstrates better performance under dynamic stresses, while acid-resistant concrete is optimal for prolonged acid exposure.
Application Suitability: Which Concrete for Your Drainage Channel?
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for drainage channels exposed to aggressive chemical environments, such as industrial waste or acidic runoff, due to its strong resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation. Polymer concrete offers superior mechanical strength and rapid curing, making it suitable for high-load applications and areas requiring quick installation but is less resistant to prolonged chemical attack. Choosing between acid-resistant and polymer concrete depends on the specific environmental conditions and load requirements of the drainage channel to ensure durability and optimal performance.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Polymer concrete for Drainage channel
 azmater.com
azmater.com