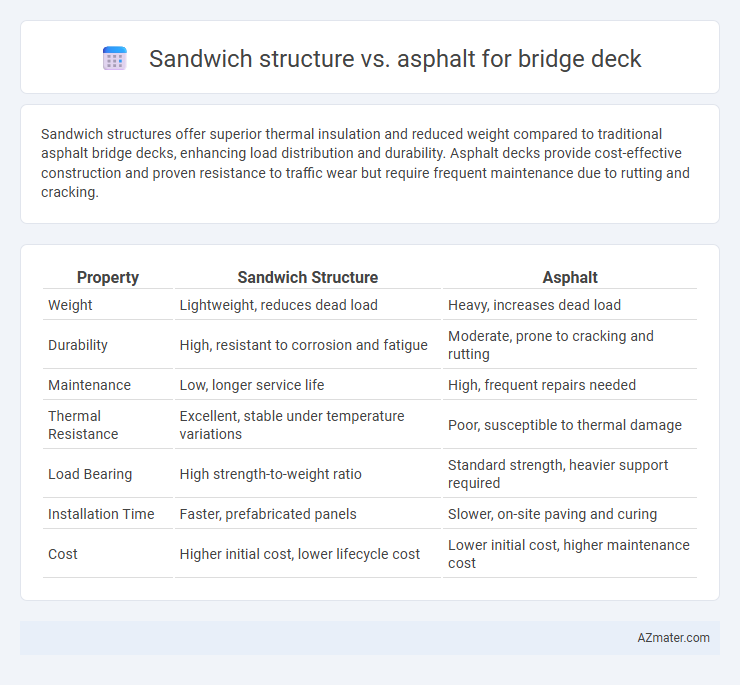
Sandwich structures offer superior thermal insulation and reduced weight compared to traditional asphalt bridge decks, enhancing load distribution and durability. Asphalt decks provide cost-effective construction and proven resistance to traffic wear but require frequent maintenance due to rutting and cracking.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sandwich Structure | Asphalt |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces dead load | Heavy, increases dead load |
| Durability | High, resistant to corrosion and fatigue | Moderate, prone to cracking and rutting |
| Maintenance | Low, longer service life | High, frequent repairs needed |
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, stable under temperature variations | Poor, susceptible to thermal damage |
| Load Bearing | High strength-to-weight ratio | Standard strength, heavier support required |
| Installation Time | Faster, prefabricated panels | Slower, on-site paving and curing |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower lifecycle cost | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance cost |
Introduction to Bridge Deck Materials
Bridge deck materials significantly impact the durability and performance of structures, with sandwich structures offering a lightweight, high-strength alternative to traditional asphalt. Sandwich decks typically consist of composite layers incorporating foam or honeycomb cores between concrete or steel plates, enhancing stiffness and reducing dead load. Asphalt decks provide flexibility and easy maintenance but are prone to rutting and fatigue under heavy traffic, making sandwich structures more suitable for long-span and high-load bridge applications.
Overview of Sandwich Structure Bridge Decks
Sandwich structure bridge decks consist of a lightweight core material, such as foam or honeycomb, bonded between two structural face sheets, typically made of fiber-reinforced polymer or steel. This design offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced durability, and improved thermal insulation compared to traditional asphalt decks. Their reduced self-weight decreases live load demands on the bridge substructure, leading to potential cost savings in foundation and support design.
Asphalt Bridge Deck Systems Explained
Asphalt bridge deck systems consist of multiple layers including a waterproofing membrane and an asphalt topping that provide superior waterproofing and durability compared to sandwich structures. The flexible nature of asphalt accommodates thermal expansion and contraction, reducing cracking and maintenance costs over time. Asphalt bridge decks offer enhanced skid resistance and noise reduction, making them a preferred choice in heavy traffic and high-load bridge applications.
Material Composition and Engineering
Sandwich structures for bridge decks typically consist of two high-strength composite face sheets bonded to a lightweight core material such as foam or honeycomb, providing superior stiffness-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability compared to traditional asphalt layers. Asphalt bridge decks rely on a dense, flexible aggregate bituminous mixture that offers excellent surface friction and ease of maintenance but can suffer from rutting and fatigue under heavy traffic loads. Engineering considerations favor sandwich structures for their resistance to cracking and corrosion, while asphalt decks remain popular due to cost-effectiveness and established construction practices.
Structural Performance Comparison
Sandwich structures for bridge decks exhibit superior load distribution and enhanced stiffness compared to traditional asphalt layers, reducing deflection and improving fatigue resistance under repeated traffic loads. The composite nature of sandwich panels, typically combining a rigid core with reinforced face sheets, results in higher strength-to-weight ratios and better resistance to environmental deterioration than conventional asphalt surfaces. While asphalt offers ease of maintenance and cost efficiency, sandwich structures provide longer service life and improved structural performance, making them ideal for bridges subjected to high traffic volumes and heavy loads.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Sandwich structures for bridge decks, composed of a lightweight core bonded between two high-strength face sheets, offer enhanced durability due to superior resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and environmental degradation compared to traditional asphalt surfaces. Asphalt decks are prone to cracking, rutting, and moisture infiltration, leading to frequent maintenance and shorter service life, typically around 15-20 years, whereas sandwich structures can extend lifespan beyond 30 years with minimal upkeep. The improved structural integrity and thermal stability of sandwich decks result in lower life-cycle costs and greater long-term performance under variable traffic loads and harsh climatic conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Maintenance Considerations
Sandwich structures for bridge decks offer enhanced durability and lower life-cycle costs compared to traditional asphalt layers due to their composite materials, which reduce the frequency of repairs and maintenance interventions. Although initial installation costs for sandwich deck systems are typically higher than asphalt, the long-term savings from decreased maintenance and improved structural performance result in better cost efficiency. Asphalt decks require regular resurfacing and are more susceptible to cracking and deformation under heavy traffic loads, leading to increased maintenance expenses and service disruptions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sandwich structures for bridge decks significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing lightweight, recyclable materials like foam cores and fiber-reinforced polymers, which lower transportation emissions and resource consumption compared to traditional asphalt. Asphalt requires frequent maintenance and resurfacing due to wear and weathering, leading to higher carbon emissions and greater material waste over the bridge's lifecycle. Sustainable bridge deck design favors sandwich structures for enhanced durability, energy efficiency, and a smaller carbon footprint, contributing to long-term ecological benefits.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies reveal that sandwich structures in bridge decks significantly reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity, exemplified by the Zeeland Bridge in the Netherlands, where a foam-core sandwich deck reduced dead load by 30%. Asphalt decks, such as those on the I-5 Bridge in Oregon, demonstrate durability and ease of maintenance under heavy traffic conditions but often require more frequent resurfacing. Comparative analyses highlight that sandwich structures offer enhanced fatigue resistance and thermal insulation, whereas asphalt provides cost-effective initial installation and repair advantages.
Choosing the Best Bridge Deck Solution
Choosing the best bridge deck solution involves evaluating the durability, weight, and maintenance requirements of sandwich structures versus asphalt. Sandwich structures offer superior load distribution and corrosion resistance due to their composite layers, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs. Asphalt decks provide cost-effective installation and straightforward repair but often require frequent resurfacing and are prone to cracking under heavy traffic conditions.
Infographic: Sandwich structure vs Asphalt for Bridge deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com