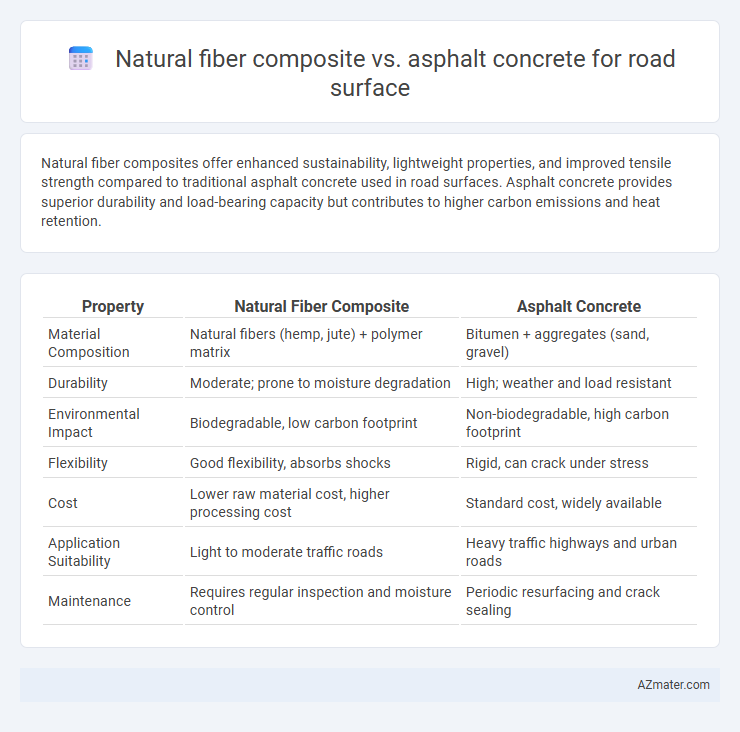
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced sustainability, lightweight properties, and improved tensile strength compared to traditional asphalt concrete used in road surfaces. Asphalt concrete provides superior durability and load-bearing capacity but contributes to higher carbon emissions and heat retention.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Natural Fiber Composite | Asphalt Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers (hemp, jute) + polymer matrix | Bitumen + aggregates (sand, gravel) |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to moisture degradation | High; weather and load resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon footprint |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, absorbs shocks | Rigid, can crack under stress |
| Cost | Lower raw material cost, higher processing cost | Standard cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability | Light to moderate traffic roads | Heavy traffic highways and urban roads |
| Maintenance | Requires regular inspection and moisture control | Periodic resurfacing and crack sealing |
Introduction to Road Surface Materials
Natural fiber composites offer lightweight and sustainable alternatives to traditional road surface materials by incorporating fibers such as hemp, coir, or jute into binding matrices. Asphalt concrete remains the most widely used road surface material due to its durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in handling diverse traffic loads and climate conditions. Comparative studies show natural fiber composites can enhance crack resistance and reduce environmental impact, positioning them as promising candidates for future eco-friendly road infrastructure.
Overview of Natural Fiber Composites
Natural fiber composites are engineered materials combining natural fibers such as hemp, jute, or coir with a polymer matrix, offering enhanced tensile strength, flexibility, and eco-friendliness compared to traditional materials. These composites reduce the carbon footprint of road construction by utilizing renewable resources and improving durability against cracking and deformation. Their lightweight nature and resistance to moisture also contribute to longer-lasting, sustainable road surfaces when compared to conventional asphalt concrete.
Asphalt Concrete: Traditional Road Material
Asphalt concrete remains the predominant material for road surfaces due to its durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. Composed of mineral aggregate bound with bitumen, it provides excellent load distribution and resistance to weathering and traffic load variations. Despite advancements in sustainable alternatives like natural fiber composites, asphalt concrete continues to dominate infrastructure projects globally because of its proven performance and extensive usage history.
Material Properties Comparison
Natural fiber composites offer improved tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to asphalt concrete, which is typically rigid and prone to cracking under stress. The higher elasticity and impact resistance of natural fiber composites contribute to better durability in varying weather conditions. Asphalt concrete exhibits superior compressive strength and load-bearing capacity, making it more suitable for heavy traffic applications despite its lower resistance to moisture-induced damage.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Natural fiber composites offer significant environmental benefits over asphalt concrete in road surface applications, including reduced carbon footprint and enhanced biodegradability. Life cycle assessments show that natural fiber composites generate lower greenhouse gas emissions during production and disposal phases compared to petroleum-based asphalt concrete. Their renewable sourcing and potential for carbon sequestration contribute to improved sustainability and reduced environmental pollution.
Durability and Performance Analysis
Natural fiber composites demonstrate enhanced durability in road surfaces through improved crack resistance and moisture absorption control, outperforming traditional asphalt concrete under varying environmental conditions. The incorporation of natural fibers like jute, hemp, or coir increases tensile strength and reduces fatigue damage, leading to extended service life compared to conventional asphalt mixtures. Performance analysis reveals that natural fiber composites maintain structural integrity with lower maintenance costs and better sustainability metrics, making them a promising alternative for durable and resilient road infrastructure.
Cost Implications and Economic Feasibility
Natural fiber composites offer cost advantages due to lower material and production expenses compared to asphalt concrete, primarily because of the renewability and abundance of fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute. Asphalt concrete requires significant investment in petrochemical binders and energy-intensive production processes, leading to higher life-cycle costs and maintenance expenses. Economic feasibility favors natural fiber composites in regions with access to affordable biomass resources, where reduced environmental impact and potential for local sourcing further enhance cost-effectiveness.
Sustainability and Resource Availability
Natural fiber composites for road surfaces offer enhanced sustainability through renewable, biodegradable materials that reduce environmental impact compared to traditional asphalt concrete derived from non-renewable petroleum resources. The use of agricultural waste fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute in composites promotes circular economy practices and decreases dependence on finite fossil fuels, improving resource availability. Asphalt concrete, while widely used for durability and ease of application, poses challenges related to carbon emissions and limited raw materials, making natural fiber composites a viable eco-friendly alternative for sustainable infrastructure development.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Natural fiber composites, such as those reinforced with hemp or jute fibers, have demonstrated improved tensile strength and durability in road surfaces compared to traditional asphalt concrete, as evidenced by case studies in India and Brazil. Real-world applications reveal that natural fiber composites offer enhanced environmental benefits, including reduced carbon emissions and better resistance to temperature fluctuations, leading to longer service life. Furthermore, pilot projects utilizing natural fiber composites report lower maintenance costs and increased resilience against cracking under heavy traffic conditions.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Natural fiber composites offer enhanced sustainability and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional asphalt concrete, positioning them as a promising alternative for future road surfaces. Research trends emphasize improving mechanical properties and durability by integrating nano additives and hybrid fibers to overcome current limitations in strength and weather resistance. Recommendations focus on large-scale pilot projects and life-cycle assessments to validate performance benefits and cost-effectiveness in diverse climatic conditions.
Infographic: Natural fiber composite vs Asphalt concrete for Road surface
 azmater.com
azmater.com