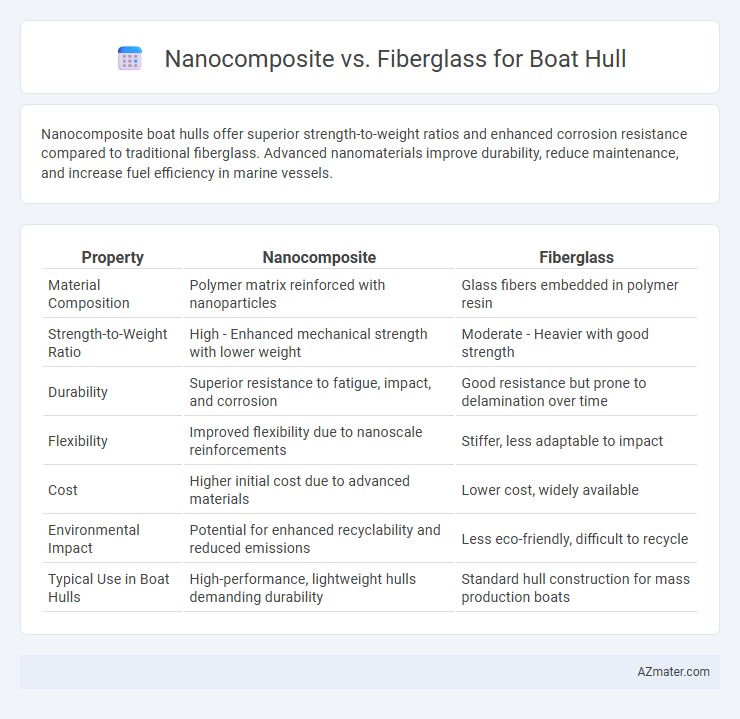
Nanocomposite boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to traditional fiberglass. Advanced nanomaterials improve durability, reduce maintenance, and increase fuel efficiency in marine vessels.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocomposite | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer matrix reinforced with nanoparticles | Glass fibers embedded in polymer resin |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High - Enhanced mechanical strength with lower weight | Moderate - Heavier with good strength |
| Durability | Superior resistance to fatigue, impact, and corrosion | Good resistance but prone to delamination over time |
| Flexibility | Improved flexibility due to nanoscale reinforcements | Stiffer, less adaptable to impact |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for enhanced recyclability and reduced emissions | Less eco-friendly, difficult to recycle |
| Typical Use in Boat Hulls | High-performance, lightweight hulls demanding durability | Standard hull construction for mass production boats |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Nanocomposite materials incorporate nanoparticles into a polymer matrix, enhancing strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion compared to traditional fiberglass used in boat hulls. Fiberglass, composed of woven glass fibers embedded in resin, remains popular for its affordability, ease of repair, and proven performance in marine environments. Recent advances in nanocomposite technology offer superior mechanical properties and weight reduction, making them an increasingly attractive choice for high-performance and lightweight boat hull construction.
Overview of Nanocomposites
Nanocomposites in boat hull construction incorporate nanoparticles into polymer matrices, significantly enhancing mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion compared to traditional fiberglass. These materials provide superior impact resistance and reduced weight, which improves fuel efficiency and overall vessel performance. The advanced molecular structure of nanocomposites ensures better stress distribution and extended lifespan, making them a promising alternative for marine applications.
Understanding Fiberglass Composites
Fiberglass composites consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance ideal for boat hulls. Nanocomposites enhance traditional fiberglass by incorporating nanoparticles, improving mechanical properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance while reducing weight. Understanding the structure and performance differences in fiberglass composites helps in selecting the best material for durability and efficiency in marine environments.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nanocomposite materials exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to fiberglass when used in boat hull construction, offering higher tensile strength and improved impact resistance. The incorporation of nanoscale fillers like carbon nanotubes or graphene enhances stiffness and durability, resulting in lighter yet stronger hulls. Fiberglass, while cost-effective and widely used, generally provides lower mechanical strength and is more prone to damage under high stress or impact conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Nanocomposite boat hulls offer exceptional durability due to their enhanced resistance to impact, corrosion, and UV degradation, resulting in longer service life compared to traditional fiberglass. Fiberglass hulls, while widely used and cost-effective, are more prone to cracking, osmotic blistering, and wear under harsh marine conditions, which can compromise longevity over time. Advanced nanocomposite materials provide superior structural integrity and reduced maintenance needs, making them a preferred choice for extended durability in marine applications.
Weight and Performance Differences
Nanocomposite boat hulls offer significantly reduced weight compared to traditional fiberglass, enhancing speed and fuel efficiency. Their superior strength-to-weight ratio allows for improved impact resistance and durability under harsh marine conditions. Fiberglass hulls, while heavier, provide reliable performance but lag behind nanocomposites in agility and long-term structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Nanocomposite vs Fiberglass
Nanocomposite boat hulls generally incur higher initial material and manufacturing costs compared to traditional fiberglass due to advanced fabrication techniques and specialized raw materials. Lifecycle expenses for nanocomposites can be lower as they offer superior durability, reduced maintenance, and enhanced resistance to corrosion and impact, contributing to long-term savings. Fiberglass remains cost-effective upfront but may require more frequent repairs and maintenance, increasing overall costs over the vessel's lifespan.
Maintenance Requirements
Nanocomposite boat hulls demand less maintenance compared to fiberglass due to their enhanced corrosion resistance and lower susceptibility to water absorption. Fiberglass hulls often require regular gel coat repairs, waxing, and periodic inspection for osmotic blistering. The durability of nanocomposites reduces the frequency of surface refinishing and structural repairs, leading to cost savings over the boat's lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocomposite boat hulls exhibit enhanced durability and reduced weight, leading to lower fuel consumption and decreased carbon emissions during operation compared to fiberglass. Fiberglass production involves energy-intensive processes and non-biodegradable materials, contributing to landfill waste and environmental pollution. Nanocomposites often incorporate eco-friendly resins and recyclable components, promoting sustainability by minimizing ecological footprint throughout the boat's lifecycle.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Materials
Nanocomposite materials are poised to revolutionize boat hull construction due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced corrosion resistance, and improved impact durability compared to traditional fiberglass. Innovations in nanotechnology enable the infusion of carbon nanotubes and graphene into polymer matrices, resulting in hulls that offer greater fuel efficiency and reduced maintenance costs. The maritime industry is increasingly adopting these advanced composites to meet stringent environmental regulations and demand for sustainable, high-performance vessels.
Infographic: Nanocomposite vs Fiberglass for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com