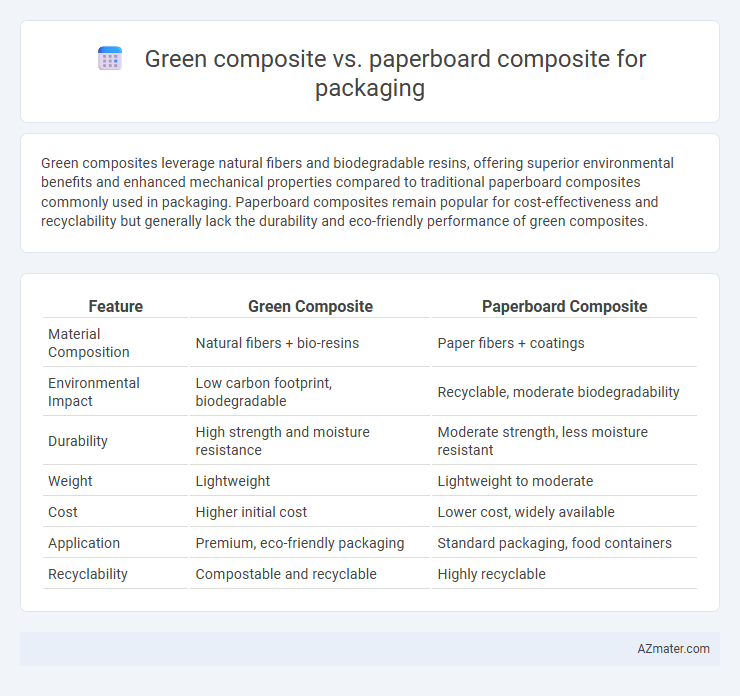
Green composites leverage natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offering superior environmental benefits and enhanced mechanical properties compared to traditional paperboard composites commonly used in packaging. Paperboard composites remain popular for cost-effectiveness and recyclability but generally lack the durability and eco-friendly performance of green composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Green Composite | Paperboard Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + bio-resins | Paper fibers + coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Recyclable, moderate biodegradability |
| Durability | High strength and moisture resistance | Moderate strength, less moisture resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight to moderate |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | Premium, eco-friendly packaging | Standard packaging, food containers |
| Recyclability | Compostable and recyclable | Highly recyclable |
Introduction to Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Green composites utilize natural fibers like hemp, jute, or flax combined with biodegradable resins, offering superior environmental benefits through reduced carbon footprint and enhanced recyclability compared to traditional materials. Paperboard composites blend cellulose fibers with minimal synthetic additives, providing lightweight, cost-effective packaging with good strength and recyclability, but typically lower moisture resistance. Selecting sustainable packaging depends on balancing factors such as biodegradability, mechanical properties, and lifecycle environmental impacts tailored to specific product requirements.
Defining Green Composites and Their Composition
Green composites for packaging consist of natural fibers such as hemp, jute, or flax reinforced with biodegradable polymers like polylactic acid (PLA), creating eco-friendly, sustainable materials with a low environmental footprint. Paperboard composites combine cellulose fibers from wood pulp with synthetic or natural binders, offering rigidity and printability but often relying on non-biodegradable additives. The key distinction lies in green composites' emphasis on renewable, compostable components, while paperboard composites primarily focus on structural integrity derived from processed wood fibers.
Understanding Paperboard Composites in Packaging
Paperboard composites in packaging combine layers of paperboard with other materials like plastic or foil to enhance strength, durability, and moisture resistance, making them ideal for protecting goods during transit. Unlike green composites that primarily utilize bio-based fibers reinforced with biodegradable resins for sustainable packaging, paperboard composites prioritize recyclability and cost-effectiveness while maintaining structural integrity. Understanding the balance between barrier properties and environmental impact is crucial for selecting paperboard composites in packaging applications.
Environmental Impact: Green Composite vs Paperboard Composite
Green composites, composed of natural fibers and bio-based resins, offer superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprints compared to traditional paperboard composites, which often rely on chemical processing and virgin materials. The reduced energy consumption in producing green composites significantly diminishes greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing sustainability in packaging applications. Lifecycle assessments reveal that green composites minimize landfill waste and promote compostability, making them an environmentally preferable option over conventional paperboard composites.
Material Strength and Performance Comparison
Green composites, typically made from natural fibers like hemp or flax combined with biodegradable resins, offer excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making them suitable for sustainable packaging requiring durability. Paperboard composites, composed of layered cellulose fibers with possible coatings for water resistance, provide good compressive strength and rigidity but may underperform in moisture-prone environments compared to green composites. Performance-wise, green composites excel in mechanical strength and environmental friendliness, while paperboard composites are cost-effective and easily recyclable, ideal for lightweight, everyday packaging.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Scenarios
Green composites, composed primarily of natural fibers and biodegradable resins, offer superior biodegradability compared to paperboard composites, which often incorporate synthetic coatings or additives reducing their compostability. In end-of-life scenarios, green composites can break down more efficiently in industrial composting facilities, minimizing environmental impact and facilitating nutrient recovery. Paperboard composites may persist longer in landfill conditions due to moisture barriers, complicating recycling efforts and contributing to waste accumulation.
Cost Analysis and Market Feasibility
Green composite packaging offers a higher initial production cost compared to traditional paperboard composite due to the use of sustainable materials like bio-based resins and natural fibers. However, green composites provide long-term cost benefits by reducing environmental compliance fees and enhancing brand value, which can drive consumer preference in eco-conscious markets. Market feasibility favors green composite packaging in regions with strong environmental regulations and increasing demand for sustainable products, while paperboard composites remain cost-effective for high-volume, low-margin packaging needs.
Regulatory Standards and Certifications
Green composites for packaging often comply with stringent environmental regulatory standards such as ASTM D6866 for biobased content and EN 13432 for compostability, ensuring reduced ecological impact and enhanced recyclability. Paperboard composites typically adhere to FDA food contact regulations and ISO 9001 certification, emphasizing safety and quality control in packaging applications. Both materials increasingly align with global sustainability certifications like FSC and PEFC, driving industry-wide adoption of eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Consumer Perception and Brand Value
Green composites enhance consumer perception by emphasizing sustainability and eco-friendliness, appealing to environmentally conscious shoppers. Paperboard composites offer recyclability and a natural aesthetic, reinforcing brand values centered on responsibility and premium quality. Brands utilizing these materials often see increased loyalty and positive market differentiation due to heightened environmental awareness.
Future Trends in Eco-friendly Packaging Materials
Green composites, made from natural fibers and biodegradable resins, exhibit significant growth potential in sustainable packaging due to their reduced environmental impact and enhanced compostability compared to traditional paperboard composites. Innovations in bio-based resins and improved fiber treatments are driving enhanced mechanical properties and moisture resistance, positioning green composites as a superior alternative for eco-friendly packaging solutions. The rising consumer demand for zero-waste packaging and stringent regulations on plastic use are accelerating the shift towards green composites, forecasting a major market expansion in the next decade.
Infographic: Green composite vs Paperboard composite for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com