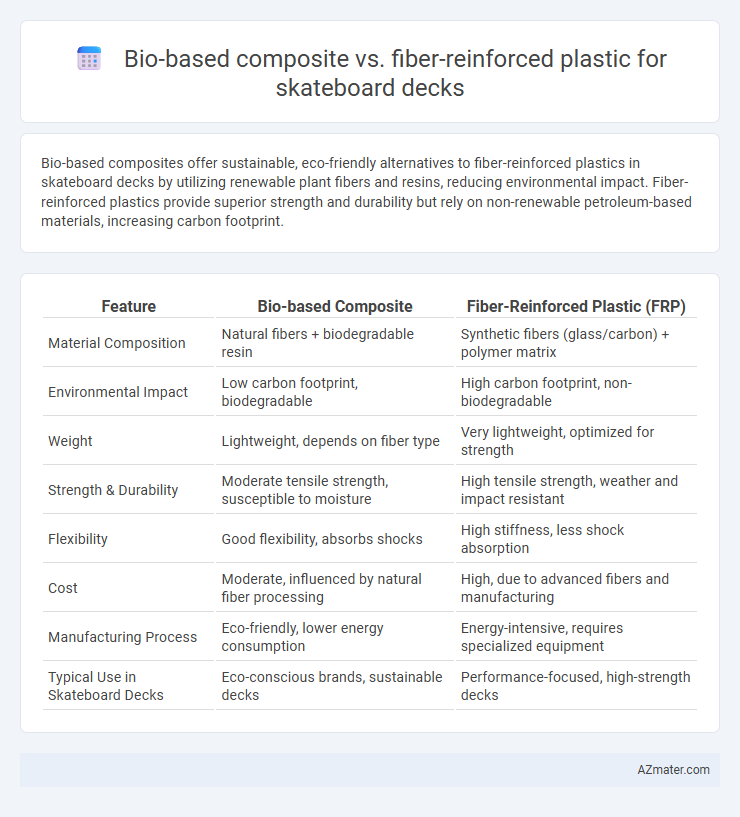
Bio-based composites offer sustainable, eco-friendly alternatives to fiber-reinforced plastics in skateboard decks by utilizing renewable plant fibers and resins, reducing environmental impact. Fiber-reinforced plastics provide superior strength and durability but rely on non-renewable petroleum-based materials, increasing carbon footprint.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bio-based Composite | Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural fibers + biodegradable resin | Synthetic fibers (glass/carbon) + polymer matrix |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Weight | Lightweight, depends on fiber type | Very lightweight, optimized for strength |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate tensile strength, susceptible to moisture | High tensile strength, weather and impact resistant |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, absorbs shocks | High stiffness, less shock absorption |
| Cost | Moderate, influenced by natural fiber processing | High, due to advanced fibers and manufacturing |
| Manufacturing Process | Eco-friendly, lower energy consumption | Energy-intensive, requires specialized equipment |
| Typical Use in Skateboard Decks | Eco-conscious brands, sustainable decks | Performance-focused, high-strength decks |
Introduction to Skateboard Deck Materials
Skateboard decks traditionally use fiber-reinforced plastic (FRP) due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and durability, primarily utilizing glass or carbon fibers embedded in a polymer matrix. Bio-based composites, incorporating natural fibers like flax or hemp combined with biodegradable resins, offer an eco-friendly alternative with comparable mechanical properties and reduced environmental impact. Material selection for skateboard decks balances performance, weight, and sustainability, with bio-based composites gaining traction for greener production without sacrificing structural integrity.
Overview of Bio-based Composites
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks utilize natural fibers such as flax, hemp, or kenaf combined with bio-resins derived from renewable sources, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact. These composites offer comparable strength and flexibility to fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP), while enhancing biodegradability and reducing carbon footprint during production and disposal. Advances in bio-based composite technology focus on optimizing fiber-matrix adhesion and mechanical properties to meet the performance standards required for durable and high-performance skateboard decks.
Understanding Fiber-Reinforced Plastics (FRPs)
Fiber-Reinforced Plastics (FRPs) are composite materials made by embedding high-strength fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid into a polymer matrix to achieve superior mechanical properties like enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and durability. In skateboard decks, FRPs provide excellent impact resistance and stiffness, improving performance and longevity compared to traditional materials. Their customizable fiber orientation and resin types allow tailored flex and strength, making them a preferred choice for high-performance skateboard manufacturing.
Material Strength and Durability Comparison
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks offer enhanced environmental sustainability with competitive tensile strength and improved impact resistance compared to traditional fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP). Fiber-reinforced plastics, typically composed of glass or carbon fibers embedded in epoxy or polyester resin, provide superior stiffness and long-term durability under repetitive stress and moisture exposure. While FRPs excel in high load-bearing capacity and resistance to fatigue, bio-based composites demonstrate promising advancements in balance between strength, biodegradability, and resistance to delamination during intensive skateboarding use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks significantly reduce carbon footprint by utilizing renewable resources like natural fibers and biodegradable resins, enhancing end-of-life compostability compared to conventional fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP). Fiber-reinforced plastics often rely on petroleum-based resins and non-renewable fibers such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, leading to higher energy consumption and problematic landfill persistence. Emphasizing environmental impact, bio-based composites promote circular economy principles and decrease toxicity, aligning closely with sustainable manufacturing goals in the skateboard industry.
Weight and Performance Analysis
Bio-based composite skateboard decks typically offer a lighter weight compared to traditional fiber-reinforced plastics, enhancing maneuverability and reducing rider fatigue. Performance analysis reveals that bio-based composites provide comparable flexural strength and vibration damping, leading to improved ride comfort without compromising durability. Fiber-reinforced plastics generally deliver higher impact resistance, but at the cost of increased weight and reduced environmental sustainability.
Cost Considerations
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks typically offer a competitive cost advantage due to renewable raw materials and lower environmental compliance expenses compared to fiber-reinforced plastics (FRPs), which often involve higher-priced synthetic fibers like carbon or glass. Manufacturing costs for fiber-reinforced plastic decks tend to be elevated because of complex fabrication processes and energy-intensive curing requirements. Long-term cost considerations also favor bio-based composites as they can reduce disposal and recycling expenses through biodegradability and sustainability incentives.
Manufacturing Processes
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks are typically produced using resin infusion or compression molding techniques that integrate natural fibers like hemp or flax with bio-resins, promoting sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Fiber-reinforced plastics (FRP) employ processes such as hand lay-up, filament winding, or injection molding, combining synthetic fibers like fiberglass or carbon fiber with thermoset or thermoplastic matrices, offering high strength-to-weight ratios. Manufacturing bio-based composites demands precise control of moisture content and curing conditions to maintain material performance, whereas FRP fabrication emphasizes fiber alignment and resin curing to achieve optimal mechanical properties.
User Experience and Ride Quality
Bio-based composite skateboard decks offer enhanced vibration damping and environmental sustainability, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable ride compared to traditional fiber-reinforced plastic decks. Fiber-reinforced plastic decks provide superior strength and stiffness, delivering responsive control and durability favored by aggressive riders. User experience with bio-based composites emphasizes eco-conscious performance without sacrificing ride quality, while fiber-reinforced plastics prioritize high performance and resilience under stress.
Future Trends in Skateboard Deck Materials
Bio-based composites for skateboard decks leverage renewable resources like hemp and flax fibers combined with biodegradable resins, offering enhanced sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional fiber-reinforced plastics (FRPs) made from fiberglass or carbon fibers with synthetic epoxy resins. Future trends emphasize the development of hybrid materials integrating advanced bio-based fibers with performance-enhancing nanomaterials to achieve lightweight, high-strength decks with improved durability and eco-friendliness. Innovations in material processing techniques and recyclability are driving the transition toward circular economy models within skateboard manufacturing, promoting the adoption of bio-based composites over conventional FRPs.
Infographic: Bio-based composite vs Fiber-reinforced plastic for Skateboard deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com