Aramid fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for reinforcing concrete in civil engineering structures, while basalt fiber provides superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance, enhancing durability in harsh environments. Both materials improve structural performance but selection depends on specific project requirements such as load conditions and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
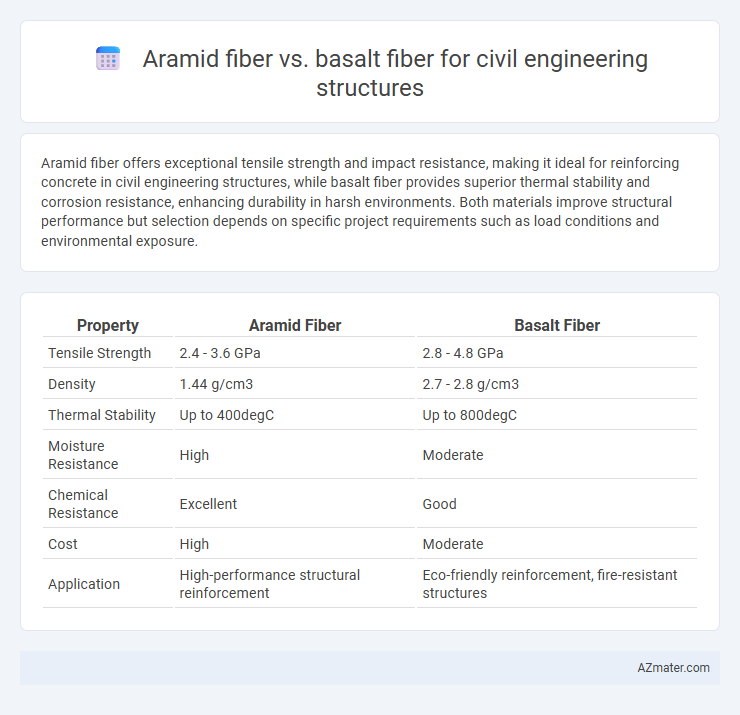
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2.4 - 3.6 GPa | 2.8 - 4.8 GPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 2.7 - 2.8 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 400degC | Up to 800degC |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Application | High-performance structural reinforcement | Eco-friendly reinforcement, fire-resistant structures |
Introduction to Aramid and Basalt Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, offer lightweight reinforcement solutions for civil engineering structures, enhancing durability and impact resistance. Basalt fibers, derived from natural volcanic rock, provide excellent corrosion resistance and superior mechanical properties, making them ideal for harsh environmental conditions in structural applications. Both fibers present advanced alternatives to traditional materials, optimizing performance and lifespan in modern infrastructure projects.
Material Composition and Properties
Aramid fiber, composed mainly of polyamide polymers with aromatic rings, offers exceptional tensile strength, high impact resistance, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for reinforcing civil engineering structures subjected to dynamic loads. Basalt fiber, derived from melted volcanic basalt rock, provides superior chemical resistance, high compressive strength, and excellent durability in harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-lasting structural performance. The choice between aramid and basalt fibers depends on specific project requirements, with aramid fibers favored for high-performance applications and basalt fibers preferred for cost-effective, corrosion-resistant reinforcement.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aramid fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, typically ranging from 3,000 to 4,000 MPa, making it highly effective in reinforcing civil engineering structures subject to dynamic loads. Basalt fiber offers commendable mechanical strength with tensile values around 2,800 to 3,100 MPa and presents excellent thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. The enhanced strength-to-weight ratio of Aramid fiber often provides a strategic advantage in lightweight structural applications, while Basalt fiber's durability and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for long-term infrastructure projects requiring robust mechanical performance.
Thermal and Fire Resistance
Aramid fiber offers superior thermal stability with decomposition temperatures exceeding 500degC, making it highly resistant to fire and maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat in civil engineering applications. Basalt fiber also exhibits excellent thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 870degC, providing enhanced fire resistance and durability for structural reinforcements exposed to high-temperature environments. Both fibers improve fire safety performance in concrete and composites, but basalt's higher melting point gives it an advantage in fire-resilient construction materials.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Aramid fiber exhibits exceptional durability with high tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemical degradation, making it ideal for civil engineering structures exposed to harsh environments. Basalt fiber offers superior corrosion resistance due to its inorganic composition, maintaining structural integrity in acidic or alkaline conditions commonly found in construction applications. Both fibers enhance the longevity of civil structures, but basalt fiber is preferred where prolonged exposure to corrosive agents is critical.
Weight and Density Considerations
Aramid fiber offers a low density around 1.44 g/cm3, providing lightweight reinforcement ideal for reducing structural dead load in civil engineering applications. Basalt fiber, with a density approximately 2.7 g/cm3, is heavier but delivers superior compressive strength and thermal stability suitable for load-bearing structures. Weight-sensitive projects benefit from aramid's lightweight properties, while basalt is preferred where strength-to-weight ratio and environmental durability are critical.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Aramid fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent durability but comes with a significantly higher cost, making it less economical for large-scale civil engineering projects compared to basalt fiber. Basalt fiber provides a more cost-effective alternative due to its abundant natural source and lower manufacturing expenses, while still delivering strong mechanical properties suitable for reinforcing concrete and other structural materials. Availability of basalt fiber is greater worldwide, particularly in regions with volcanic activity, ensuring easier procurement and reduced lead times in construction applications.
Applications in Civil Engineering Structures
Aramid fiber is extensively used in civil engineering for reinforcing concrete and enhancing tensile strength in structures such as bridges and high-rise buildings due to its exceptional toughness and lightweight properties. Basalt fiber offers superior thermal resistance and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for reinforcing structures exposed to harsh environmental conditions like coastal infrastructures and tunnels. Both fibers improve durability and load-bearing capacity but are chosen based on specific environmental and mechanical requirements within civil engineering projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, but its production involves energy-intensive processes and non-renewable petroleum-based raw materials, raising environmental concerns. Basalt fiber, derived from abundant volcanic rock, is more eco-friendly due to its natural composition, lower energy consumption during manufacturing, and recyclability, making it a sustainable alternative in civil engineering. When prioritizing environmental impact and sustainability, basalt fiber demonstrates a significantly lower carbon footprint and better alignment with green building practices compared to aramid fiber.
Selection Criteria for Optimal Fiber Usage
Aramid fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, high impact resistance, and superior flexibility, making it ideal for structures requiring enhanced durability and lightweight reinforcement. Basalt fiber provides excellent thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions or aggressive chemicals. Optimal fiber selection depends on project-specific factors such as mechanical performance requirements, environmental exposure, budget constraints, and longevity expectations in civil engineering structures.
Infographic: Aramid fiber vs Basalt fiber for Civil engineering structure
 azmater.com
azmater.com