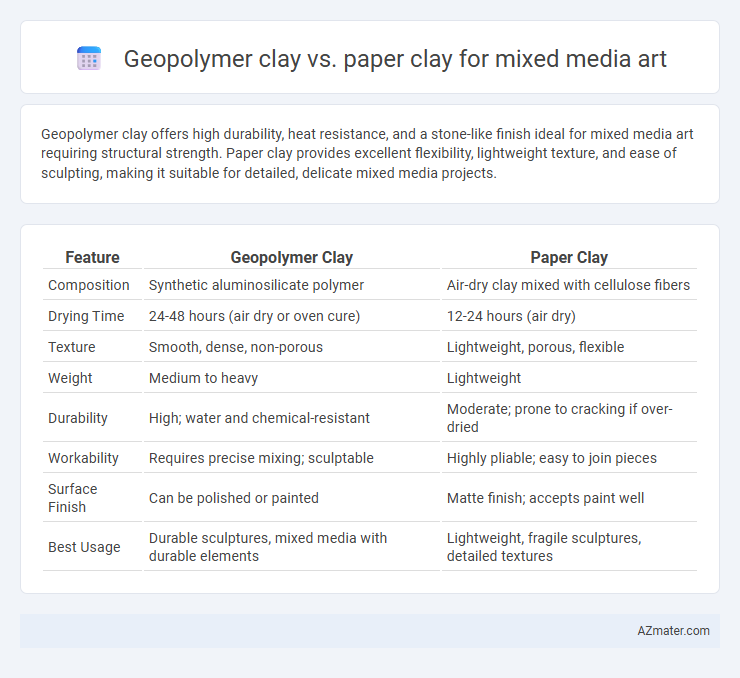
Geopolymer clay offers high durability, heat resistance, and a stone-like finish ideal for mixed media art requiring structural strength. Paper clay provides excellent flexibility, lightweight texture, and ease of sculpting, making it suitable for detailed, delicate mixed media projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Geopolymer Clay | Paper Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Synthetic aluminosilicate polymer | Air-dry clay mixed with cellulose fibers |
| Drying Time | 24-48 hours (air dry or oven cure) | 12-24 hours (air dry) |
| Texture | Smooth, dense, non-porous | Lightweight, porous, flexible |
| Weight | Medium to heavy | Lightweight |
| Durability | High; water and chemical-resistant | Moderate; prone to cracking if over-dried |
| Workability | Requires precise mixing; sculptable | Highly pliable; easy to join pieces |
| Surface Finish | Can be polished or painted | Matte finish; accepts paint well |
| Best Usage | Durable sculptures, mixed media with durable elements | Lightweight, fragile sculptures, detailed textures |
Introduction to Geopolymer Clay and Paper Clay
Geopolymer clay is an advanced, eco-friendly material composed of aluminosilicate minerals that chemically harden without firing, offering exceptional strength and durability for mixed media art. Paper clay integrates cellulose fibers into traditional clay, enhancing flexibility, reducing shrinkage, and allowing for easier manipulation and joining of pieces. Both materials provide unique textures and structural benefits, expanding creative possibilities in mixed media artwork.
Composition and Material Differences
Geopolymer clay consists mainly of aluminosilicate materials activated by alkaline solutions, creating a durable, heat-resistant matrix ideal for structural components in mixed media art. Paper clay incorporates cellulose fibers from paper pulp mixed with traditional clay, enhancing flexibility, reducing shrinkage, and allowing thinner, lighter forms. The differences in composition affect drying time, firing range, and texture, with geopolymer clay offering superior mechanical strength and paper clay providing greater workability and surface texture variety.
Workability in Mixed Media Art
Geopolymer clay offers excellent adhesion to a variety of surfaces and maintains structural integrity when combined with mixed media elements, making it highly suitable for sculptures requiring durability and fine detail. Paper clay provides superior workability and flexibility due to its lightweight, fibrous composition, allowing artists to easily manipulate, carve, and blend it with materials like paper, fabric, and paint. Both clays dry hard, but paper clay's porosity enhances paint absorption and texture effects, while geopolymer clay excels in achieving smooth finishes and complex shapes without cracking.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Geopolymer clay exhibits exceptional strength and durability due to its inorganic aluminosilicate composition, making it highly resistant to cracking and weathering in mixed media art projects. In contrast, paper clay, reinforced with cellulose fibers, offers moderate strength and flexibility but is more susceptible to moisture damage and less resilient under heavy structural stress. Artists seeking long-lasting, robust sculptures typically prefer geopolymer clay for its superior mechanical properties and longevity.
Surface Texture and Finish
Geopolymer clay offers a dense, stone-like surface texture with a smooth, durable finish ideal for mixed media art requiring strength and minimal porosity. Paper clay features a lighter, more porous texture due to its cellulose fiber content, allowing for intricate detailing and a matte, somewhat rough finish that enhances paint adhesion. Artists often select geopolymer clay for robust, polished sculptures while paper clay excels in delicate, textured applications and layered effects.
Compatibility with Other Art Materials
Geopolymer clay offers excellent compatibility with various mixed media art materials, including metals, glass, and acrylics, due to its strong adhesion and durability when cured. Paper clay, enriched with cellulose fibers, provides enhanced flexibility and can be easily combined with water-based paints, textiles, and collage elements, making it ideal for intricate mixed media applications. Both clays support the integration of diverse materials, but geopolymer clay tends to withstand environmental stress better, while paper clay allows for more detailed surface manipulation and lightweight structures.
Drying and Curing Processes
Geopolymer clay requires a controlled curing process involving low-temperature heat or ambient curing to develop its strength and durability, often taking 24 to 72 hours depending on the formula. Paper clay dries faster due to its lightweight fiber content, allowing artists to work with thin sections and join dry to dry, but it remains more fragile post-drying compared to geopolymer clay. Understanding these drying and curing differences is crucial for mixed media artists aiming for structural integrity and optimal surface texture in their finished pieces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer clay, made from industrial byproducts like fly ash, offers a sustainable alternative by reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to traditional ceramic clays. Paper clay incorporates recycled cellulose fibers, enhancing flexibility and drying times while promoting eco-friendly practices through the reuse of paper waste. Both materials provide environmentally conscious options for mixed media artists seeking to minimize ecological footprints and support sustainable art production.
Cost and Availability
Geopolymer clay offers a cost-effective option for mixed media art due to its affordable raw materials, such as fly ash and metakaolin, which are widely available in industrial supply stores. Paper clay, incorporating cellulose fibers into traditional clay, tends to be pricier and less accessible, often requiring specialty art supply vendors or DIY preparation. Availability of geopolymer clay raw ingredients generally surpasses that of paper clay, making it a practical choice for artists prioritizing budget and material access.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Mixed Media Projects
Selecting the right clay for mixed media projects depends on material properties and project goals, with geopolymer clay offering high durability, heat resistance, and a stone-like finish ideal for outdoor or structurally demanding pieces. Paper clay, composed of clay mixed with cellulose fibers, excels in lightweight, flexible applications, allowing artists to join damp and dry pieces seamlessly, making it perfect for intricate details and sculptural versatility. Understanding the specific performance characteristics of geopolymer versus paper clay ensures optimal compatibility with mixed media elements and enhances the longevity and aesthetic of the final artwork.
Infographic: Geopolymer clay vs Paper clay for Mixed media art
 azmater.com
azmater.com