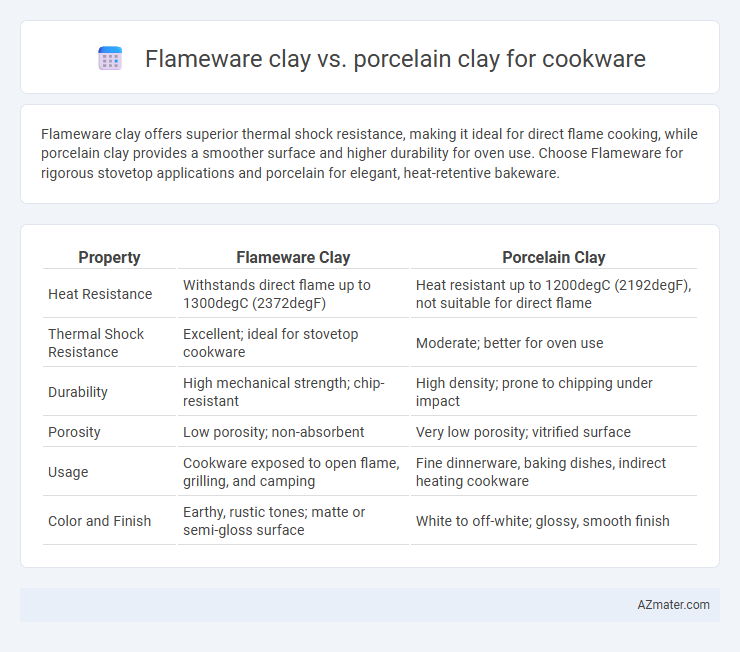
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for direct flame cooking, while porcelain clay provides a smoother surface and higher durability for oven use. Choose Flameware for rigorous stovetop applications and porcelain for elegant, heat-retentive bakeware.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flameware Clay | Porcelain Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Withstands direct flame up to 1300degC (2372degF) | Heat resistant up to 1200degC (2192degF), not suitable for direct flame |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Excellent; ideal for stovetop cookware | Moderate; better for oven use |
| Durability | High mechanical strength; chip-resistant | High density; prone to chipping under impact |
| Porosity | Low porosity; non-absorbent | Very low porosity; vitrified surface |
| Usage | Cookware exposed to open flame, grilling, and camping | Fine dinnerware, baking dishes, indirect heating cookware |
| Color and Finish | Earthy, rustic tones; matte or semi-gloss surface | White to off-white; glossy, smooth finish |
Introduction to Flameware Clay and Porcelain Clay
Flameware clay is specially formulated to withstand direct flame and rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for cookware used on stovetops and open flames. Porcelain clay is a fine, high-fired ceramic known for its smooth, non-porous surface and durability, often used in elegant bakeware and serving dishes. Both materials offer unique thermal properties, with Flameware providing heat resistance and porcelain delivering aesthetic appeal and effortless cleaning.
Material Composition and Properties
Flameware clay is composed primarily of dense stoneware with enhanced heat retention and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for stovetop and open flame use. Porcelain clay features a finer, more vitrified texture with high strength and a smooth, non-porous surface, which provides excellent durability but reduced heat tolerance compared to flameware. The material composition of flameware supports direct flame exposure, whereas porcelain clay is better suited for oven and microwave cooking due to its brittleness under rapid temperature changes.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock Performance
Flameware clay demonstrates superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1500degF, making it ideal for direct flame cooking, whereas porcelain clay typically endures temperatures up to 1300degF, suited for oven and microwave use. Flameware's composition allows excellent thermal shock performance, minimizing cracking when exposed to rapid temperature changes, unlike porcelain clay which is more prone to thermal shock due to its denser, less porous structure. Cookware made from flameware clay offers enhanced durability and versatility in high-heat cooking environments compared to porcelain clay cookware.
Cooking Efficiency and Even Heat Distribution
Flameware clay offers superior heat retention and distributes heat evenly, making it ideal for slow cooking and simmering dishes with consistent temperatures. Porcelain clay, though less heat-retentive, heats up quickly and provides a smooth, non-porous surface that resists staining and absorbs less moisture, enhancing cooking efficiency for high-heat applications. Both materials optimize heat management, but Flameware excels in prolonged heat retention while Porcelain delivers rapid heating and easy maintenance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Flameware clay offers superior thermal resistance and can withstand direct high heat, making it highly durable for stovetop cooking and increasing its lifespan under frequent temperature changes. Porcelain clay, while strong and elegant, is more prone to chipping and cracking due to its finer, denser composition, which can reduce its overall durability with heavy use. In cookware applications, Flameware's robust structure typically outlasts porcelain clay by maintaining integrity through rigorous cooking conditions.
Safety and Food Reactivity
Flameware clay offers exceptional heat retention and is typically non-reactive, making it safe for cooking a variety of foods without altering flavors or leaching harmful substances. Porcelain clay, while also resistant to high temperatures, is often glazed with materials that ensure a non-porous, food-safe surface, reducing the risk of chemical reactions with acidic or alkaline foods. Both materials prioritize food safety, but porcelain's vitrified structure generally provides enhanced resistance to food reactivity and easier cleaning.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Flameware clay cookware requires careful hand washing and thorough drying to prevent cracking and maintain its porous surface, while porcelain clay is typically glazed, making it more resistant to stains and easier to clean with standard dishwashing detergents. Porcelain clay's non-porous glaze reduces the need for seasoning and frequent oiling, unlike flameware which demands regular maintenance to preserve its natural, absorbent qualities. Cleaning porcelain cookware often involves less effort, as it resists odors and residue buildup better than the more delicate, unglazed flameware clay.
Aesthetics and Design Versatility
Flameware clay offers a rustic, earthy aesthetic with natural textures and warm tones that enhance artisanal cookware designs, while porcelain clay provides a sleek, smooth surface with a bright white finish ideal for modern and minimalist styles. Porcelain's fine particle structure allows for intricate detailing and thin-walled pieces, expanding design versatility compared to the denser, heavier Flameware. Both materials support customization, but porcelain's translucency and color-retention capabilities make it a preferred choice for visually striking, elegant cookware collections.
Price and Accessibility
Flameware clay typically costs less and is more widely accessible than porcelain clay, making it a budget-friendly option for cookware enthusiasts. Porcelain clay cookware often demands a higher price due to its finer materials and more intricate manufacturing process, which can limit availability in local markets. Consumers seeking affordable and easily obtainable cookware usually prefer flameware clay for everyday use.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Cookware
Flameware clay, known for its heat-resistant properties and durability, is ideal for cookware that requires direct flame exposure and thermal shock resistance, ensuring even cooking and long-lasting performance. Porcelain clay offers a smoother texture and non-porous surface, making it excellent for elegant, heat-retentive cookware suitable for baking and serving. Selecting between Flameware and Porcelain clay hinges on the intended cooking method and durability needs, with Flameware favored for stovetop use and Porcelain preferred for oven-to-table versatility.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Porcelain clay for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com