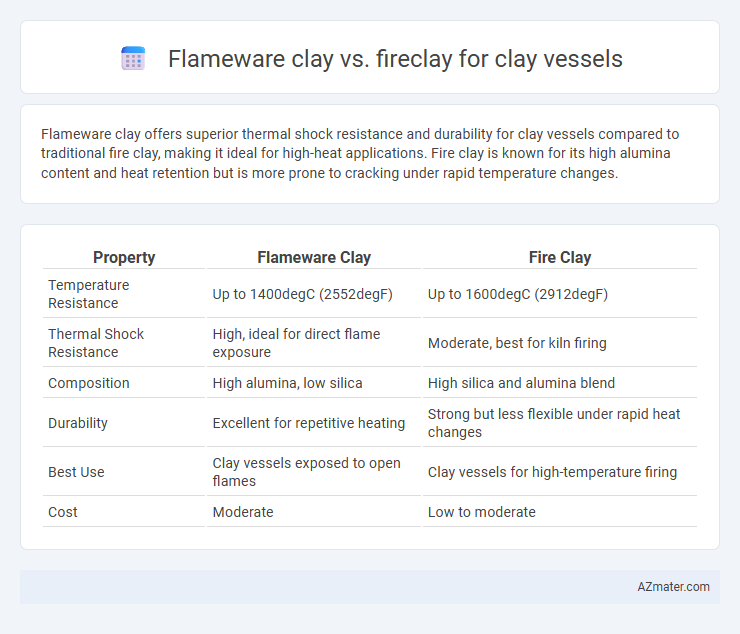
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability for clay vessels compared to traditional fire clay, making it ideal for high-heat applications. Fire clay is known for its high alumina content and heat retention but is more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flameware Clay | Fire Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1400degC (2552degF) | Up to 1600degC (2912degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High, ideal for direct flame exposure | Moderate, best for kiln firing |
| Composition | High alumina, low silica | High silica and alumina blend |
| Durability | Excellent for repetitive heating | Strong but less flexible under rapid heat changes |
| Best Use | Clay vessels exposed to open flames | Clay vessels for high-temperature firing |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction: Understanding Flameware Clay and Fire Clay
Flameware clay and fire clay are both essential materials for crafting durable clay vessels, with flameware clay specifically formulated to withstand high temperatures and direct flame exposure. Fire clay contains a high percentage of alumina and silica, providing exceptional thermal shock resistance and structural integrity during intense heat cycles. Understanding their distinct thermal properties helps artisans select the best clay type for applications such as pottery, cookware, and kiln components.
Key Properties of Flameware Clay
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal shock resistance and higher fusion temperatures, making it ideal for clay vessels subjected to direct flame exposure. Its key properties include enhanced durability, low thermal expansion, and the ability to withstand intense heat without cracking, unlike standard fire clay which may lack these attributes. These characteristics ensure flameware clay maintains vessel integrity during rapid temperature changes, crucial for cooking and heat-intensive applications.
Key Properties of Fire Clay
Fire clay is known for its high refractory strength, making it ideal for clay vessels exposed to extreme temperatures above 1500degC. It has excellent thermal shock resistance and low thermal expansion, ensuring durability and crack prevention during rapid temperature changes. Compared to flameware clay, fire clay offers superior heat retention and structural stability, enhancing the longevity and performance of clay vessels in high-heat environments.
Thermal Shock Resistance Comparison
Flameware clay offers moderate thermal shock resistance suitable for gradual heating, whereas fire clay excels with superior thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for rapid temperature changes in clay vessels. Fire clay's high alumina content enhances its structural integrity during extreme heating and cooling cycles, reducing crack formation. This makes fire clay the preferred choice for durable clay vessels exposed to fluctuating thermal conditions.
Suitability for Direct Flame Cooking
Flameware clay is specifically formulated to withstand direct flame exposure, making it highly suitable for clay vessels intended for direct flame cooking, such as stovetop pots and open flame grills. Fire clay, known for its high refractory properties and thermal shock resistance, is also used in clay vessels but often requires additional processing or layering to ensure durability under direct flames. Flameware clay's balanced composition enhances heat distribution and durability without cracking, providing superior performance in direct flame applications compared to standard fire clay.
Durability and Longevity of Clay Vessels
Flameware clay exhibits superior durability in clay vessels due to its high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for repeated heating and cooling cycles. Fire clay, while also durable, is traditionally valued for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures but may be more prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. The longevity of vessels made from flameware clay is often extended by its dense, fine-grained structure, which enhances resistance to wear and thermal stress compared to standard fire clay.
Safety Considerations for Food Use
Flameware clay offers enhanced thermal shock resistance compared to traditional fire clay, making it safer for vessels exposed to rapid temperature changes in cooking. Fire clay, while durable and heat-resistant, may contain impurities that could leach harmful substances if not properly vitrified during firing. Ensuring both clays are certified lead-free and food-safe is essential to prevent contamination and maintain health standards in clay vessel use.
Manufacturing and Firing Techniques
Flameware clay is formulated with a balanced flux ratio, allowing it to withstand direct flame exposure and rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for cookware exposed to open flames. Fire clay contains higher refractory alumina content, providing excellent thermal shock resistance and durability during high-temperature firing, typically between 1200degC to 1300degC. Manufacturing Flameware requires precise control of impurities for smooth surfaces and thermal conduction, while Fire clay manufacturing emphasizes particle size and purity to enhance vitrification and mechanical strength during kiln firing.
Aesthetic Differences in Finished Vessels
Flameware clay produces finished vessels with a rich, variegated surface texture and warm, earthy tones due to its high iron content and flame interaction during firing. Fire clay results in smoother, denser vessel surfaces with a more uniform color palette, often ranging from light gray to buff, enhancing a refined aesthetic. Artists seeking dynamic, rustic appearances favor Flameware, while those preferring subtle, polished finishes opt for Fire clay.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Clay Vessel
Flameware clay offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for clay vessels exposed to direct flames and high temperatures. Fire clay is prized for its thermal shock resistance and structural strength, ensuring longevity in vessels used for cooking or storage. Choosing the right clay depends on your vessel's intended use, with flameware clay suited for intense heat applications and fire clay better for general durability and heat retention.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Fire clay for Clay vessel
 azmater.com
azmater.com