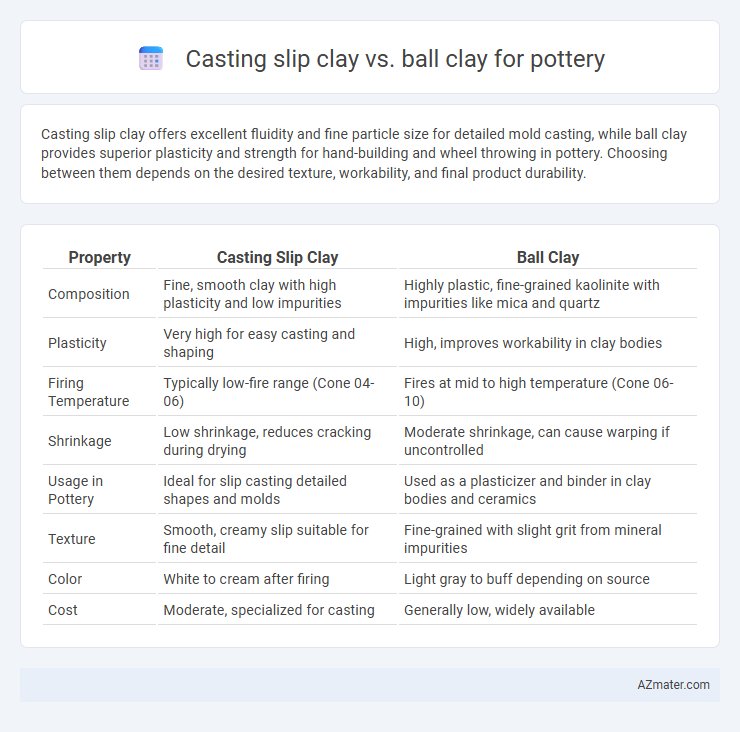
Casting slip clay offers excellent fluidity and fine particle size for detailed mold casting, while ball clay provides superior plasticity and strength for hand-building and wheel throwing in pottery. Choosing between them depends on the desired texture, workability, and final product durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Casting Slip Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine, smooth clay with high plasticity and low impurities | Highly plastic, fine-grained kaolinite with impurities like mica and quartz |
| Plasticity | Very high for easy casting and shaping | High, improves workability in clay bodies |
| Firing Temperature | Typically low-fire range (Cone 04-06) | Fires at mid to high temperature (Cone 06-10) |
| Shrinkage | Low shrinkage, reduces cracking during drying | Moderate shrinkage, can cause warping if uncontrolled |
| Usage in Pottery | Ideal for slip casting detailed shapes and molds | Used as a plasticizer and binder in clay bodies and ceramics |
| Texture | Smooth, creamy slip suitable for fine detail | Fine-grained with slight grit from mineral impurities |
| Color | White to cream after firing | Light gray to buff depending on source |
| Cost | Moderate, specialized for casting | Generally low, widely available |
Introduction to Pottery Clays
Casting slip clay, characterized by its fine particle size and smooth texture, is ideal for creating detailed ceramic molds and thin-walled pottery pieces due to its excellent fluidity and workability. Ball clay, rich in kaolinite and organic matter, offers high plasticity and strength, making it suitable for shaping durable and intricate pottery forms. Understanding the distinct properties of casting slip clay and ball clay helps potters select the right material to achieve desired surface finishes and structural integrity in their ceramic creations.
What is Casting Slip Clay?
Casting slip clay is a liquid form of clay, finely ground and suspended in water, primarily used in slip casting techniques to create detailed and uniform ceramic pieces by pouring the slip into plaster molds. Its fine particle size and smooth consistency allow for precise reproduction of intricate shapes, setting it apart from ball clay, which is more commonly utilized as a plastic component in clay bodies due to its plasticity and strength. The key advantage of casting slip clay lies in its ability to achieve thin walls and fine surface details, making it essential for mass production of ceramics with complex designs.
What is Ball Clay?
Ball clay is a highly plastic, fine-grained clay composed primarily of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, valued for its exceptional plasticity and binding properties in pottery. Its unique particle size and mineral composition allow it to enhance the strength and workability of ceramic bodies, making it essential in slip casting and clay body formulations. Unlike casting slip clays, ball clay contributes to the plasticity and leather-hard strength but requires blending with other clays to optimize drying and firing performance.
Key Differences Between Casting Slip Clay and Ball Clay
Casting slip clay is a liquid mixture primarily used for creating fine, detailed ceramic molds and is formulated for smooth, thin application with high plasticity and low shrinkage. Ball clay, in contrast, is a highly plastic, fine-grained natural clay used to enhance the strength and workability of clay bodies, with a coarser texture and higher impurity content. Key differences include casting slip's emphasis on fluidity and purity for slip casting, while ball clay contributes plasticity and binding properties to the clay mixture.
Properties and Composition Comparison
Casting slip clay features fine particles and high plasticity, ideal for producing smooth, detailed ceramic casts due to its low shrinkage and excellent flow characteristics. Ball clay, composed primarily of kaolinite with impurities like mica and quartz, offers superior plasticity and strength but can cause higher shrinkage and drying times in pottery. The key distinction lies in casting slip's formulation for slip casting with minimal defects, whereas ball clay enhances clay bodies by improving workability and fired strength.
Applications in Pottery Making
Casting slip clay features fine, smooth particles ideal for producing detailed ceramic molds and thin-walled pottery through slip casting techniques, enhancing surface finish and precision. Ball clay, known for its plasticity and workability, is preferred in hand-building and wheel-throwing processes, enabling potters to shape durable and flexible ceramic forms. Both clays complement each other when blended, improving the overall strength, texture, and casting performance in pottery production.
Workability and Handling Characteristics
Casting slip clay offers excellent fluidity and smooth consistency, making it ideal for intricate molds and fine detail reproduction in pottery. Ball clay provides superior plasticity and cohesion, enhancing workability during hand-building and wheel throwing by allowing easier shaping and higher shrinkage tolerance. Potters often prefer casting slip clay for slip casting techniques, while ball clay suits forms requiring durability and flexible handling.
Firing Behavior and Shrinkage Rates
Casting slip clay exhibits lower firing shrinkage rates, typically around 5-8%, due to its fine particle size and higher plasticity, which enhances mold filling without excessive contraction. Ball clay, known for its high plasticity and organic content, tends to display higher firing shrinkage, often between 8-12%, which can lead to more warping but offers increased green strength for shaping. The firing behavior of casting slip clay is generally more stable and predictable at mid-range temperatures (cone 5-6), while ball clay can withstand higher firing temperatures but requires careful control to minimize deformation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Casting slip clay offers the advantage of producing intricate and delicate shapes due to its fine particle size and smooth consistency, ideal for slip casting techniques. However, it can be more prone to cracking during drying and firing because of its higher shrinkage rate compared to ball clay. Ball clay, with its plasticity and strength, enhances workability and durability in pottery but may require blending with other clays to reduce shrinkage and improve casting properties.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Pottery Projects
Casting slip clay offers a smooth, fluid consistency ideal for detailed mold work and fine surface finishes, while ball clay provides excellent plasticity and strength for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. Selecting the right clay depends on the project requirements: casting slip suits intricate shapes and delicate designs, whereas ball clay supports structural stability and durability in functional pottery. Understanding the properties of each clay type ensures optimal workability, firing behavior, and final product quality.
Infographic: Casting slip clay vs Ball clay for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com