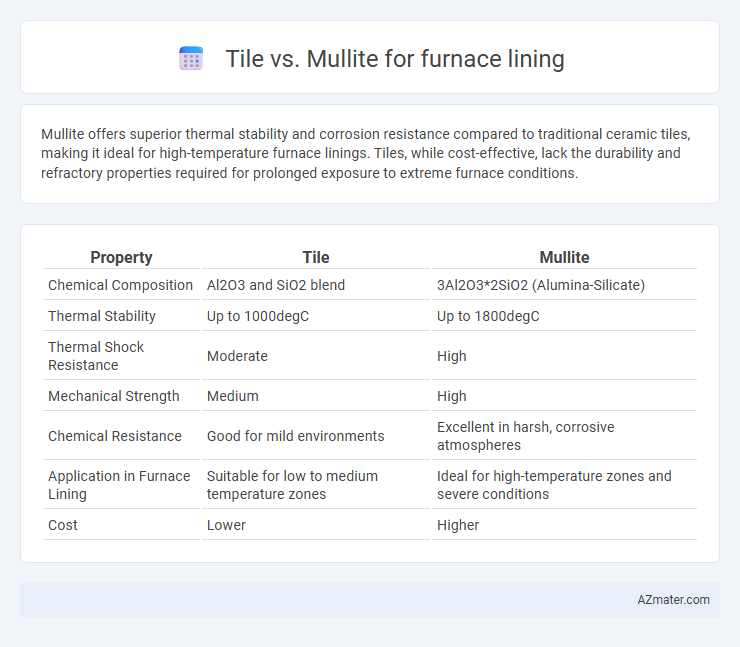
Mullite offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional ceramic tiles, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings. Tiles, while cost-effective, lack the durability and refractory properties required for prolonged exposure to extreme furnace conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tile | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Al2O3 and SiO2 blend | 3Al2O3*2SiO2 (Alumina-Silicate) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Mechanical Strength | Medium | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good for mild environments | Excellent in harsh, corrosive atmospheres |
| Application in Furnace Lining | Suitable for low to medium temperature zones | Ideal for high-temperature zones and severe conditions |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace linings require materials that withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock, with tiles and mullite being two prominent options. Mullite offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in industrial furnaces. Tiles, while easier to install and more cost-effective, generally have lower thermal resistance and durability compared to mullite, influencing their selection based on specific furnace operating conditions.
Overview of Tile and Mullite
Tile used in furnace lining typically consists of alumina or fireclay materials, offering high thermal resistance and durability at moderate temperatures. Mullite, a rare silicate mineral composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2, provides superior thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and excellent resistance to slag and thermal shock. The choice between tile and mullite hinges on operating temperature, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure inside the furnace environment.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Mullite offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to ceramic tiles, with a higher melting point around 1840degC and excellent thermal stability under high-temperature furnace conditions. Mullite's low thermal conductivity minimizes heat loss, enhancing furnace efficiency, whereas standard ceramic tiles typically exhibit higher thermal conductivity, reducing insulation performance. The inherent refractory nature of mullite also provides greater resistance to thermal shock and mechanical stress, making it a more durable choice for furnace linings.
Resistance to Chemical Attack
Mullite exhibits superior resistance to chemical attack compared to standard ceramic tiles, making it ideal for harsh furnace environments exposed to slags and acidic gases. Its stable crystalline structure effectively withstands corrosive agents, reducing degradation over time. Tile materials, while cost-effective, typically offer lower chemical durability, leading to more frequent maintenance and replacement in chemically aggressive conditions.
Durability and Mechanical Strength
Mullite offers superior durability and mechanical strength compared to standard refractory tiles due to its high thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for furnace linings exposed to extreme temperatures. Its crystalline structure provides excellent resistance to abrasion and chemical corrosion, ensuring a longer service life under harsh operational conditions. Tile linings, while easier to install and cost-effective, generally exhibit lower mechanical strength and are more prone to cracking or spalling under rapid temperature changes and mechanical stress.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Tile furnace linings offer straightforward installation with modular, pre-cast components that reduce downtime and enable quick replacement, minimizing maintenance efforts. Mullite linings require specialized installation techniques such as casting or spraying, demanding skilled labor and longer curing times, which increases initial setup complexity and maintenance frequency. Maintenance of tile linings often involves inspecting joints and grout, while mullite linings require regular monitoring for cracks and spalling due to thermal stress, impacting long-term durability and repair costs.
Cost Analysis: Tile vs Mullite
Tile furnace linings generally offer a lower initial cost compared to mullite, making them a budget-friendly option for many industrial applications. Mullite, while more expensive upfront due to its superior refractory properties and longer lifespan, provides better thermal stability and durability, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses over time. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, mullite's higher performance can offset its initial price through enhanced energy efficiency and minimized downtime in high-temperature furnace operations.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Mullite exhibits superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock compared to standard ceramic tiles, making it ideal for furnace lining in high-temperature environments exceeding 1500degC. Its low thermal expansion and excellent mechanical strength ensure prolonged durability under repeated heating cycles, reducing maintenance costs. Tile materials often lack this high refractoriness and can degrade faster, compromising furnace performance and operational efficiency.
Common Applications and Suitability
Mullite is highly suitable for furnace linings in high-temperature environments reaching up to 1850degC due to its excellent thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, making it common in industrial kilns and glass melting furnaces. Tiles, often made from ceramic materials such as alumina or silicon carbide, are preferred for moderate-temperature furnace linings because they offer ease of installation and resistance to abrasion, commonly used in heat treatment furnaces and incinerators. Industrial applications select mullite for prolonged exposure to intense heat and corrosive atmospheres, whereas tile linings are ideal where mechanical wear and quicker maintenance cycles are primary concerns.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Furnace Lining
Tile linings offer cost-effective and easy installation benefits but lack the thermal shock resistance and durability necessary for high-temperature furnace environments. Mullite linings provide superior refractory performance, including excellent thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for intense and prolonged heating conditions. Selecting mullite ensures enhanced furnace longevity and efficiency, whereas tile linings suit lower-temperature or less demanding applications.
Infographic: Tile vs Mullite for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com