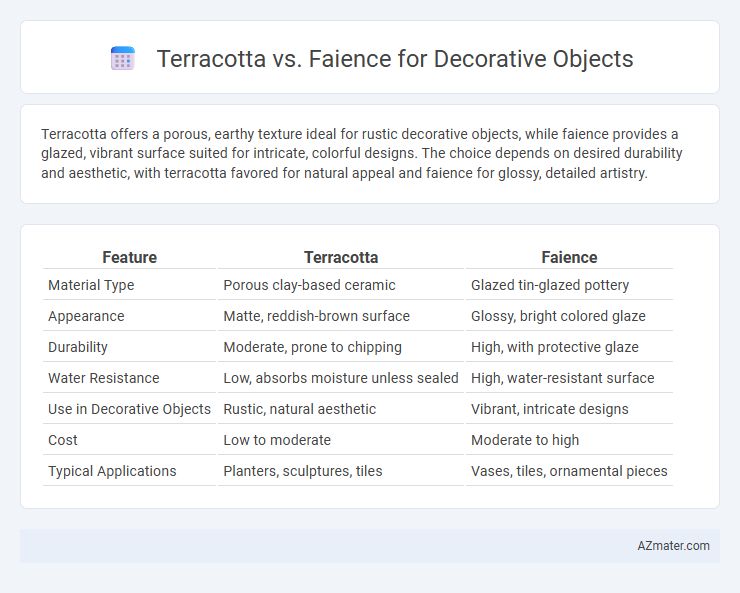
Terracotta offers a porous, earthy texture ideal for rustic decorative objects, while faience provides a glazed, vibrant surface suited for intricate, colorful designs. The choice depends on desired durability and aesthetic, with terracotta favored for natural appeal and faience for glossy, detailed artistry.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Terracotta | Faience |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Porous clay-based ceramic | Glazed tin-glazed pottery |
| Appearance | Matte, reddish-brown surface | Glossy, bright colored glaze |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, with protective glaze |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture unless sealed | High, water-resistant surface |
| Use in Decorative Objects | Rustic, natural aesthetic | Vibrant, intricate designs |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Typical Applications | Planters, sculptures, tiles | Vases, tiles, ornamental pieces |
Introduction to Terracotta and Faience
Terracotta, a porous clay-based ceramic, is prized for its earthy texture and warm reddish-brown hue, commonly used in decorative objects and sculptures due to its durability and ease of molding. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic material, features a bright, glossy surface often characterized by vibrant blues and greens, primarily produced through a silica-based composition coated with a vitreous glaze. Both materials hold significant historical importance in art and architecture, with terracotta favored for its natural rustic appeal and faience valued for its ornamental, colorful finish.
Historical Significance of Terracotta and Faience
Terracotta and faience hold profound historical significance, with terracotta dating back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley, celebrated for its durability and earthy aesthetic in sculpture and architecture. Faience, originating in ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE, is known for its vibrant glazed surface made from ground quartz, often used to create intricate jewelry, amulets, and small decorative objects symbolizing rebirth and protection. Both materials reflect the cultural and artistic achievements of their periods, showcasing advances in craftsmanship and symbolic expression across different societies.
Material Composition: Terracotta vs Faience
Terracotta is a porous clay-based ceramic material primarily composed of natural earthen clay fired at relatively low temperatures, resulting in a warm, reddish-brown finish ideal for rustic decorative objects. Faience, on the other hand, is a glazed ceramic made from a mixture of ground quartz or sand and clay, coated with a vibrant, glass-like opaque glaze rich in silica and alkaline flux, creating bright and glossy decorative surfaces. The key material difference lies in terracotta's unglazed, porous texture versus faience's non-porous, brightly glazed appearance, influencing durability and aesthetic appeal in decorative applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Terracotta is crafted by molding natural clay and firing it at temperatures between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a porous, earthy material ideal for rustic decorative objects. Faience, on the other hand, involves a more complex manufacturing process where a core of quartz or crushed glass is coated with a vitreous glaze and fired at lower temperatures around 900degC, producing a glossy, brightly colored surface. The key distinction lies in terracotta's simplicity and earthy texture versus faience's intricate glazing and vibrant finish, which influence durability and aesthetic appeal in decorative applications.
Aesthetic Qualities and Visual Appeal
Terracotta offers a warm, earthy texture and deep reddish-brown hues that enhance rustic and natural decorative objects, providing a tactile, handmade aesthetic. Faience, characterized by its glossy, glazed surface and vibrant colors like turquoise and cobalt, delivers a luminous and refined appearance ideal for intricate, ornamental pieces. The choice between the two hinges on whether a matte, organic look or a polished, colorful finish best complements the design vision.
Durability and Longevity
Terracotta decorative objects, crafted from porous clay and often unglazed, tend to be less durable and more susceptible to chipping and weathering over time compared to faience. Faience, a glazed ceramic material composed primarily of silica and alkalis, offers enhanced durability and resistance to moisture and environmental wear, making it ideal for long-lasting decorative pieces. The vitrified surface of faience significantly extends the longevity of decorative objects, preserving intricate designs and colors far better than terracotta.
Applications in Decorative Objects
Terracotta offers a natural, earthy appeal ideal for rustic decorative objects such as plant pots, sculptures, and garden ornaments due to its porous nature and warm reddish-brown color. Faience, characterized by its glossy, glazed surface and vibrant colors, excels in intricate decorative items like tiles, vases, and ornamental plaques, providing a delicate and refined finish. Both materials suit different aesthetic preferences and functional requirements, with terracotta favored for outdoor durability and faience prized for detailed indoor embellishments.
Cost and Accessibility
Terracotta offers a cost-effective option for decorative objects due to its abundant natural clay and simple firing process, making it widely accessible for artisans and consumers. Faience, composed of glazed non-clay ceramic materials, involves a more complex production technique that raises manufacturing costs and limits availability. The affordability and ease of terracotta production contribute to its popularity in budget-conscious markets, while faience remains a premium choice for intricate, glossy finishes.
Maintenance and Care Considerations
Terracotta requires regular sealing to prevent moisture absorption and staining, with gentle cleaning using a soft brush or damp cloth to maintain its porous surface. Faience, being a glazed ceramic, is more resistant to moisture and stains but needs careful handling to avoid glaze chipping or cracking; mild soap and water are recommended for cleaning. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals and extreme temperature changes to preserve their decorative quality over time.
Choosing Between Terracotta and Faience
Choosing between terracotta and faience for decorative objects depends on desired texture and durability; terracotta offers a porous, earthy aesthetic ideal for rustic or warm designs, while faience provides a glossy, colorful finish suited for intricate, vibrant displays. Terracotta is more porous and less resistant to moisture, making it better for indoor use or dry environments, whereas faience's glazed surface enhances water resistance and longevity, particularly in humid conditions. Consider the object's placement and maintenance needs to determine whether the natural, matte quality of terracotta or the polished, decorative appeal of faience best complements your style and functionality requirements.
Infographic: Terracotta vs Faience for Decorative Object
 azmater.com
azmater.com