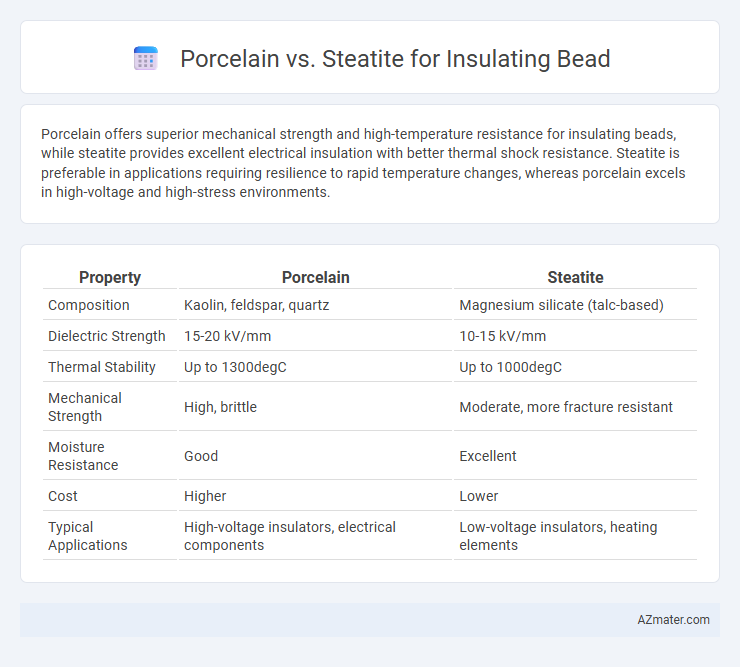
Porcelain offers superior mechanical strength and high-temperature resistance for insulating beads, while steatite provides excellent electrical insulation with better thermal shock resistance. Steatite is preferable in applications requiring resilience to rapid temperature changes, whereas porcelain excels in high-voltage and high-stress environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Porcelain | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Kaolin, feldspar, quartz | Magnesium silicate (talc-based) |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-20 kV/mm | 10-15 kV/mm |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1300degC | Up to 1000degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High, brittle | Moderate, more fracture resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High-voltage insulators, electrical components | Low-voltage insulators, heating elements |
Introduction to Insulating Beads
Insulating beads are crucial components in electrical assemblies, designed to provide high resistance to heat, electricity, and mechanical stress. Porcelain and steatite are two common materials used for insulating beads, each offering distinct thermal conductivity, dielectric strength, and mechanical durability. Porcelain provides excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength, while steatite offers superior dielectric properties and higher resistance to thermal shock, making material choice vital based on application requirements.
What is Porcelain?
Porcelain is a dense, vitrified ceramic material made primarily from kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, renowned for its high electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength. It exhibits excellent resistance to heat, moisture, and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for use as an insulating bead in electrical applications. The smooth, non-porous surface of porcelain ensures minimal electrical leakage and long-lasting durability in high-voltage environments.
What is Steatite?
Steatite, also known as soapstone, is a dense, heat-resistant ceramic material commonly used for insulating beads due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and high thermal stability. It offers superior mechanical strength and moisture resistance compared to porcelain, making it ideal for high-temperature and high-stress applications in electrical components. Steatite's unique combination of durability and insulating capability enhances the reliability and longevity of electrical assemblies where thermal and electrical isolation is critical.
Material Composition Comparison
Porcelain insulating beads are made primarily from kaolin clay, feldspar, and quartz, providing excellent electrical insulation and high thermal resistance due to their dense ceramic structure. Steatite beads consist mainly of natural talc (magnesium silicate), offering superior mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock but slightly lower dielectric properties compared to porcelain. Both materials excel in high-voltage insulator applications, with porcelain offering better long-term environmental durability, while steatite is favored for its cost-effectiveness and machinability.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Porcelain exhibits high thermal resistance with a melting point above 1300degC, making it suitable for high-temperature insulating bead applications. Steatite, composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers excellent thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and can withstand temperatures up to 1000degC. Porcelain's denser structure provides superior mechanical strength, while steatite's lightweight nature enhances thermal shock resistance in insulating bead components.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Porcelain insulating beads offer superior mechanical strength with high compressive resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical applications requiring long-lasting durability. Steatite beads provide excellent thermal stability but generally exhibit lower mechanical strength compared to porcelain, leading to potential wear under high mechanical stress. Porcelain's dense, non-porous structure enhances its durability and resistance to cracking, outperforming steatite in demanding insulation environments.
Electrical Insulation Performance
Porcelain offers superior electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for high-voltage applications. Steatite, a type of ceramic with excellent thermal and electrical insulation but lower mechanical strength than porcelain, provides reliable performance in medium-voltage conditions. The choice between porcelain and steatite insulating beads depends on the required electrical insulation level, environmental exposure, and mechanical durability in specific applications.
Cost and Availability
Porcelain insulating beads generally cost more due to their higher durability and temperature resistance, making them ideal for demanding electrical applications. Steatite beads are more affordable and widely available, favored for moderate temperature insulation needs and budget-conscious projects. Availability of porcelain beads can be limited in some regions, whereas steatite is often easier to source from multiple suppliers worldwide.
Typical Applications
Porcelain insulating beads are commonly used in high-voltage electrical insulators and power transmission due to their excellent dielectric strength and thermal stability. Steatite beads are preferred in electronic components and high-frequency applications for their superior machinability and moisture resistance. Both materials serve critical roles in electrical insulation, with porcelain favored for heavy-duty, high-voltage environments and steatite for precision electronic and industrial uses.
Choosing Between Porcelain and Steatite
Choosing between porcelain and steatite for insulating beads depends on factors like thermal resistance, electrical insulation properties, and mechanical strength. Porcelain offers high dielectric strength and excellent resistance to heat and moisture, making it suitable for high-voltage and outdoor applications. Steatite provides superior resistance to thermal shock and mechanical impact with good insulating capabilities, ideal for environments with rapid temperature changes or mechanical stress.
Infographic: Porcelain vs Steatite for Insulating Bead
 azmater.com
azmater.com