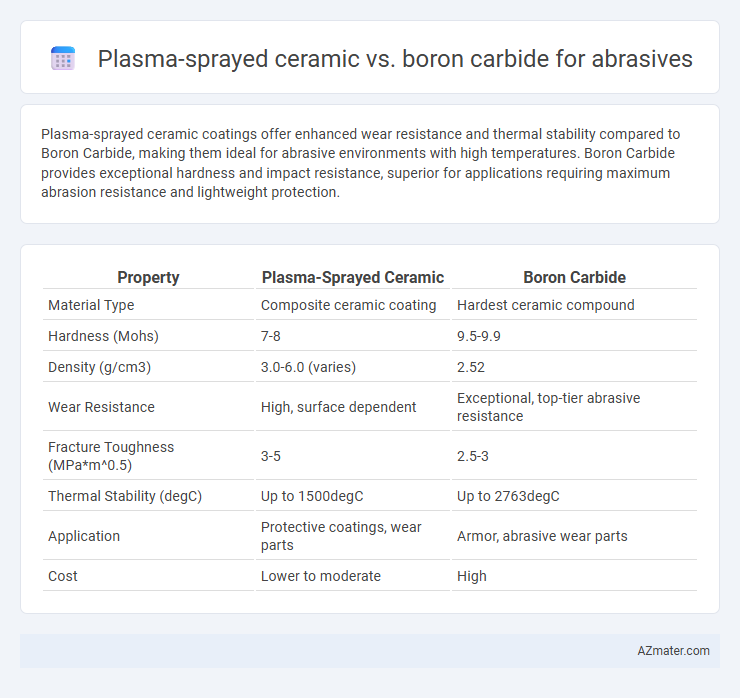
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer enhanced wear resistance and thermal stability compared to Boron Carbide, making them ideal for abrasive environments with high temperatures. Boron Carbide provides exceptional hardness and impact resistance, superior for applications requiring maximum abrasion resistance and lightweight protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic | Boron Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite ceramic coating | Hardest ceramic compound |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7-8 | 9.5-9.9 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.0-6.0 (varies) | 2.52 |
| Wear Resistance | High, surface dependent | Exceptional, top-tier abrasive resistance |
| Fracture Toughness (MPa*m^0.5) | 3-5 | 2.5-3 |
| Thermal Stability (degC) | Up to 1500degC | Up to 2763degC |
| Application | Protective coatings, wear parts | Armor, abrasive wear parts |
| Cost | Lower to moderate | High |
Introduction to Abrasive Materials in Industry
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer enhanced wear resistance and thermal stability, making them suitable for abrasive applications in harsh industrial environments. Boron carbide, known for its exceptional hardness and low density, excels in abrasive wear protection and impact resistance. Comparing these materials reveals distinct performance advantages depending on operational conditions and specific industrial demands.
Overview of Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic Coatings
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer exceptional wear resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for abrasive environments where high hardness and corrosion resistance are required. These coatings typically consist of materials like alumina or zirconia, applied through a high-temperature plasma jet that produces a dense, adherent layer protecting underlying substrates from erosion and abrasive damage. Compared to boron carbide, plasma-sprayed ceramics provide superior coating versatility and repairability, though boron carbide excels in bulk hardness and impact resistance for extreme abrasive applications.
Boron Carbide: Properties and Industrial Uses
Boron carbide exhibits exceptional hardness, ranking just below diamond and cubic boron nitride, which makes it a superior choice for abrasive applications requiring extreme wear resistance. Its lightweight nature coupled with high fracture toughness enables effective use in industrial sectors such as armor plating, cutting tools, and abrasive blasting media. In contrast to plasma-sprayed ceramics, boron carbide offers enhanced performance in high-stress environments due to its superior chemical inertness and thermal stability.
Comparative Hardness: Plasma-Sprayed Ceramic vs Boron Carbide
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings typically exhibit hardness values ranging from 800 to 1200 Vickers Hardness Number (VHN), whereas boron carbide achieves superior hardness levels around 2900 VHN, making it one of the hardest synthetic materials available. The higher hardness of boron carbide directly translates to enhanced wear resistance and improved performance in abrasive environments compared to plasma-sprayed ceramics. This significant difference in hardness makes boron carbide the preferred choice for applications requiring extreme abrasion resistance and durability.
Wear Resistance and Durability Analysis
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings exhibit high wear resistance due to their dense microstructure and strong adhesion to substrates, making them suitable for moderate abrasive environments. Boron carbide, with a hardness of approximately 9.5 on the Mohs scale, surpasses most ceramics in wear resistance and durability, providing superior protection against extreme abrasive wear and mechanical impact. Comparative studies reveal that boron carbide outperforms plasma-sprayed ceramics in long-term durability, especially in highly abrasive, high-stress applications such as armor and cutting tools.
Thermal Stability in Abrasive Applications
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer exceptional thermal stability, maintaining hardness and structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, which is critical for abrasive applications involving high heat generation. Boron carbide, while slightly less thermally stable, provides superior hardness and wear resistance but may degrade when exposed to prolonged temperatures above 900degC. In abrasive environments with intense thermal cycling, plasma-sprayed ceramics outperform boron carbide by resisting thermal shock and preserving abrasive efficiency.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer a cost-effective solution for abrasive applications due to lower material costs and ease of application compared to boron carbide, which has a higher raw material and processing expense. Boron carbide provides superior hardness and wear resistance, justifying its premium price in high-performance, long-life applications where reduced downtime and replacement frequency translate into long-term economic benefits. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including initial investment, maintenance intervals, and operational efficiency, is critical in selecting between plasma-sprayed ceramics and boron carbide for abrasive resistance.
Suitability for Different Abrasive Environments
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer excellent thermal stability and strong resistance to high-velocity abrasive particles, making them suitable for environments with intense heat and erosive wear. Boron carbide, due to its exceptional hardness and low density, excels in highly abrasive settings involving sharp, high-impact particles, such as in ballistic and heavy-duty industrial applications. Each material's unique microstructure and wear resistance properties determine optimal performance depending on the specific abrasive conditions like particle size, velocity, and operational temperature.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Plasma-sprayed ceramic coatings offer high hardness and thermal resistance but typically require frequent maintenance due to micro-cracking and delamination under abrasive conditions. Boron carbide, known for its extreme hardness and fracture toughness, demonstrates superior longevity and lower maintenance requirements in abrasive environments by resisting wear and impact damage more effectively. The choice between these materials impacts operational costs significantly, with boron carbide extending service life and reducing downtime compared to plasma-sprayed ceramics.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations for Industry
Plasma-sprayed ceramics offer superior wear resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for industries requiring high durability under extreme abrasion conditions. Boron carbide provides exceptional hardness and lightweight properties, suited for applications demanding impact resistance and reduced material weight. Key considerations for choosing the right material include abrasion resistance requirements, operational environment, cost-effectiveness, and mechanical strength specific to the industrial application.
Infographic: Plasma-sprayed ceramic vs Boron carbide for Abrasive
 azmater.com
azmater.com