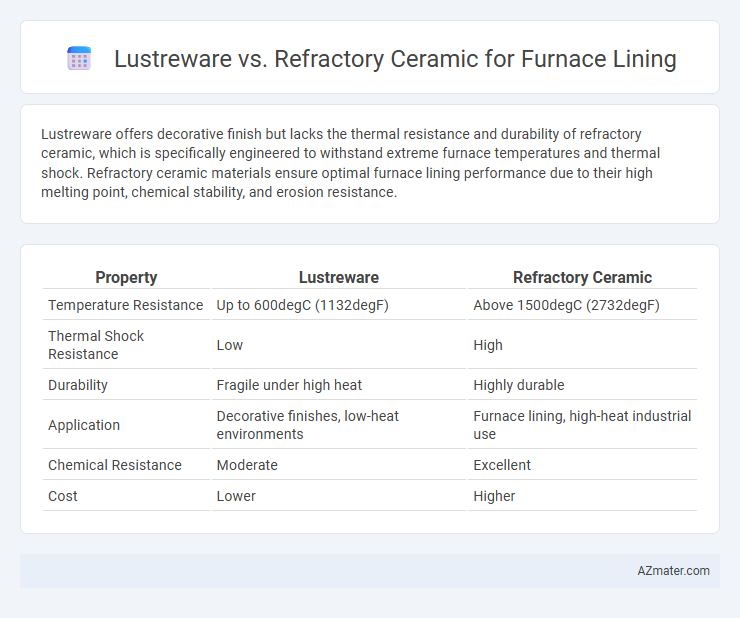
Lustreware offers decorative finish but lacks the thermal resistance and durability of refractory ceramic, which is specifically engineered to withstand extreme furnace temperatures and thermal shock. Refractory ceramic materials ensure optimal furnace lining performance due to their high melting point, chemical stability, and erosion resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lustreware | Refractory Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 600degC (1132degF) | Above 1500degC (2732degF) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low | High |
| Durability | Fragile under high heat | Highly durable |
| Application | Decorative finishes, low-heat environments | Furnace lining, high-heat industrial use |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace linings require durable materials to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock, making lustreware and refractory ceramics critical choices. Lustreware offers aesthetic appeal with a glossy finish but lacks the thermal resistance necessary for industrial furnace applications. Refractory ceramics provide superior heat resistance, structural stability, and chemical inertness, essential for maintaining furnace integrity in extreme environments.
What is Lustreware?
Lustreware is a type of ceramic characterized by its metallic glaze created through a complex firing process that produces an iridescent effect, often used for decorative purposes. Unlike refractory ceramics designed for furnace linings that prioritize high thermal resistance and durability at extreme temperatures, lustreware focuses on aesthetic appeal rather than structural heat performance. When selecting materials for furnace lining, refractory ceramics are preferred due to their ability to withstand thermal shock and corrosive environments critical in high-temperature industrial processes.
Overview of Refractory Ceramics
Refractory ceramics offer exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for furnace linings operating at extremely high temperatures. These materials can withstand thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ensuring durability and extended service life in industrial applications such as steelmaking and glass production. Compared to lustreware, refractory ceramics provide superior insulation and structural integrity under harsh operating conditions.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Lustreware exhibits moderate thermal resistance suitable for decorative furnace linings but lacks the high-temperature endurance required for industrial applications. Refractory ceramics offer superior thermal resistance, often withstanding temperatures exceeding 1600degC, making them ideal for furnace lining in heavy-duty environments. Their ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme thermal stress significantly surpasses that of Lustreware, ensuring enhanced durability and efficiency in thermal insulation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Lustreware exhibits moderate mechanical strength but falls short in durability compared to refractory ceramics, which are engineered to withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses in furnace linings. Refractory ceramics offer superior resistance to thermal shock, corrosion, and abrasion, ensuring extended service life and reduced maintenance costs. The high compressive strength and thermal stability of refractory ceramics make them the optimal choice for industrial furnace lining applications demanding long-term durability and mechanical resilience.
Chemical Stability in High-Temperature Environments
Lustreware exhibits limited chemical stability in high-temperature furnace environments due to its decorative glaze that can degrade under intense heat and reactive atmospheres. Refractory ceramics, specifically designed for furnace linings, maintain exceptional chemical stability by resisting oxidation, slag corrosion, and thermal shock at temperatures often exceeding 1500degC. This durability ensures prolonged operational lifespan and minimal contamination risks in industrial thermal processes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lifespan
Lustreware furnace linings offer moderate cost-effectiveness due to lower initial expenses but typically have a shorter lifespan compared to refractory ceramics, which provide superior durability and thermal resistance. Refractory ceramic linings, despite a higher upfront investment, result in lower maintenance costs and longer operational periods, making them more cost-efficient over time. Choosing between the two depends on balancing immediate budget constraints against long-term performance and replacement frequency.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Lustreware furnace linings generally require careful installation involving skilled artisans to apply their decorative metallic glazes, which may be sensitive to thermal shock and mechanical wear. Refractory ceramics offer robust installation flexibility with prefabricated shapes or cast materials that ensure high thermal resistance and durability under extreme furnace conditions. Maintenance for lustreware involves delicate handling and periodic inspections to preserve surface integrity, while refractory ceramics demand routine checks for cracks or spalling but benefit from higher longevity and easier repairs.
Typical Applications in Industrial Furnaces
Lustreware is typically used in decorative furnace linings due to its aesthetic glaze properties, making it suitable for low-temperature applications and ornamental installations. Refractory ceramic, characterized by high thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion, is predominantly applied in high-temperature industrial furnaces such as steel, glass, and cement kilns. This material provides essential durability and insulation in environments subjected to extreme thermal and mechanical stresses.
Choosing the Right Material: Lustreware or Refractory Ceramic
Selecting the appropriate furnace lining material depends on durability, thermal resistance, and chemical stability; refractory ceramics offer superior high-temperature tolerance and resistance to thermal shock compared to lustreware. Lustreware's glazed surface provides aesthetic appeal but lacks the robustness and heat endurance required for industrial furnace environments. Refractory ceramics are engineered to withstand extreme furnace conditions, making them the optimal choice for long-term performance and structural integrity in high-heat applications.
Infographic: Lustreware vs Refractory ceramic for Furnace Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com