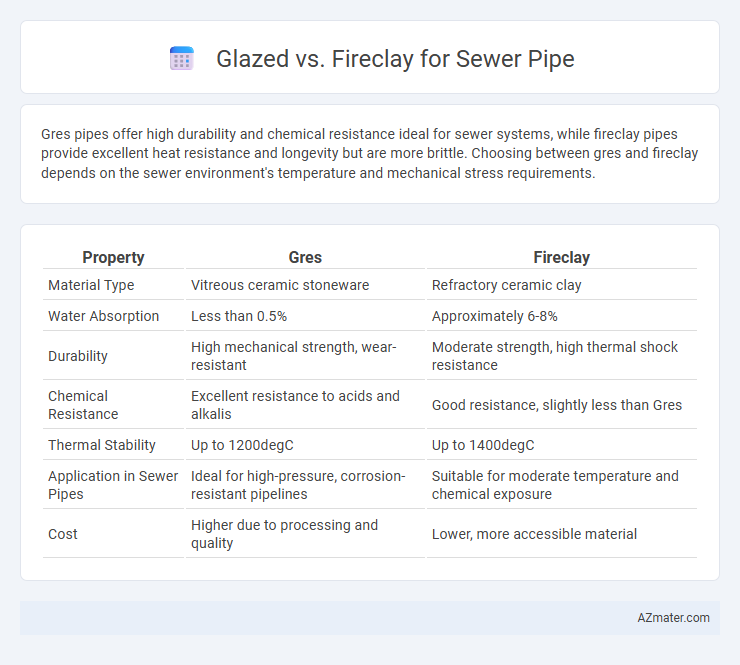
Gres pipes offer high durability and chemical resistance ideal for sewer systems, while fireclay pipes provide excellent heat resistance and longevity but are more brittle. Choosing between gres and fireclay depends on the sewer environment's temperature and mechanical stress requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Fireclay |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Vitreous ceramic stoneware | Refractory ceramic clay |
| Water Absorption | Less than 0.5% | Approximately 6-8% |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, wear-resistant | Moderate strength, high thermal shock resistance |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis | Good resistance, slightly less than Gres |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1400degC |
| Application in Sewer Pipes | Ideal for high-pressure, corrosion-resistant pipelines | Suitable for moderate temperature and chemical exposure |
| Cost | Higher due to processing and quality | Lower, more accessible material |
Gres vs Fireclay Sewer Pipes: An Overview
Gres and fireclay sewer pipes differ primarily in material composition and durability; gres pipes are made from vitrified clay known for high density and low water absorption, resulting in excellent corrosion resistance and long service life. Fireclay pipes, formed from high-temperature ceramic firing of clay, offer superior strength and heat resistance but are generally more brittle and prone to cracking under heavy load or ground movement. Choosing between gres and fireclay sewer pipes depends on project-specific requirements such as soil conditions, load-bearing needs, and budget considerations.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Gres sewer pipes are made from vitrified ceramic materials that undergo high-temperature firing, resulting in a dense, impermeable surface resistant to chemical corrosion and abrasion. Fireclay pipes consist primarily of refined clay mixed with kaolin and other minerals, fired at lower temperatures than gres, producing a porous structure that is typically glazed to enhance durability. The manufacturing process of gres involves precise controlled vitrification to achieve superior strength and impermeability, whereas fireclay relies on a combination of natural clay constituents and glazing to improve water resistance and mechanical performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gres sewer pipes exhibit superior compressive strength with resistance to high pressure and impact, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Fireclay pipes demonstrate excellent chemical resistance and durability in acidic environments but have lower tensile strength compared to gres. The dense, vitrified composition of gres enhances longevity under mechanical stress, while fireclay's rigidity offers reliability in stable, low-impact conditions.
Resistance to Corrosion and Chemical Attack
Gres sewer pipes exhibit excellent resistance to chemical attack due to their dense, vitrified composition, making them highly durable against acidic and alkaline waste. Fireclay pipes also offer strong corrosion resistance but are generally less effective than gres in withstanding aggressive chemical environments, especially in industrial applications. The superior chemical resistance of gres pipes ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in corrosive sewage systems.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Gres sewer pipes are generally denser and heavier, making transportation and installation more labor-intensive and requiring sturdier support systems. Fireclay pipes, being lighter, offer easier handling and faster installation, which reduces labor costs and time on-site. Weight differences directly impact logistics, with fireclay favored in projects where weight constraints and ease of maneuverability are critical.
Installation Procedures and Challenges
Gres sewer pipes require precise handling due to their rigidity and weight, demanding specialized equipment during installation to prevent cracking. Fireclay pipes, while more brittle, allow for straightforward fitting but pose challenges in joint sealing to maintain leak-proof performance under high pressure. Both materials necessitate careful alignment and bedding to avoid structural failures, with Fireclay often requiring more frequent inspections post-installation to address potential fractures.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Value
Gres sewer pipes offer cost efficiency due to lower initial material and installation expenses compared to Fireclay pipes, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects. Fireclay pipes provide superior long-term value with high durability, resistance to chemical corrosion, and minimal maintenance needs, extending the service life significantly. Evaluating project requirements against lifecycle costs reveals that Fireclay is ideal for infrastructure demanding longevity, whereas Gres fits short- to medium-term applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Gres sewer pipes, made from refined clay baked at high temperatures, offer excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, contributing to long-term sustainability by minimizing replacement frequency and waste. Fireclay pipes, produced by mixing clay with fire-resistant minerals and fired to achieve high strength, provide enhanced thermal stability and lower environmental impact due to their natural material composition and energy-efficient manufacturing process. Both materials support eco-friendly infrastructure, but Fireclay pipes often have a smaller carbon footprint and better recyclability, making them a preferred choice for sustainable sewer systems.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Sewer Pipes
Gres sewer pipes are highly durable with a lifespan that can exceed 50 years due to their dense, vitrified ceramic composition, making them resistant to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical damage, thus requiring minimal maintenance over time. Fireclay pipes also offer excellent durability and resistance to acidic wastewater but generally have a slightly shorter lifespan of around 40-50 years and may need periodic inspections for joint integrity and minor repairs. Both materials provide long-term reliability; however, Gres pipes are often preferred in sewer systems where low maintenance and extended service life are critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sewer System
Gres and fireclay are popular materials for sewer pipes due to their durability and resistance to corrosion, but gres offers superior strength and longer lifespan in high-pressure sewer systems. Fireclay provides excellent chemical resistance and is cost-effective for residential or low-traffic applications, making it suitable for smaller sewer lines. Selecting the right material depends on factors like soil conditions, load requirements, and budget, with gres favored for industrial use and fireclay ideal for standard residential installations.
Infographic: Gres vs Fireclay for Sewer Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com