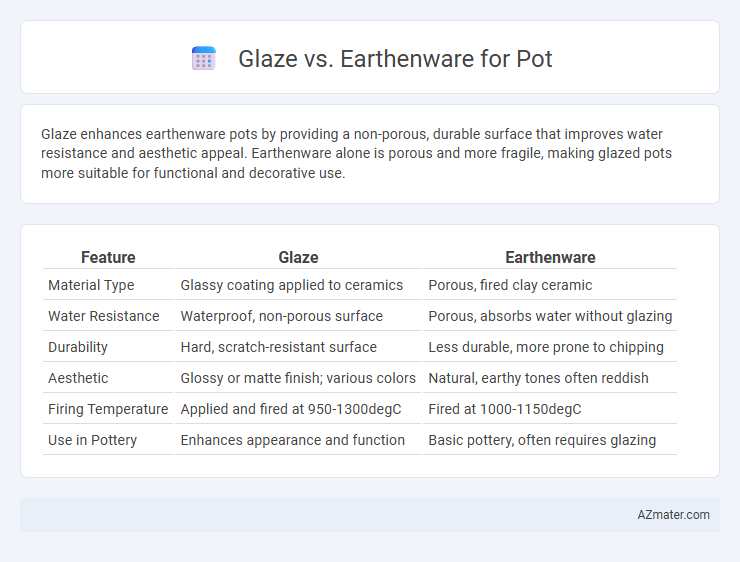
Glaze enhances earthenware pots by providing a non-porous, durable surface that improves water resistance and aesthetic appeal. Earthenware alone is porous and more fragile, making glazed pots more suitable for functional and decorative use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glaze | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glassy coating applied to ceramics | Porous, fired clay ceramic |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, non-porous surface | Porous, absorbs water without glazing |
| Durability | Hard, scratch-resistant surface | Less durable, more prone to chipping |
| Aesthetic | Glossy or matte finish; various colors | Natural, earthy tones often reddish |
| Firing Temperature | Applied and fired at 950-1300degC | Fired at 1000-1150degC |
| Use in Pottery | Enhances appearance and function | Basic pottery, often requires glazing |
Understanding Glaze and Earthenware: Key Definitions
Glaze is a glass-like coating applied to earthenware pottery, transforming its porous surface into a smooth, waterproof finish essential for functionality and aesthetic appeal. Earthenware refers to one of the oldest types of pottery, characterized by its porous, low-fired clay body that inherently requires glazing to enhance durability and prevent liquid absorption. Understanding the role of glaze in sealing earthenware is crucial for distinguishing the functional and decorative qualities that define each pottery type.
Composition Differences: Glaze vs Earthenware
Glaze is a glassy coating composed mainly of silica, fluxes, and alumina that fuses to pottery at high temperatures, providing a waterproof and decorative surface. Earthenware, made from clay-rich materials like kaolin and ball clays mixed with quartz and feldspar, is fired at lower temperatures and remains porous unless coated with a glaze. The key composition difference lies in glaze's vitrification properties versus earthenware's porous clay body, influencing durability and functionality of the pot.
Visual Appeal: Surface Texture and Color Variations
Glaze on pots creates a smooth, glossy surface that enhances color vibrancy and provides reflective qualities, making designs stand out with depth and brightness. Earthenware, in contrast, showcases a more natural, matte texture with earthy tones and subtle color variations that emphasize rustic and handcrafted aesthetics. The choice between glazed and earthenware surfaces significantly impacts visual appeal through differences in texture smoothness and color intensity.
Porosity and Durability Comparison
Glazed pottery offers significantly lower porosity compared to earthenware, as the glaze forms a non-porous, glass-like surface that seals the clay body and prevents water absorption. Earthenware is more porous due to its lower firing temperature and lack of a vitreous glaze, which makes it less durable and more susceptible to cracking and moisture damage. The enhanced durability and impermeability of glazed pots make them ideal for functional use, while unglazed earthenware is better suited for decorative purposes.
Water Resistance: Glazed Pottery vs Earthenware
Glazed pottery offers superior water resistance compared to earthenware due to its glass-like coating that seals the porous clay body, preventing water absorption and enhancing durability. Earthenware, being more porous and unglazed or only partially glazed, tends to absorb water, leading to potential weakening and increased susceptibility to cracking over time. For functional pots exposed to moisture, glazed pottery is the optimal choice to ensure longevity and resistance against water damage.
Suitability for Functional vs Decorative Pottery
Glaze adds a durable, waterproof layer to earthenware, making it highly suitable for functional pottery such as bowls and mugs, where food safety and ease of cleaning are essential. Earthenware alone is porous and less resistant to liquids, limiting its use primarily to decorative pottery that doesn't require frequent washing or food contact. For functional pots, glazed earthenware provides longevity and practicality, while unglazed earthenware offers a rustic aesthetic preferred for purely decorative pieces.
Health and Food Safety Considerations
Glaze on ceramic pots serves as a non-porous barrier that prevents food and liquids from seeping into the porous earthenware, reducing the risk of bacterial contamination and foodborne illnesses. Unglazed earthenware, being porous, can absorb moisture, oils, and food particles, leading to potential harboring of harmful bacteria and making thorough cleaning difficult. Choosing food-safe, lead-free glazes certified for kitchen use ensures that pots do not leach toxic substances into food, prioritizing health and safety in cooking and serving.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Glaze for pots varies in cost depending on the type, with commercial glazes typically priced between $10 and $30 per pound, offering extensive color and finish options but sometimes requiring specialized firing conditions. Earthenware clay is generally more affordable and widely accessible, often available at art supply stores for around $5 to $15 per kilogram, making it a popular choice for beginners due to its low firing temperature and ease of use. While glaze materials may increase overall project expenses, the combined cost of earthenware clay and glaze remains budget-friendly for most hobbyists and small-scale potters.
Popular Uses and Applications in Pottery
Glaze enhances earthenware pots by providing a waterproof, decorative surface suitable for functional items like tableware, flower pots, and cooking vessels, improving durability and aesthetic appeal. Earthenware itself is favored for its porous composition and ease of shaping, commonly used for garden pots, terracotta sculptures, and rustic cookware due to its affordability and traditional look. Combining glaze with earthenware expands its applications, making it ideal for both practical household items and artistic pottery pieces.
Choosing the Right Option: Factors to Consider
When choosing between glaze and earthenware for pots, consider factors such as durability, porosity, and aesthetic appeal. Glazed pots offer a waterproof, non-porous surface ideal for retaining moisture and preventing stains, while earthenware is more porous, requiring sealing for water resistance but providing a rustic, breathable quality. Assess your intended use, exposure to moisture, and desired finish to select the option that best suits your gardening or decorative needs.
Infographic: Glaze vs Earthenware for Pot
 azmater.com
azmater.com