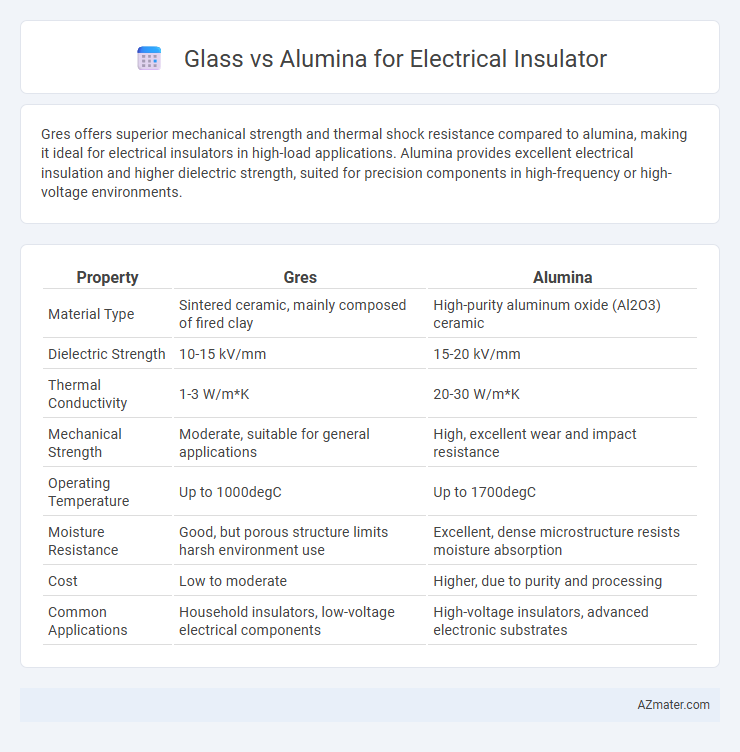
Gres offers superior mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance compared to alumina, making it ideal for electrical insulators in high-load applications. Alumina provides excellent electrical insulation and higher dielectric strength, suited for precision components in high-frequency or high-voltage environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gres | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Sintered ceramic, mainly composed of fired clay | High-purity aluminum oxide (Al2O3) ceramic |
| Dielectric Strength | 10-15 kV/mm | 15-20 kV/mm |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1-3 W/m*K | 20-30 W/m*K |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, suitable for general applications | High, excellent wear and impact resistance |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 1000degC | Up to 1700degC |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, but porous structure limits harsh environment use | Excellent, dense microstructure resists moisture absorption |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher, due to purity and processing |
| Common Applications | Household insulators, low-voltage electrical components | High-voltage insulators, advanced electronic substrates |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators such as gres and alumina play crucial roles in preventing electrical current flow and ensuring safety in high-voltage applications. Gres, a type of hard ceramic material, offers excellent mechanical strength and good insulating properties, making it suitable for medium-voltage systems. Alumina, composed primarily of aluminum oxide, provides superior electrical insulation, high thermal resistance, and exceptional durability, making it the preferred choice in advanced, high-performance electrical insulator applications.
What is Gres?
Gres, also known as porcelain, is a dense, vitrified ceramic material primarily composed of kaolin, feldspar, and quartz, widely used in electrical insulators due to its excellent mechanical strength and high dielectric resistance. Its low porosity and high firing temperature contribute to superior moisture resistance and long-term durability in outdoor electrical insulation applications. Compared to alumina, gres offers cost-effective reliability with adequate electrical insulation properties but generally lower thermal conductivity and mechanical toughness.
What is Alumina?
Alumina, also known as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is a highly durable ceramic material used extensively in electrical insulators due to its excellent dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It offers superior mechanical strength and can withstand high temperatures, making it ideal for insulating components in harsh electrical environments. Compared to gres, alumina provides enhanced electrical insulation performance and longer service life in high-voltage applications.
Material Composition Comparison
Gres, primarily composed of feldspar, quartz, and clay minerals, offers a dense, vitrified structure with lower porosity and good thermal stability, making it suitable for electrical insulation applications. Alumina (Aluminum Oxide), with a high purity level typically exceeding 99%, provides superior dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and mechanical hardness compared to gres, resulting in enhanced performance in high-voltage insulators. The significant difference in chemical composition, where alumina's crystalline structure contributes to better electrical resistance and heat dissipation, makes it more desirable for advanced electrical insulation needs.
Electrical Properties: Gres vs Alumina
Gres and alumina exhibit distinct electrical properties critical for insulating applications; gres typically offers moderate dielectric strength and resistivity, suitable for low to medium voltage insulators. Alumina, with its high dielectric strength exceeding 10 kV/mm and excellent electrical resistivity above 10^14 ohm-cm, provides superior insulation performance, especially in high-voltage and high-temperature environments. The enhanced purity and crystalline structure of alumina enable lower dielectric losses and improved stability under electrical stress compared to gres materials.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gres ceramics exhibit superior mechanical strength with high fracture toughness and impact resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty electrical insulator applications. Alumina offers excellent durability due to its high hardness, thermal stability, and resistance to corrosion and wear under harsh environmental conditions. Both materials ensure reliable insulation, but gres is favored in scenarios requiring enhanced mechanical robustness, while alumina excels in environments demanding long-term chemical and thermal stability.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Gres ceramics exhibit superior thermal conductivity and higher heat resistance compared to alumina, making them ideal for electrical insulators exposed to extreme temperatures. Alumina offers excellent electrical insulation properties but has lower thermal stability and is prone to thermal shock at elevated temperatures above 1600degC. The thermal performance of gres insulators ensures minimal deformation and consistent dielectric strength in high-heat environments, while alumina insulators are better suited for applications with moderate thermal demands.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Gres offers superior cost efficiency compared to alumina due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it ideal for budget-sensitive electrical insulator applications. Alumina boasts higher availability in industrial markets, supported by extensive global supply chains and well-established production facilities. Both materials ensure reliable electrical insulation, but selecting Gres or alumina depends largely on balancing budget constraints with supply chain reliability.
Typical Applications in Electrical Systems
Gres and alumina ceramics are essential materials in electrical insulators, with alumina favored for high-voltage applications due to its superior dielectric strength and thermal conductivity. Alumina insulators are commonly used in transformers, circuit breakers, and high-frequency transmission systems where enhanced mechanical strength and electrical performance are critical. Gres, with its cost-effectiveness and good insulating properties, is typically applied in low to medium voltage systems such as distribution networks and switchgear components.
Choosing the Right Material: Gres or Alumina
Choosing between Gres and Alumina for electrical insulators depends on application-specific requirements such as dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and mechanical durability. Alumina offers superior electrical insulation properties and higher resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for high-voltage and high-temperature environments. Gres, though more cost-effective and offering good thermal stability, is typically preferred for lower voltage applications where mechanical toughness is prioritized over extreme dielectric performance.
Infographic: Gres vs Alumina for Electrical insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com