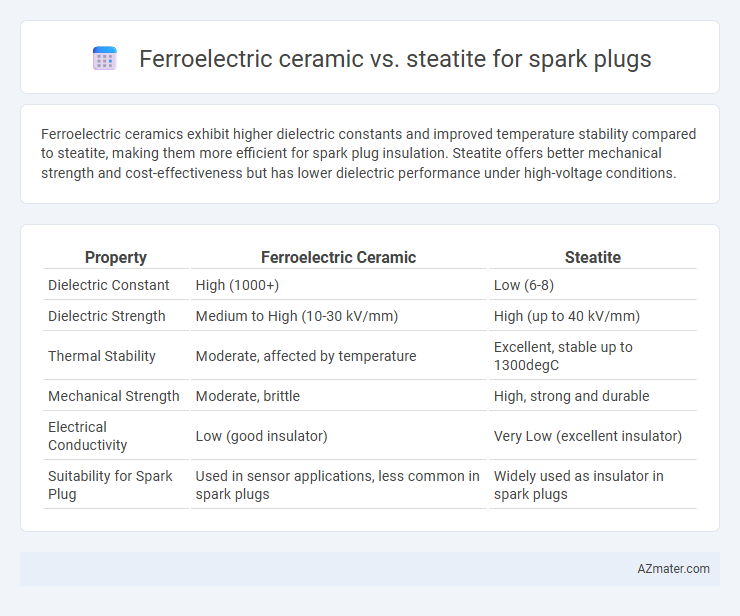
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit higher dielectric constants and improved temperature stability compared to steatite, making them more efficient for spark plug insulation. Steatite offers better mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness but has lower dielectric performance under high-voltage conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Steatite |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant | High (1000+) | Low (6-8) |
| Dielectric Strength | Medium to High (10-30 kV/mm) | High (up to 40 kV/mm) |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, affected by temperature | Excellent, stable up to 1300degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle | High, strong and durable |
| Electrical Conductivity | Low (good insulator) | Very Low (excellent insulator) |
| Suitability for Spark Plug | Used in sensor applications, less common in spark plugs | Widely used as insulator in spark plugs |
Introduction to Spark Plug Materials
Ferroelectric ceramics offer superior dielectric properties and high temperature resistance, making them ideal for spark plug insulators under extreme combustion conditions. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides good electrical insulation and thermal stability but generally falls short in mechanical strength and dielectric performance compared to ferroelectric ceramics. The choice between ferroelectric ceramic and steatite hinges on the specific engine requirements, with ferroelectric ceramics favored for high-performance, high-voltage spark plug applications.
What Are Ferroelectric Ceramics?
Ferroelectric ceramics are materials that exhibit spontaneous electric polarization, which can be reversed by an external electric field, making them highly effective for energy storage and piezoelectric applications. Unlike steatite, a type of refractory ceramic primarily used for its insulating properties in spark plugs, ferroelectric ceramics enhance spark generation due to their dielectric characteristics and high permittivity. These properties enable ferroelectric ceramics to improve ignition efficiency and spark plug durability in demanding automotive environments.
Overview of Steatite in Spark Plugs
Steatite, a ceramic composed primarily of magnesium silicate, offers excellent electrical insulation and thermal stability, making it a reliable insulator in spark plugs. Its high dielectric strength and resistance to thermal shock ensure consistent performance under the engine's extreme conditions. Compared to ferroelectric ceramics, steatite provides superior mechanical durability and a cost-effective solution for spark plug insulators.
Electrical Insulation Properties: Ferroelectric Ceramic vs Steatite
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit high dielectric constants and strong polarization under an electric field, offering excellent capacitance and electrical insulation for spark plugs. Steatite, composed mainly of magnesium silicate, provides good but comparatively lower dielectric strength and superior thermal shock resistance. Ferroelectric ceramics generally enable more stable electrical insulation performance at varying voltages, while steatite's mechanical durability supports longevity in harsh combustion environments.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit higher thermal conductivity compared to steatite, enabling more efficient heat dissipation in spark plug applications. Steatite, with its lower thermal conductivity, tends to retain more heat, potentially affecting spark plug performance under high-temperature conditions. The superior thermal management properties of ferroelectric ceramics contribute to improved durability and consistent ignition in automotive engines.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to steatite, making them highly resistant to thermal shock and mechanical stress in spark plug applications. Steatite, while cost-effective and electrically insulating, tends to have lower fracture toughness and is more prone to cracking under repeated thermal cycling. The advanced microstructure of ferroelectric ceramics provides greater reliability and lifespan for spark plugs operating under intense combustion conditions.
Dielectric Performance in High-Voltage Applications
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior dielectric properties compared to steatite, featuring higher dielectric constants and excellent polarization retention essential for efficient spark plug insulation in high-voltage environments. Steatite offers good thermal stability and mechanical strength, but its lower dielectric constant limits its effectiveness in minimizing leakage currents under high-voltage stress. The enhanced dielectric breakdown strength of ferroelectric ceramics makes them more suitable for spark plug applications where reliable insulation and energy storage are critical.
Cost Analysis: Material and Manufacturing
Ferroelectric ceramic spark plugs exhibit higher material costs due to the complex raw materials like barium titanate and the precision required in their manufacturing process. Steatite spark plugs, composed primarily of inexpensive magnesium silicate, offer lower material expenses and simpler ceramic molding techniques, reducing overall production costs. Manufacturing ferroelectric ceramics demands advanced sintering and quality control steps, which elevate expenses compared to the more straightforward production of steatite spark plugs.
Longevity and Reliability in Automotive Use
Ferroelectric ceramic spark plugs exhibit superior longevity and reliability in automotive use due to their enhanced thermal stability and resistance to dielectric breakdown, which ensures consistent performance under high voltage and extreme temperature conditions. In contrast, steatite ceramics, while cost-effective, tend to degrade faster because of lower thermal shock resistance, leading to increased risk of premature failure. Ferroelectric ceramic materials improve ignition efficiency and minimize misfires, making them more suitable for long-term, high-performance automotive applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Spark Plugs
Ferroelectric ceramics offer superior dielectric properties and higher temperature resistance compared to steatite, making them ideal for high-performance spark plugs requiring stable insulation and durability under extreme conditions. Steatite, while more cost-effective and easier to manufacture, falls short in thermal stability and dielectric strength, limiting its suitability for advanced automotive applications. For optimal spark plug performance and longevity, ferroelectric ceramics are the preferred material choice due to their enhanced electrical and thermal characteristics.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Steatite for Spark plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com