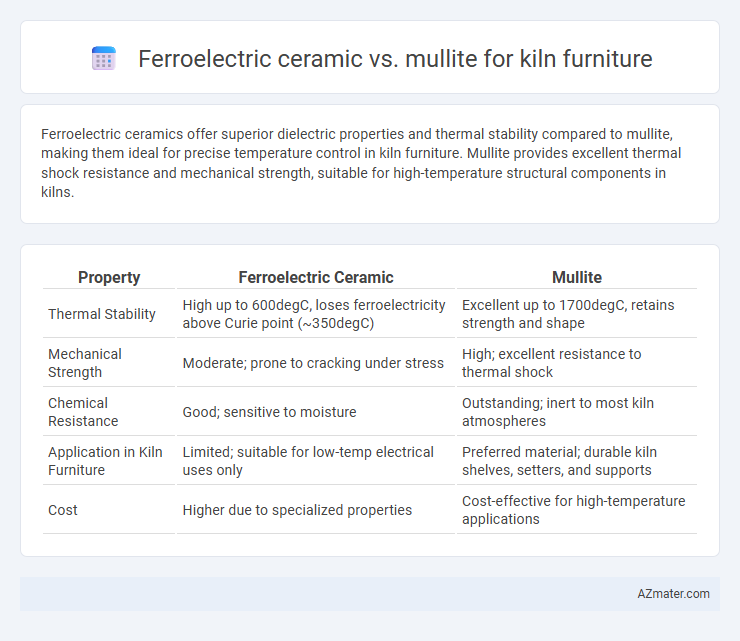
Ferroelectric ceramics offer superior dielectric properties and thermal stability compared to mullite, making them ideal for precise temperature control in kiln furniture. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for high-temperature structural components in kilns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ferroelectric Ceramic | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | High up to 600degC, loses ferroelectricity above Curie point (~350degC) | Excellent up to 1700degC, retains strength and shape |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; prone to cracking under stress | High; excellent resistance to thermal shock |
| Chemical Resistance | Good; sensitive to moisture | Outstanding; inert to most kiln atmospheres |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Limited; suitable for low-temp electrical uses only | Preferred material; durable kiln shelves, setters, and supports |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized properties | Cost-effective for high-temperature applications |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Ferroelectric ceramic and mullite are essential materials used in kiln furniture, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties critical for supporting wares during high-temperature firing. Ferroelectric ceramics provide excellent dielectric properties and temperature stability, making them suitable for applications requiring precise thermal control, while mullite is valued for its superior thermal shock resistance and high melting point around 1840degC. The selection between ferroelectric ceramic and mullite depends on specific kiln operating conditions, including temperature profiles and load-bearing requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in kiln furniture components.
Overview of Ferroelectric Ceramics
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field, making them valuable for sensors, actuators, and capacitors in high-temperature environments. These ceramics, typically composed of barium titanate or lead zirconate titanate, offer excellent piezoelectric properties and thermal stability up to about 500degC, which is advantageous for kiln furniture requiring precise dimensional stability and resistance to thermal shock. Compared to mullite, which is prized for its mechanical strength and resistance to thermal creep above 1400degC, ferroelectric ceramics provide functional electric properties that enable advanced monitoring and control capabilities within kiln operations.
Properties and Characteristics of Mullite
Mullite, a refractory ceramic commonly used in kiln furniture, exhibits excellent thermal stability with a high melting point above 1840degC and low thermal expansion, minimizing deformation under rapid temperature changes. Its outstanding mechanical strength and resistance to thermal shock enable prolonged durability in high-temperature environments, outperforming many ferroelectric ceramics. Mullite's chemical inertness and resistance to corrosion from kiln atmospheres make it ideal for supporting heavy loads during firing processes.
Thermal Stability: Ferroelectric Ceramic vs Mullite
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit higher thermal stability than mullite, maintaining their structural integrity and performance at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, crucial for demanding kiln environments. Mullite, while thermally stable up to approximately 1400degC, shows slower thermal response and can experience microcracking under rapid thermal cycling. The superior thermal shock resistance and dielectric properties of ferroelectric ceramics make them more suitable for precision kiln furniture applications requiring consistent temperature tolerance and mechanical strength.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit higher mechanical strength and fracture toughness compared to mullite, making them more resistant to thermal shock and mechanical wear in kiln furniture applications. Mullite, while valued for its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, generally has lower flexural strength, which can limit its durability under heavy loading conditions. The superior mechanical properties of ferroelectric ceramics enhance kiln furniture lifespan and performance in high-stress environments.
Thermal Shock Resistance Analysis
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior thermal shock resistance due to their high dielectric constants and intrinsic ability to tolerate rapid temperature changes without cracking, making them highly durable for kiln furniture applications. Mullite, while valued for its low thermal expansion and good thermal stability, generally shows lower resistance to thermal shock compared to ferroelectric ceramics because of its brittleness under sudden temperature variations. Thermal shock resistance analysis confirms that ferroelectric ceramic materials outperform mullite in maintaining structural integrity during frequent thermal cycling in high-temperature kiln environments.
Chemical Resistance in Firing Environments
Ferroelectric ceramics exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to mullite in aggressive firing environments due to their stable perovskite crystal structure, which resists alkali and acidic vapors. Mullite, while thermally stable, is more susceptible to chemical attack from fluxes and molten slags, leading to surface degradation and reduced lifespan in kiln furniture applications. The enhanced chemical durability of ferroelectric ceramics ensures longer operational cycles and reduced contamination risk in high-temperature industrial firing processes.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Ferroelectric ceramic materials demonstrate superior energy efficiency in kiln furniture applications due to their high dielectric constant and excellent thermal stability, enabling uniform heat distribution and reduced energy consumption. Mullite, while offering strong mechanical strength and excellent thermal shock resistance, typically has lower thermal conductivity, which can result in longer heating cycles and less efficient energy use compared to ferroelectric ceramics. The enhanced performance of ferroelectric ceramics in maintaining consistent kiln temperatures directly contributes to faster firing times and improved overall energy savings.
Cost and Longevity Considerations
Ferroelectric ceramics offer high durability and thermal stability but come with a higher initial cost compared to Mullite, which is more budget-friendly and widely used in kiln furniture applications. Mullite provides excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, ensuring long service life at a lower price point, making it ideal for large-scale or cost-sensitive operations. When balancing cost and longevity, Mullite often outperforms ferroelectric ceramics in practical kiln environments due to its optimal combination of affordability and dependable lifespan.
Choosing the Right Material for Kiln Furniture Applications
Ferroelectric ceramic offers superior thermal shock resistance and high dielectric strength, making it ideal for kiln furniture applications that require precise temperature control and electrical insulation. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, provides durability and resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures, ensuring long service life under high-temperature cycling. Selecting the right material depends on operational conditions: ferroelectric ceramic suits applications demanding electrical insulation and rapid temperature fluctuations, while mullite excels in structural support where mechanical strength and thermal stability are critical.
Infographic: Ferroelectric ceramic vs Mullite for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com