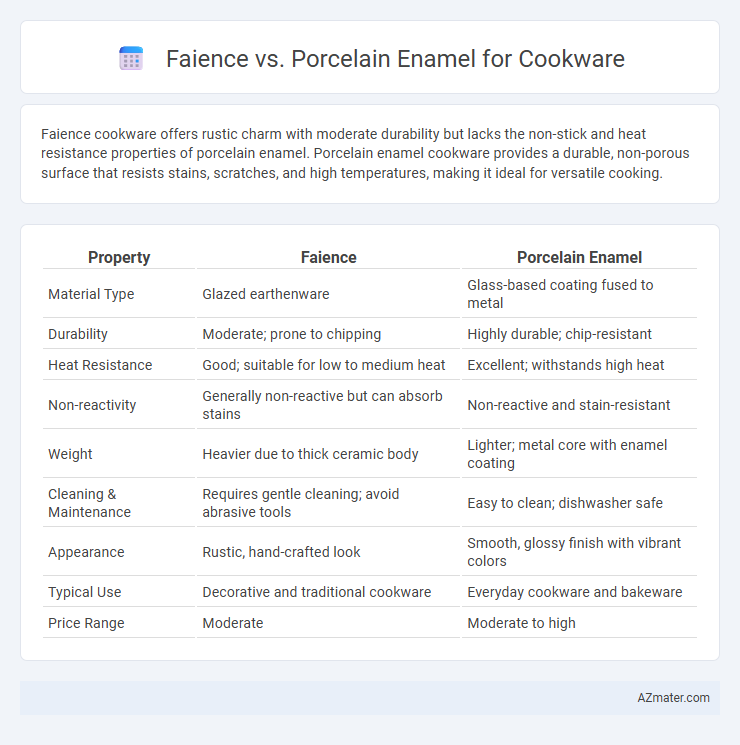
Faience cookware offers rustic charm with moderate durability but lacks the non-stick and heat resistance properties of porcelain enamel. Porcelain enamel cookware provides a durable, non-porous surface that resists stains, scratches, and high temperatures, making it ideal for versatile cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Porcelain Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed earthenware | Glass-based coating fused to metal |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping | Highly durable; chip-resistant |
| Heat Resistance | Good; suitable for low to medium heat | Excellent; withstands high heat |
| Non-reactivity | Generally non-reactive but can absorb stains | Non-reactive and stain-resistant |
| Weight | Heavier due to thick ceramic body | Lighter; metal core with enamel coating |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Requires gentle cleaning; avoid abrasive tools | Easy to clean; dishwasher safe |
| Appearance | Rustic, hand-crafted look | Smooth, glossy finish with vibrant colors |
| Typical Use | Decorative and traditional cookware | Everyday cookware and bakeware |
| Price Range | Moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Faience and Porcelain Enamel Cookware
Faience cookware is characterized by its tin-glazed earthenware, offering a porous and decorative surface often hand-painted for aesthetic appeal. Porcelain enamel cookware features a glassy, non-porous coating fused onto metal substrates, providing durability and resistance to stains and corrosion. Both materials deliver distinct cookware experiences, with faience prized for artistic value and porcelain enamel favored for longevity and ease of maintenance.
What is Faience? Origins and Characteristics
Faience is a type of tin-glazed earthenware pottery that originated in the Mediterranean region during the Renaissance, known for its opaque white glaze and vibrant, hand-painted designs. Its porous and relatively soft ceramic body contrasts with the dense, vitrified surface of porcelain enamel, making faience more decorative but less durable for heavy-duty cookware. Faience cookware is prized for its artisanal aesthetic, cultural heritage, and ability to retain heat evenly, though it requires careful handling to avoid chipping.
Defining Porcelain Enamel: Composition and Uses
Porcelain enamel is a durable coating made by fusing powdered glass to a metal substrate, typically cast iron or steel, at high temperatures, creating a smooth, non-porous surface. This composition provides excellent resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemical damage, making it ideal for cookware that requires even heat distribution and easy cleaning. Porcelain enamel cookware is commonly used for baking dishes, pots, and pans, favored for its aesthetic versatility and non-reactive qualities with acidic foods.
Durability Comparison: Faience vs Porcelain Enamel
Faience cookware, made from tin-glazed earthenware, tends to be more porous and less durable compared to porcelain enamel-coated cookware, which features a robust glassy coating fused to metal surfaces. Porcelain enamel provides superior resistance to chipping, scratching, and thermal shock, making it highly durable for everyday use and high-heat cooking. Faience is more prone to cracking and staining over time, whereas porcelain enamel maintains its integrity and appearance through prolonged usage.
Heat Resistance and Cooking Performance
Porcelain enamel offers superior heat resistance compared to faience, enabling cookware to withstand higher cooking temperatures without cracking or damage. This makes porcelain enamel ideal for searing, frying, and oven use, as it maintains even heat distribution and prevents food from sticking. Faience cookware, while decorative and attractive, generally has lower thermal durability and may not perform as well under intense or prolonged heat conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Faience cookware requires gentle cleaning with mild detergents to prevent surface damage and maintain its porous glaze, making it susceptible to staining if not properly cared for. Porcelain enamel cookware offers a non-porous, durable surface that resists staining and can withstand more rigorous scrubbing, simplifying maintenance and cleaning processes. Both materials should avoid sudden temperature changes to prevent cracking, but porcelain enamel provides greater ease of use for routine cleaning.
Aesthetic Differences and Design Choices
Faience cookware features a rustic, handcrafted appeal with intricate, often colorful patterns made from glazed earthenware, lending a vintage and artisanal aesthetic ideal for decorative kitchen displays. Porcelain enamel cookware offers a sleek, smooth, and glossy finish with vibrant solid colors or minimalist designs, attracting those who prefer modern, durable, and easy-to-clean surfaces. Design choices between the two hinge on whether the user favors the traditional charm and varied textures of faience or the contemporary, uniform appearance and enhanced resistance of porcelain enamel.
Health and Safety Considerations
Faience cookware, made from glazed earthenware, may contain lead or cadmium in older or low-quality glazes, posing health risks if used with acidic foods. Porcelain enamel cookware, fused with a durable glass coating free from harmful chemicals, provides a non-toxic cooking surface that resists chipping and leaching, ensuring safe food preparation. Choosing porcelain enamel cookware enhances safety by minimizing exposure to toxic substances and maintaining hygienic cooking conditions.
Cost and Market Availability
Faience cookware generally offers a more affordable option compared to porcelain enamel, making it accessible for budget-conscious consumers. Porcelain enamel cookware tends to dominate the market with widespread availability in diverse styles and high-end brands, reflecting its durability and aesthetic appeal. Consumers often find faience in local or artisanal markets, while porcelain enamel is readily available in large retail stores and online platforms.
Which is Better? Final Verdict for Home Cooks
Porcelain enamel cookware offers superior durability, non-porous surfaces, and resistance to staining and scratching compared to faience, making it a better choice for home cooks seeking long-lasting, easy-to-clean pots and pans. Faience, with its porous nature and less durable glaze, tends to absorb flavors and is more prone to chipping, which affects cooking performance and maintenance. For everyday use, porcelain enamel cookware provides enhanced heat retention and compatibility with various stovetops, delivering a reliable and hygienic cooking experience.
Infographic: Faience vs Porcelain Enamel for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com