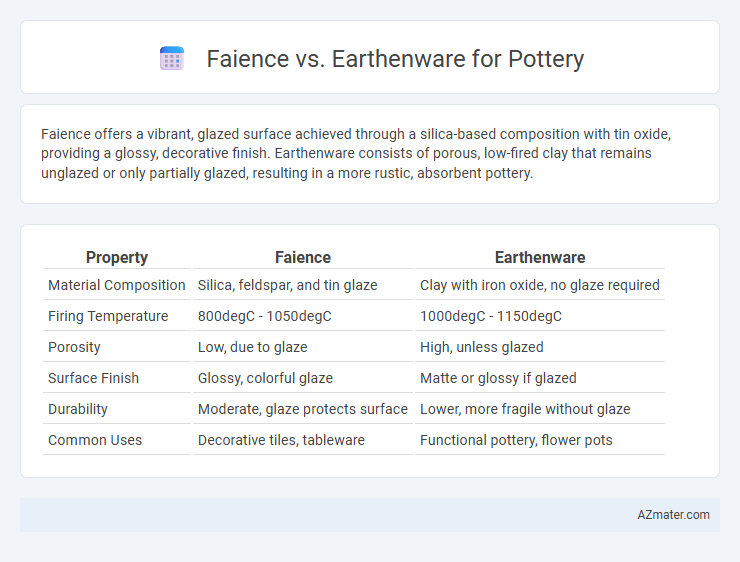
Faience offers a vibrant, glazed surface achieved through a silica-based composition with tin oxide, providing a glossy, decorative finish. Earthenware consists of porous, low-fired clay that remains unglazed or only partially glazed, resulting in a more rustic, absorbent pottery.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Silica, feldspar, and tin glaze | Clay with iron oxide, no glaze required |
| Firing Temperature | 800degC - 1050degC | 1000degC - 1150degC |
| Porosity | Low, due to glaze | High, unless glazed |
| Surface Finish | Glossy, colorful glaze | Matte or glossy if glazed |
| Durability | Moderate, glaze protects surface | Lower, more fragile without glaze |
| Common Uses | Decorative tiles, tableware | Functional pottery, flower pots |
Introduction to Faience and Earthenware
Faience is a type of fine tin-glazed pottery known for its bright, opaque surface and intricate painted designs, traditionally made from a refined clay body. Earthenware, made from coarse, porous clay, is fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less durable ceramic. Understanding the key differences in composition, firing processes, and surface treatments allows artisans to choose the ideal material for distinct artistic and functional purposes.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Faience pottery originated in ancient Egypt around 4000 BCE, characterized by its tin-glazed, brightly colored surfaces that imitated precious stones, evolving through Mediterranean cultures such as the Greeks and Romans. Earthenware dates back to prehistoric times, with simple, unglazed clay vessels shaped by hand or wheel, fundamental to early agricultural societies worldwide. Over centuries, faience developed into a sophisticated art form with complex glazing techniques, while earthenware remained a widespread, versatile material for everyday utilitarian pottery.
Key Material Differences
Faience is a glazed non-clay ceramic material made primarily from quartz or sand mixed with a small amount of clay, characterized by its glassy surface created through a high-temperature glaze firing. Earthenware consists of porous clay fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a more porous and less durable body that often requires a glaze for waterproofing. The key material difference lies in faience's silica-rich composition and vitrified glaze, while earthenware relies on natural clay with open pores and lower firing temperatures.
Firing Temperatures and Techniques
Faience pottery typically undergoes a firing process at higher temperatures ranging from 900degC to 1050degC, enabling a strong, vitrified body with a characteristic glossy, opaque glaze formed by silica and alkaline compounds. Earthenware is fired at lower temperatures, typically between 1000degC and 1150degC, resulting in a porous, less vitrified body that often requires a glaze to make it watertight. The firing techniques for Faience involve controlled oxidation to develop bright colors and a smooth surface, while earthenware firing allows for more variation in atmosphere, often producing a more rustic or matte finish.
Color and Surface Finish Comparison
Faience pottery is characterized by its vibrant, glossy glaze achieved through a high-temperature firing process that creates a smooth, glass-like surface, often in bright blues, greens, and turquoises. Earthenware typically features a matte or satin finish with more muted earth tones such as reds, browns, and ochres, resulting from lower firing temperatures and porous clay bodies. The color palette of faience is more vivid and reflective, while earthenware exhibits a natural, rustic appearance with a textured surface.
Strength and Durability Factors
Faience pottery, made from finely ground quartz with a vitreous glaze, offers superior strength and durability compared to earthenware, which is more porous and less resilient due to its lower firing temperature. Earthenware typically fires between 1,000degC and 1,150degC, resulting in a softer, more absorbent ceramic, while faience can withstand higher temperatures around 1,200degC, enhancing its hardness and resistance to chipping. The vitreous glaze on faience forms a glass-like surface that improves water resistance and structural integrity, making it more suitable for functional and decorative pottery that requires long-term durability.
Artistic and Decorative Applications
Faience pottery, known for its bright, glossy glaze created through tin oxide and other metallic compounds, offers vibrant colors and intricate patterns that enhance artistic and decorative applications. Earthenware, with its porous, unglazed texture and natural earthy tones, provides a rustic aesthetic favored for organic, handcrafted designs and matte finishes. Artists choose faience for detailed, colorful embellishments and earthenware for textured, naturalistic effects in their decorative pottery projects.
Practical Uses in Pottery
Faience pottery, characterized by its glossy, tin-glazed surface, is ideal for decorative and ceremonial objects due to its vibrant colors and smooth finish, but it is less durable for everyday use. Earthenware, being more porous and thicker, excels in practical applications like cooking pots, storage jars, and tableware where sturdiness and heat resistance are essential. Both materials serve distinct functions in pottery, with earthenware favored for utilitarian purposes and faience prized for ornamental craftsmanship.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Faience pottery, characterized by its lead-glazed surface, typically requires higher firing temperatures and includes chemical additives that can pose environmental hazards if not managed properly. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures and made from natural clay, generally has a smaller carbon footprint and is more biodegradable, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious artisans. Choosing earthenware over faience reduces energy consumption and minimizes the release of harmful substances, aligning better with environmentally responsible pottery practices.
Choosing Between Faience and Earthenware
Choosing between faience and earthenware for pottery depends on desired aesthetic and durability requirements. Faience offers a glazed, glossy finish with intricate designs, ideal for decorative pieces, while earthenware provides a more porous, rustic texture suited for functional, everyday use. Consider factors such as firing temperature, water absorption rate, and artistic style to select the appropriate ceramic material for your project.
Infographic: Faience vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com