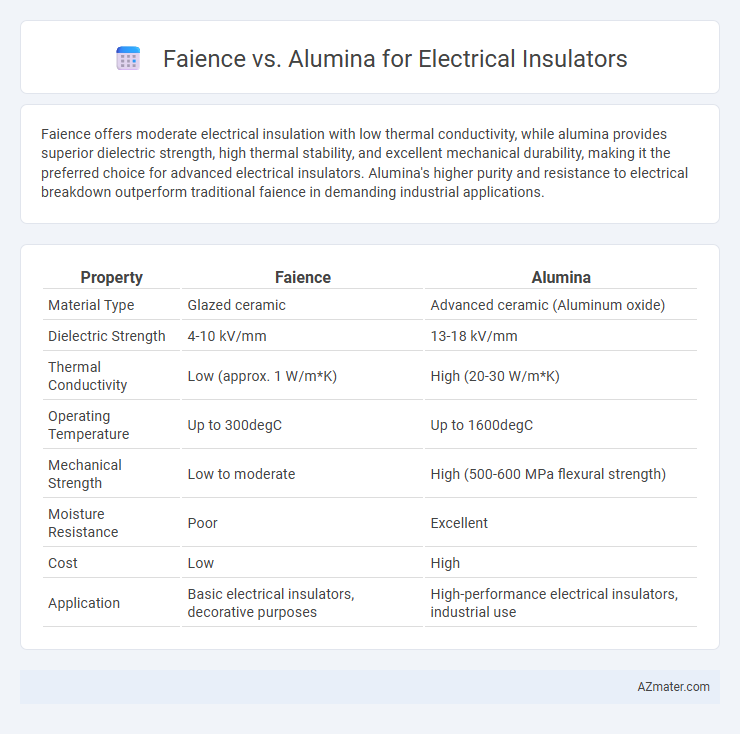
Faience offers moderate electrical insulation with low thermal conductivity, while alumina provides superior dielectric strength, high thermal stability, and excellent mechanical durability, making it the preferred choice for advanced electrical insulators. Alumina's higher purity and resistance to electrical breakdown outperform traditional faience in demanding industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Faience | Alumina |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glazed ceramic | Advanced ceramic (Aluminum oxide) |
| Dielectric Strength | 4-10 kV/mm | 13-18 kV/mm |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (approx. 1 W/m*K) | High (20-30 W/m*K) |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 300degC | Up to 1600degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Low to moderate | High (500-600 MPa flexural strength) |
| Moisture Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Application | Basic electrical insulators, decorative purposes | High-performance electrical insulators, industrial use |
Introduction to Electrical Insulators
Electrical insulators are materials that inhibit the flow of electric current, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. Faience, a glazed non-clay ceramic, offers moderate insulating properties with aesthetic appeal, while alumina (aluminum oxide) is a high-performance ceramic known for superior dielectric strength, thermal stability, and mechanical robustness. Alumina's excellent electrical resistivity and heat resistance make it a preferred choice in demanding industrial electrical insulation applications over faience.
Overview of Faience as an Insulator Material
Faience is a glazed ceramic material known for its excellent electrical insulating properties due to its high resistivity and low dielectric loss. Its composition, primarily silica with alkaline fluxes, provides durability and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for electrical insulators in moderate voltage applications. Compared to alumina, faience offers good mechanical strength but lower thermal conductivity and dielectric strength, limiting its use in high-temperature or high-voltage environments.
Alumina: Properties and Applications in Insulation
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, exhibits exceptional electrical insulation properties due to its high dielectric strength, excellent thermal conductivity, and outstanding chemical stability, making it a preferred material for high-performance electrical insulating components. Its mechanical robustness and resistance to moisture and corrosion outperform faience, which is prone to brittleness and lower thermal resistance. Applications of alumina in electrical insulation include substrates for electronic circuits, insulators in high-voltage equipment, and components in microelectronic devices where reliability and durability are critical.
Material Composition: Faience vs Alumina
Faience is composed primarily of glazed ceramic materials with a mixture of silica, alkali, and lime, providing moderate electrical insulation properties. Alumina, or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), consists of a dense crystalline structure offering superior thermal conductivity, high dielectric strength, and excellent electrical insulation performance. The high purity and mechanical strength of alumina make it a preferred material in advanced electrical insulators over the more porous and less durable faience.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Faience, made primarily from glazed ceramic materials, exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to alumina, which is a highly dense and robust ceramic oxide known for its superior hardness and fracture toughness. Alumina's mechanical strength typically ranges from 300 to 600 MPa in flexural strength, significantly outperforming faience, which often demonstrates brittleness and lower load-bearing capacity. This difference makes alumina the preferred choice for electrical insulators requiring high mechanical durability and resistance to mechanical stress.
Electrical Performance and Reliability
Faience offers moderate electrical insulation properties but exhibits lower dielectric strength and higher susceptibility to moisture absorption compared to alumina. Alumina demonstrates superior electrical performance with high dielectric strength, excellent insulation resistance, and exceptional thermal stability, resulting in enhanced reliability in demanding electrical environments. The high pureness and density of alumina minimize conductivity variations, ensuring consistent performance in high-voltage and high-temperature applications.
Thermal Stability and Resistance
Faience, a glazed ceramic material, exhibits moderate thermal stability and resistance, making it suitable for low to medium temperature electrical insulation. Alumina, a highly crystalline oxide ceramic, offers superior thermal stability withstanding temperatures above 1700degC and exceptional resistance to electrical and thermal stress. The enhanced thermal conductivity and robustness of alumina ensure reliable performance in high-temperature and high-voltage insulation applications compared to faience.
Cost Analysis: Faience vs Alumina
Faience offers a lower initial material cost compared to alumina, making it a budget-friendly option for basic electrical insulators, but it typically exhibits higher wear and lower durability, increasing long-term maintenance expenses. Alumina, although more expensive upfront due to its superior mechanical strength, high dielectric strength, and thermal stability, delivers enhanced longevity and reduced replacement frequency, resulting in better cost-effectiveness over the product lifecycle. When analyzing total cost of ownership, alumina's robust performance properties justify the higher initial investment for critical or high-performance electrical insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Faience, a ceramic material composed mainly of quartz and feldspar, has a lower environmental footprint due to its natural raw materials and lower energy consumption in production compared to alumina, which requires high-temperature processing and bauxite mining. Alumina, derived from bauxite ore, contributes to significant environmental degradation and energy-intensive refining processes, influencing its sustainability negatively. Faience also offers better biodegradability and less toxic waste generation, making it a more environmentally sustainable choice for electrical insulators in applications prioritizing ecological considerations.
Choosing the Right Insulator Material
Faience, a glazed ceramic material, offers moderate electrical insulation but lacks the high dielectric strength and thermal stability of alumina, making it less suitable for high-voltage or high-temperature applications. Alumina, with its excellent electrical insulation properties, high mechanical strength, and thermal resistance up to 1700degC, is the preferred choice for advanced electrical insulators in demanding environments. Choosing the right insulator material depends on the application's voltage requirements, thermal conditions, and mechanical stresses, where alumina generally outperforms faience in reliability and longevity.
Infographic: Faience vs Alumina for Electrical Insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com