Enamel tiles offer a durable, glass-like coating that resists stains and scratches, making them ideal for high-traffic areas. Porcelain tiles provide superior hardness and water resistance due to their dense composition, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Table of Comparison
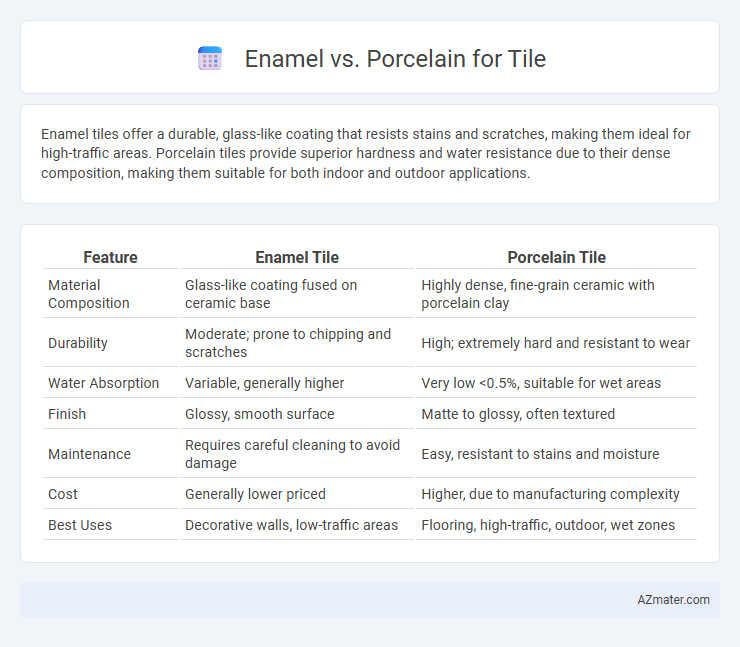
| Feature | Enamel Tile | Porcelain Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass-like coating fused on ceramic base | Highly dense, fine-grain ceramic with porcelain clay |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chipping and scratches | High; extremely hard and resistant to wear |
| Water Absorption | Variable, generally higher | Very low <0.5%, suitable for wet areas |
| Finish | Glossy, smooth surface | Matte to glossy, often textured |
| Maintenance | Requires careful cleaning to avoid damage | Easy, resistant to stains and moisture |
| Cost | Generally lower priced | Higher, due to manufacturing complexity |
| Best Uses | Decorative walls, low-traffic areas | Flooring, high-traffic, outdoor, wet zones |
Introduction to Enamel and Porcelain Tiles
Enamel tiles feature a glassy coating fused to a ceramic base, offering vibrant colors and a durable, scratch-resistant surface ideal for both walls and floors. Porcelain tiles, made from highly refined clay fired at higher temperatures, provide exceptional density, low porosity, and enhanced strength, making them suitable for high-traffic areas and outdoor use. Both enamel and porcelain tiles deliver aesthetic appeal and functional benefits but differ in manufacturing process, composition, and performance characteristics.
Key Differences Between Enamel and Porcelain Tiles
Enamel tiles feature a glassy, colored coating fused onto a base material, offering vibrant colors and glossy finishes, while porcelain tiles are made from dense, refined clay fired at high temperatures for superior durability and water resistance. Porcelain tiles exhibit higher hardness and lower porosity compared to enamel tiles, making them ideal for high-traffic and moisture-prone areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Enamel tiles provide more design variety and color intensity but may chip more easily, whereas porcelain tiles offer long-lasting strength and require less maintenance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Enamel tiles are made by fusing powdered glass to a metal base through high-temperature firing, creating a smooth, durable surface resistant to stains and scratches. Porcelain tiles consist of a fine, dense ceramic clay mixture that is fired at higher temperatures than traditional ceramics, resulting in a hard, moisture-resistant material. The manufacturing process of porcelain involves pressing and firing at approximately 1,200-1,400degC, whereas enamel requires coating metal substrates with glass powder before firing around 800-900degC.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Porcelain tiles demonstrate superior durability and strength compared to enamel tiles, with a higher density and reduced porosity that enhances resistance to cracks and chips under heavy foot traffic. Enamel tiles, while offering a vibrant glossy finish, tend to be more prone to surface scratching and chipping due to a thinner glaze layer. Porcelain's hardness rating on the Mohs scale typically ranges from 6 to 7, outperforming enamel tiles, which generally rate lower, making porcelain ideal for high-impact and commercial flooring applications.
Aesthetic Options and Design Versatility
Enamel tiles offer vibrant color options and glossy finishes, making them ideal for bold, artistic designs with a smooth, reflective surface. Porcelain tiles provide exceptional design versatility through their ability to mimic natural materials like stone and wood, with varied textures and matte or polished finishes. Both materials support diverse aesthetic choices, but porcelain's durability and extensive pattern options make it preferred for both contemporary and traditional interiors.
Water Resistance and Maintenance Requirements
Enamel tiles offer moderate water resistance due to their glazed surface, making them suitable for areas with occasional moisture but requiring regular sealing to prevent water damage. Porcelain tiles provide superior water resistance as they are denser and less porous, ensuring minimal water absorption and enhanced durability in wet environments. Maintenance for enamel tiles involves careful cleaning to avoid glaze damage, while porcelain requires less frequent sealing and is easier to clean due to its dense composition.
Cost Analysis: Enamel vs Porcelain Tiles
Enamel tiles generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to porcelain tiles, making them a budget-friendly choice for residential projects. Porcelain tiles, while more expensive initially, provide superior durability and resistance to wear, often resulting in lower long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. The overall cost analysis favors enamel tiles for short-term budgets, whereas porcelain tiles deliver better value through enhanced longevity and performance in high-traffic areas.
Ideal Applications for Enamel Tiles
Enamel tiles are ideal for areas requiring durability and vibrant color retention, such as kitchen backsplashes and bathroom walls, due to their resistance to stains and water. Their smooth, glossy surface enhances hygiene, making them perfect for hospitals and commercial spaces. Enamel tiles also perform well in moderate foot traffic zones, offering an affordable, low-maintenance alternative to porcelain without compromising on aesthetic appeal.
Best Uses for Porcelain Tiles
Porcelain tiles offer exceptional durability and water resistance, making them ideal for high-traffic areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and commercial spaces. Their dense composition provides superior stain resistance compared to enamel tiles, ensuring long-lasting beauty and easy maintenance. Porcelain's versatility allows for a wide range of designs and finishes, perfectly suited for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Choosing the Right Tile: Factors to Consider
When choosing between enamel and porcelain tiles, consider durability, water resistance, and maintenance requirements; porcelain offers superior hardness and low porosity, making it ideal for high-traffic or wet areas. Enamel tiles provide vibrant colors and a glossy finish but may chip more easily under heavy use. Prioritize the tile's intended location, expected wear, and aesthetic preferences for optimal functionality and design harmony.
Infographic: Enamel vs Porcelain for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com