Ceramic resin offers flexibility and esthetic advantages in dental implants, while zirconia provides superior strength and biocompatibility for long-lasting durability. Zirconia's high fracture resistance and low plaque affinity make it a preferred choice for patients seeking metal-free, durable dental implants.
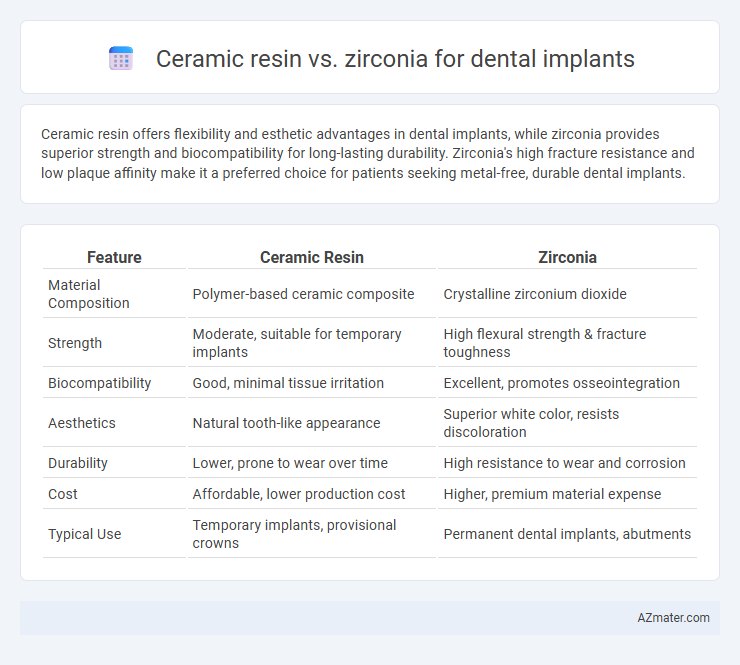
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Resin | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymer-based ceramic composite | Crystalline zirconium dioxide |
| Strength | Moderate, suitable for temporary implants | High flexural strength & fracture toughness |
| Biocompatibility | Good, minimal tissue irritation | Excellent, promotes osseointegration |
| Aesthetics | Natural tooth-like appearance | Superior white color, resists discoloration |
| Durability | Lower, prone to wear over time | High resistance to wear and corrosion |
| Cost | Affordable, lower production cost | Higher, premium material expense |
| Typical Use | Temporary implants, provisional crowns | Permanent dental implants, abutments |
Introduction to Dental Implant Materials
Dental implant materials primarily include ceramic resin and zirconia, each offering distinct benefits for biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal. Ceramic resin provides a tooth-like appearance with flexibility but may have lower strength and wear resistance compared to zirconia. Zirconia, known for its exceptional durability and fracture resistance, is favored in dental implants for its ability to integrate well with bone and resist corrosion, making it a long-lasting choice for restorative dentistry.
Overview of Ceramic Resins in Dentistry
Ceramic resins in dentistry offer a versatile and esthetic alternative for dental restorations, combining the natural appearance of ceramics with the flexibility of resin materials. These composites provide excellent bonding capabilities and wear resistance, making them suitable for crowns, veneers, and bridges. Compared to zirconia, ceramic resins allow easier intraoral adjustments and better shading options, though zirconia remains superior in strength and long-term durability for implant frameworks.
Understanding Zirconia in Dental Implants
Zirconia in dental implants offers superior biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal compared to ceramic resin, making it an ideal choice for patients seeking metal-free solutions. Its high fracture toughness and resistance to corrosion ensure long-term durability in the oral environment. Clinically, zirconia implants demonstrate excellent osseointegration, promoting stable bone integration and reducing the risk of peri-implantitis.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Zirconia dental implants exhibit superior strength and durability due to their high fracture toughness and resistance to wear, making them ideal for long-term load-bearing applications. Ceramic resin implants, while aesthetically pleasing and biocompatible, generally have lower mechanical strength and may be more prone to microcracks and wear under sustained stress. Clinical studies indicate zirconia implants outperform ceramic resin in maintaining structural integrity and longevity in demanding oral environments.
Esthetic Benefits: Ceramic Resin vs. Zirconia
Ceramic resin offers superior esthetic benefits in dental implants with its excellent translucency and color-matching capabilities, closely mimicking natural tooth enamel. Zirconia provides high strength and durability but can sometimes appear more opaque and less natural compared to ceramic resin. For patients prioritizing esthetics, ceramic resin often achieves a more life-like, seamless integration with surrounding teeth.
Biocompatibility and Safety Factors
Ceramic resin dental implants offer superior biocompatibility by minimizing allergic reactions and promoting better integration with gum tissue compared to traditional materials. Zirconia implants are highly biocompatible as well, featuring strong resistance to corrosion and bacterial adhesion, which enhances safety in the oral environment. Both materials reduce the risk of inflammation and peri-implantitis, but zirconia's proven durability and inert properties make it a preferred choice for long-term implant success.
Clinical Applications and Suitability
Ceramic resin offers excellent aesthetics and biocompatibility, making it suitable for front teeth restorations and patients with metal sensitivities. Zirconia implants provide superior strength and durability, ideal for posterior restorations and areas with high masticatory forces. Both materials demonstrate low plaque affinity, but zirconia exhibits better osseointegration and long-term clinical success in implantology.
Longevity and Maintenance Needs
Ceramic resin dental implants typically offer moderate longevity, lasting approximately 10-15 years with proper care, but they may require more frequent maintenance due to their susceptibility to wear and discoloration. Zirconia implants provide superior durability, often lasting 20 years or more, with high resistance to corrosion and fracture, minimizing long-term maintenance compared to ceramic resin. Maintenance needs for zirconia involve routine dental hygiene and occasional professional evaluations, while ceramic resin demands more vigilant cleaning to prevent staining and structural degradation.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Ceramic resin dental implants typically offer a lower upfront cost compared to zirconia implants, making them more affordable for budget-conscious patients. Zirconia implants, while more expensive, provide superior durability and longer lifespan, which can reduce replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating both initial costs and long-term value is essential for determining the most cost-effective dental implant option.
Making the Right Choice for Dental Implants
Ceramic resin and zirconia are two popular materials used for dental implants, with zirconia offering superior biocompatibility, strength, and aesthetic appeal due to its tooth-like color and resistance to corrosion. Ceramic resin, while more affordable and easier to manipulate, lacks the durability and longevity that zirconia provides, making it less ideal for patients seeking long-term solutions. Selecting the right dental implant material requires evaluating patient-specific factors such as bone density, potential allergies, and desired cosmetic outcomes, where zirconia often emerges as the preferred choice for optimal integration and durability.
Infographic: Ceramic resin vs Zirconia for Dental implant
 azmater.com
azmater.com