Ceramic coatings provide a protective layer with high chemical resistance and thermal stability for kiln furniture, enhancing durability during high-temperature firing. Mullite, a dense aluminosilicate ceramic, offers exceptional mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for structural kiln components.
Table of Comparison
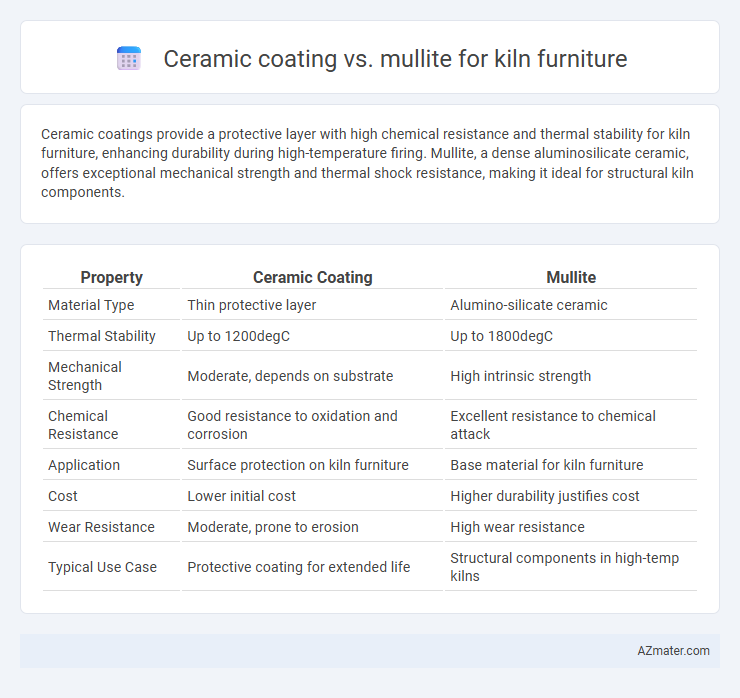
| Property | Ceramic Coating | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thin protective layer | Alumino-silicate ceramic |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, depends on substrate | High intrinsic strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oxidation and corrosion | Excellent resistance to chemical attack |
| Application | Surface protection on kiln furniture | Base material for kiln furniture |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher durability justifies cost |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate, prone to erosion | High wear resistance |
| Typical Use Case | Protective coating for extended life | Structural components in high-temp kilns |
Introduction to Kiln Furniture Materials
Kiln furniture materials such as ceramic coatings and mullite play a crucial role in withstanding extreme temperatures and thermal stress during firing processes. Mullite, a high-alumina silicate mineral, offers excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for prolonged exposure to kiln heat. Ceramic coatings enhance surface durability, resist chemical attack, and improve lifespan by forming protective layers on kiln furniture components.
Overview of Ceramic Coating
Ceramic coating for kiln furniture provides a high-temperature resistant barrier that enhances durability and extends the service life of the components by reducing wear and corrosion. It improves thermal insulation, allowing for better heat retention and energy efficiency in kiln operations, while also preventing adherence of molten materials. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, is often used as a base material, but ceramic coatings applied over mullite offer superior protection against thermal shock and chemical attack.
Understanding Mullite: Properties and Uses
Mullite is a highly refractory ceramic material characterized by excellent thermal stability, low thermal expansion, and strong mechanical strength, making it ideal for kiln furniture in high-temperature applications. Its chemical composition, primarily 3Al2O3*2SiO2, ensures resistance to thermal shock and corrosion from molten glass or metal, outperforming many other ceramic coatings. Commonly used in kiln shelves, setters, and supports, mullite maintains structural integrity and dimensional stability during prolonged exposure to temperatures exceeding 1600degC, enhancing the durability and performance of industrial kilns.
Thermal Performance: Ceramic Coating vs Mullite
Ceramic coatings offer superior thermal insulation and lower thermal conductivity compared to mullite, enhancing kiln furniture's heat resistance and energy efficiency. Mullite provides excellent thermal shock resistance and stability at high temperatures but has higher thermal conductivity than ceramic coatings. Choosing ceramic coatings improves heat retention and reduces energy consumption, while mullite ensures durability during rapid temperature fluctuations.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Ceramic coatings enhance kiln furniture by providing a protective barrier that increases resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, significantly extending the lifespan of the underlying material. Mullite, a high-temperature ceramic with excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength, offers superior durability under repeated firing cycles and high-temperature conditions. Compared to ceramic coatings, mullite kiln furniture generally exhibits longer service life due to its inherent material properties, reducing maintenance and replacement frequency in industrial kiln operations.
Resistance to Thermal Shock
Ceramic coating enhances kiln furniture by providing a protective layer that improves resistance to thermal shock through reduced surface cracking and enhanced durability at high temperatures. Mullite, a refractory material with excellent thermal stability, inherently resists thermal shock due to its low thermal expansion and high mechanical strength under rapid temperature changes. Comparing both, ceramic coatings add a supplementary protective barrier, while mullite's intrinsic properties offer robust thermal shock resistance crucial for maintaining kiln furniture integrity during extreme heating cycles.
Surface Quality and Reactivity
Ceramic coating on kiln furniture enhances surface smoothness and reduces particle adherence, resulting in superior fired product quality. Mullite, a robust aluminosilicate, offers excellent thermal stability but may exhibit higher surface roughness leading to potential contamination risks. The inertness of ceramic coatings minimizes chemical reactivity with kiln atmospheres, whereas mullite's reactive sites can interact with fluxes, affecting the kiln furniture's longevity and surface integrity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ceramic coatings on kiln furniture typically involve higher upfront costs due to specialized materials and application processes but offer extended lifespan and improved thermal efficiency, reducing long-term expenses. Mullite, known for its excellent thermal stability and lower material cost, provides a cost-effective solution with moderate durability but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including downtime and replacement frequency, is critical for economic decision-making between ceramic-coated and mullite kiln furniture.
Suitability for Various Firing Environments
Ceramic coating enhances kiln furniture by providing a protective barrier against thermal shock and chemical reactions during high-temperature firings, making it suitable for environments with fluctuating temperatures and aggressive atmospheres. Mullite, with its excellent thermal stability and low thermal expansion, excels in consistent high-temperature firings typical in ceramics and glass industries, offering durability under prolonged heat exposure. Selecting between ceramic coating and mullite depends on firing conditions: ceramic coating is ideal for variable and chemically active environments, while mullite suits stable, extreme high-temperature applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Kiln Furniture
Selecting the right material for kiln furniture hinges on balancing thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance. Ceramic coatings enhance kiln furniture by providing a protective barrier that resists oxidation and chemical attack, extending the lifespan of mullite substrates known for their excellent thermal shock resistance and high melting point around 1840degC. Mullite's inherent durability coupled with tailored ceramic coatings optimizes performance in high-temperature environments, offering superior longevity and reduced maintenance costs for industrial kilns.
Infographic: Ceramic coating vs Mullite for Kiln furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com