Brick crockery offers a rustic aesthetic and superior thermal insulation due to its porous texture, while stoneware provides enhanced durability, chip resistance, and non-porous surface ideal for everyday use. Stoneware's vitrification process creates a dense, glass-like finish, making it more hygienic and dishwasher safe compared to brick crockery.
Table of Comparison
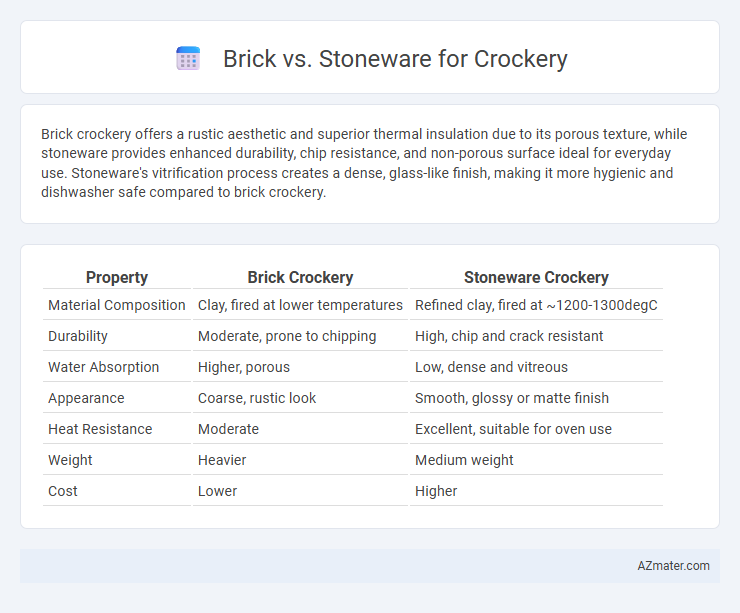
| Property | Brick Crockery | Stoneware Crockery |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clay, fired at lower temperatures | Refined clay, fired at ~1200-1300degC |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to chipping | High, chip and crack resistant |
| Water Absorption | Higher, porous | Low, dense and vitreous |
| Appearance | Coarse, rustic look | Smooth, glossy or matte finish |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate | Excellent, suitable for oven use |
| Weight | Heavier | Medium weight |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Brick and Stoneware Crockery
Brick crockery, typically made from red clay and fired at lower temperatures, offers a rustic and porous surface ideal for traditional cooking and serving. Stoneware crockery is crafted from denser, non-porous clay fired at higher temperatures, resulting in durable, chip-resistant dishes that retain heat well. Both materials provide unique aesthetic and functional benefits, with brick favoring artisanal appeal and stoneware emphasizing strength and versatility.
Material Composition: Brick vs Stoneware
Brick crockery is typically composed of clay mixed with sand and fired at lower temperatures, resulting in a porous and less vitrified material. Stoneware, made from denser clay fired at higher temperatures between 1,100degC and 1,300degC, achieves a non-porous, durable, and vitrified finish suited for tableware. The higher firing temperature and composition of stoneware provide enhanced strength and resistance to chipping compared to brick crockery.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Stoneware offers superior durability for crockery due to its dense, non-porous composition, resisting chipping and cracking under regular use and temperature changes. Brick crockery, while aesthetically rustic, tends to be less durable, as the material is more porous and susceptible to wear and breakage over time. Longevity favors stoneware, making it ideal for everyday use in both domestic kitchens and commercial settings.
Heat Retention and Cooking Performance
Stoneware offers superior heat retention compared to brick, maintaining consistent temperatures essential for even cooking and slow heat distribution. Its dense, non-porous surface ensures efficient moisture retention, enhancing flavor and preventing food from drying out. Brick, while durable and rustic in appearance, tends to have less uniform heat conduction, making it less ideal for precision cooking or prolonged heat exposure.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Stoneware offers a wide range of colors, textures, and finishes that enhance the aesthetic appeal of crockery, making it a versatile choice for both rustic and modern designs. Brick crockery, characterized by its earthy tones and rugged texture, lends a natural and handmade look ideal for traditional or farmhouse-style table settings. The variety in glazing techniques for stoneware allows for detailed patterns and vibrant designs, while brick crockery often emphasizes organic imperfections, providing unique charm.
Maintenance and Cleaning Guide
Stoneware offers superior durability and ease of cleaning compared to brick crockery due to its non-porous surface that resists stains and odors. Brick crockery tends to be more porous, requiring gentle hand washing and avoiding prolonged soaking to prevent damage and retain its natural texture. Regular maintenance of stoneware involves simple wiping or dishwasher-safe cleaning, while brick demands careful drying and occasional seasoning to maintain its integrity.
Cost Analysis: Brick vs Stoneware
Brick crockery generally incurs lower initial production costs due to the abundance and affordability of clay materials, making it a budget-friendly option for everyday use. Stoneware, made from denser clay and fired at higher temperatures, demands more energy and time, resulting in a higher price point but greater durability and chip resistance. Cost analysis reveals brick crockery suits cost-conscious consumers, while stoneware justifies its premium price with enhanced longevity and aesthetic appeal.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Stoneware crockery tends to be more eco-friendly due to its natural clay composition, high durability, and lower firing temperatures compared to traditional brick-based ceramics. The sustainable production process of stoneware minimizes resource consumption and waste, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Brick crockery, often less durable and requiring higher energy for manufacturing, generally has a larger carbon footprint and reduced lifespan.
Popular Uses in Modern Kitchens
Brick crockery is favored for its rustic, handcrafted appearance and durability, making it ideal for casual dining and decorative purposes in modern kitchens. Stoneware offers versatility with its dense, non-porous surface that resists chipping and retains heat well, popular for everyday dinnerware and oven-to-table use. Both materials excel in functionality, but stoneware's ease of maintenance and dishwasher compatibility make it a preferred choice for busy households.
Choosing the Best Crockery for Your Needs
Choosing the best crockery depends on durability, aesthetics, and intended use, with brick offering rustic, heavy-duty appeal and excellent heat retention, while stoneware provides versatility, chip resistance, and a smoother finish ideal for daily use. Stoneware crockery, fired at high temperatures, offers non-porous surfaces and superior resistance to scratches and stains, making it perfect for families or frequent entertainers. Brick crockery's earthy texture and sturdiness are preferred for heavy use in casual dining environments or for those seeking a natural, handcrafted look.
Infographic: Brick vs Stoneware for Crockery
 azmater.com
azmater.com