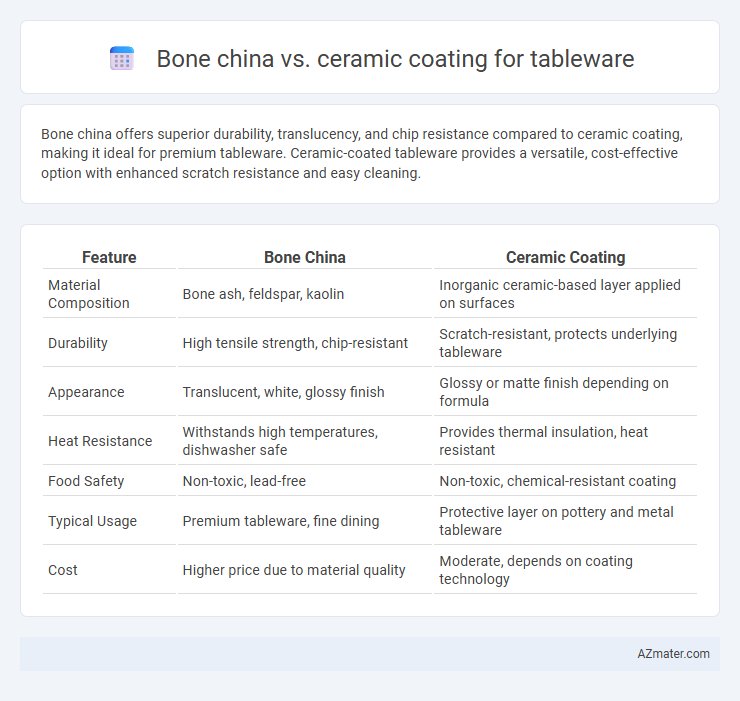
Bone china offers superior durability, translucency, and chip resistance compared to ceramic coating, making it ideal for premium tableware. Ceramic-coated tableware provides a versatile, cost-effective option with enhanced scratch resistance and easy cleaning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bone China | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Bone ash, feldspar, kaolin | Inorganic ceramic-based layer applied on surfaces |
| Durability | High tensile strength, chip-resistant | Scratch-resistant, protects underlying tableware |
| Appearance | Translucent, white, glossy finish | Glossy or matte finish depending on formula |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands high temperatures, dishwasher safe | Provides thermal insulation, heat resistant |
| Food Safety | Non-toxic, lead-free | Non-toxic, chemical-resistant coating |
| Typical Usage | Premium tableware, fine dining | Protective layer on pottery and metal tableware |
| Cost | Higher price due to material quality | Moderate, depends on coating technology |
Introduction to Bone China and Ceramic Coating
Bone china is a type of porcelain made from bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, known for its high whiteness, translucency, and strength. Ceramic coating, used in tableware, involves applying a durable, heat-resistant layer that enhances surface hardness and stain resistance. Both materials offer unique benefits in durability and aesthetics, with bone china prized for its delicate appearance and ceramic coating valued for its protective qualities.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Bone china consists of a refined mixture of bone ash, feldspar, and kaolin, giving it exceptional whiteness and translucency, whereas ceramic coatings are typically composed of silica, alumina, and titania used to enhance surface properties. Bone china undergoes a complex firing process at high temperatures, ensuring strength and delicate texture, while ceramic coatings are applied through techniques such as spraying or dipping and cured to create a durable, protective layer. The bone ash content in bone china contributes to its unique translucence and chip resistance, contrasting with ceramic coatings designed primarily for scratch and heat resistance on various substrates.
Visual Appeal and Aesthetic Differences
Bone china offers a delicate translucency and a smooth, glossy finish that enhances the visual appeal of tableware with its sophisticated, elegant look. Ceramic coatings provide a more varied aesthetic, featuring matte or glossy textures with vibrant colors and intricate patterns, catering to diverse design preferences. The refined whiteness and lightweight feel of bone china contrast with the durability and artistic versatility of ceramic-coated pieces, influencing their use in formal versus casual dining settings.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Bone china exhibits superior durability and strength compared to ceramic coatings due to its high proportions of bone ash, which enhance resistance to chipping and cracking. Ceramic coatings, while providing a hard, protective layer, can be prone to wear over time and may not offer the same impact resistance as bone china. The inherent toughness and density of bone china ensure prolonged longevity for tableware subjected to frequent use and thermal stress.
Weight and Handling Experience
Bone china tableware is lighter and thinner than ceramic coating alternatives, offering enhanced ease of handling and a more delicate feel. Ceramic-coated tableware tends to be heavier due to the added coating layer, which can affect comfort during extended use. The lightweight nature of bone china contributes to a refined dining experience with less strain on the hands.
Heat Resistance and Temperature Tolerance
Bone china exhibits superior heat resistance and can tolerate temperatures up to 1,200degC, making it ideal for tableware exposed to high-temperature environments like ovens and microwaves. Ceramic coatings offer moderate heat resistance, generally withstanding temperatures between 600degC and 900degC, which suits everyday use but may degrade under extreme heat. The enhanced durability and thermal stability of bone china provide better resistance to thermal shock and maintain structural integrity under rapid temperature changes.
Safety and Food Compatibility
Bone china is renowned for its high calcium phosphate content, making it non-toxic, lead-free, and safe for food use, while ceramic coatings provide a durable, non-reactive surface that resists scratches and chemicals. Both materials are FDA-approved for food contact, but bone china offers superior resistance to chipping and thermal shock, reducing contamination risks. Ceramic coatings may require careful maintenance to avoid degradation that could lead to potential leaching of substances, whereas bone china's dense composition ensures long-term safety and food compatibility.
Maintenance: Cleaning and Stain Resistance
Bone china offers superior stain resistance and requires gentle cleaning with mild detergents and soft sponges to maintain its delicate glaze and translucency. Ceramic-coated tableware provides a durable, non-porous surface that resists stains and is typically dishwasher safe, allowing for more straightforward maintenance and stronger abrasion resistance. Both materials benefit from avoiding harsh chemicals and abrasive scrubbers to preserve their finish and longevity.
Cost and Value for Money
Bone china offers a higher initial cost due to its refined composition and translucent appearance, but it provides exceptional durability and a luxurious aesthetic, enhancing long-term value for special occasions. Ceramic coatings, while more affordable upfront, deliver considerable scratch resistance and ease of maintenance, making them a practical choice for everyday use. Evaluating both options involves balancing bone china's premium quality against ceramic coating's cost-effective resilience, depending on user priorities and frequency of use.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Bone china is made from a mixture of bone ash, kaolin, and feldspar, offering durability with a lower firing temperature that reduces energy consumption compared to traditional ceramics. Ceramic coatings involve applying a silica-based layer to various substrates, enhancing scratch resistance and longevity but often require high-temperature kilns, increasing carbon emissions. Evaluating sustainability, bone china's biodegradability and longer lifespan contribute to reduced waste, while ceramic coatings' synthetic components and energy-intensive production pose greater environmental challenges.
Infographic: Bone china vs Ceramic coating for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com