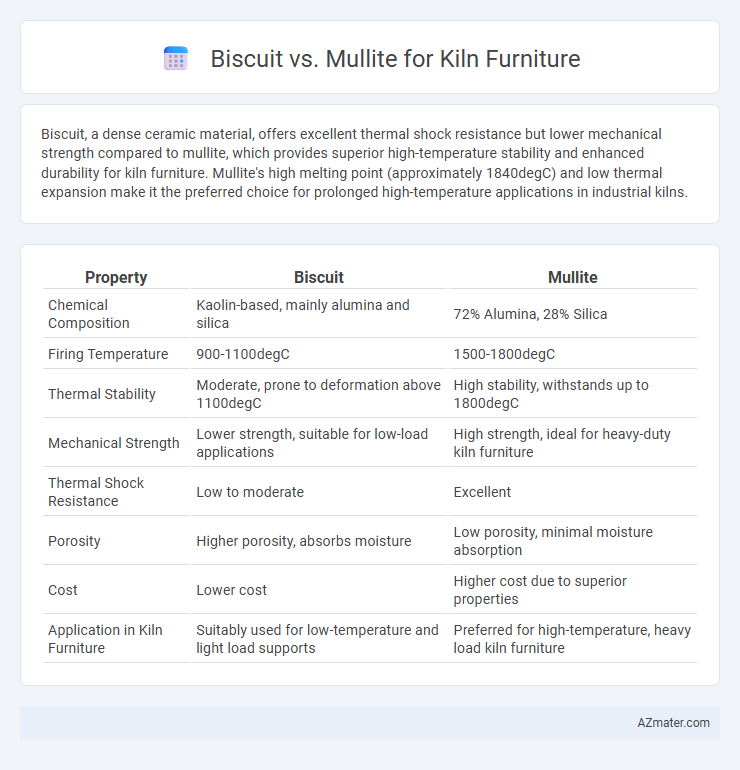
Biscuit, a dense ceramic material, offers excellent thermal shock resistance but lower mechanical strength compared to mullite, which provides superior high-temperature stability and enhanced durability for kiln furniture. Mullite's high melting point (approximately 1840degC) and low thermal expansion make it the preferred choice for prolonged high-temperature applications in industrial kilns.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Biscuit | Mullite |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Kaolin-based, mainly alumina and silica | 72% Alumina, 28% Silica |
| Firing Temperature | 900-1100degC | 1500-1800degC |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, prone to deformation above 1100degC | High stability, withstands up to 1800degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower strength, suitable for low-load applications | High strength, ideal for heavy-duty kiln furniture |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Low to moderate | Excellent |
| Porosity | Higher porosity, absorbs moisture | Low porosity, minimal moisture absorption |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to superior properties |
| Application in Kiln Furniture | Suitably used for low-temperature and light load supports | Preferred for high-temperature, heavy load kiln furniture |
Introduction: Understanding Kiln Furniture Materials
Biscuit and mullite are essential materials for kiln furniture, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties suited for high-temperature applications. Biscuit, a type of dense fireclay, provides excellent thermal shock resistance and affordability, while mullite excels in strength and thermal stability at temperatures above 1600degC. Selecting the appropriate material depends on specific kiln conditions, including maximum operating temperature and load-bearing requirements.
What is Biscuit Kiln Furniture?
Biscuit kiln furniture consists of ceramic components made from high-quality refractory materials designed to support and separate ceramic wares during the biscuit firing stage. These pieces provide excellent thermal stability and resistance to warping under high temperatures typically between 900degC and 1100degC, ensuring even heat distribution and minimal deformation. Compared to mullite, biscuit kiln furniture is often tailored for lower firing temperatures and offers a more cost-effective solution for initial bisque firings.
What is Mullite Kiln Furniture?
Mullite kiln furniture is composed of a high-purity alumino-silicate ceramic known for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures up to 1750degC. Unlike traditional biscuit kiln furniture, mullite provides superior strength, reduced thermal expansion, and enhanced chemical inertness, making it ideal for demanding firing processes. Its durability and ability to maintain dimensional stability under thermal stress significantly improve kiln efficiency and lifespan.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Biscuit kiln furniture is primarily composed of high-alumina clay combined with kaolin and fireclay, offering moderate thermal resistance due to its porous structure formed through low-temperature firing. Mullite kiln furniture consists mainly of synthetic mullite crystals (3Al2O3*2SiO2) produced via high-temperature sintering or sol-gel processing, resulting in superior thermal stability and mechanical strength. The manufacturing process of mullite involves controlled crystallization to enhance resistance against thermal shock and deformation, whereas biscuit materials are typically shaped by pressing and fired at lower temperatures for cost-effectiveness.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Biscuit kiln furniture exhibits moderate thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications requiring gradual heat distribution and thermal shock resistance. Mullite, with superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion coefficient, provides enhanced durability at high temperatures, resulting in better dimensional stability and longer service life in extreme firing conditions. The choice between biscuit and mullite depends on specific kiln operating temperatures and required thermal efficiency for optimized ceramic processing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Mullite kiln furniture exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to biscuit ware, making it more resistant to high-stress environments within kilns. Its enhanced durability allows it to withstand repeated thermal cycles and resist deformation over extended periods. This makes mullite the preferred choice for high-temperature applications requiring long-lasting structural integrity.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Biscuits made from low-fire clays are significantly lighter than mullite kiln furniture, reducing strain during handling and making them ideal for manual loading and unloading. Mullite, composed primarily of aluminum silicate, offers higher density and durability but can be cumbersome due to its heavier weight, impacting ease of transport and positioning within the kiln. For applications requiring frequent repositioning or lightweight support, biscuit kiln furniture presents a practical advantage over heavier mullite pieces.
Cost Analysis: Biscuit vs Mullite
Biscuit kiln furniture generally offers a lower initial cost compared to mullite, making it a budget-friendly option for short-term or low-temperature applications. Mullite, despite its higher upfront price, provides superior thermal stability and longer lifespan, reducing replacement frequency and overall maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors mullite for high-temperature and repeated-use scenarios where durability outweighs initial investment.
Suitability for Various Kiln Atmospheres
Biscuits made from high-alumina clay offer excellent resistance to oxidation atmospheres but can degrade in reducing environments due to limited chemical stability. Mullite kiln furniture provides superior thermal shock resistance and maintains structural integrity across both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres, making it ideal for diverse kiln applications. The high melting point of mullite (approximately 1840degC) ensures durability in high-temperature firing processes compared to biscuits, which typically soften above 900degC.
Choosing the Right Kiln Furniture for Your Application
Biscuit kiln furniture, made from high-strength refractory clay, offers excellent thermal shock resistance and is ideal for general ceramics firing where cost efficiency is important. Mullite kiln furniture, composed of 3Al2O3*2SiO2 crystals, provides superior mechanical strength, chemical stability, and higher temperature tolerance, making it suitable for advanced applications requiring prolonged high-temperature exposure or harsh environments. Selecting the right kiln furniture depends on the firing temperature, load weight, and chemical atmosphere--biscuit suits lower to medium temperatures, while mullite excels in high-temperature industrial settings.
Infographic: Biscuit vs Mullite for Kiln Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com