Yew veneer offers a dense, fine-grained texture with rich reddish-brown hues ideal for high-end furniture, while poplar veneer is lighter, with a pale yellow-green tone and a soft, uniform grain suited for budget-friendly, paint-grade applications. Yew provides superior durability and aesthetic appeal compared to the more economical and readily available poplar.
Table of Comparison
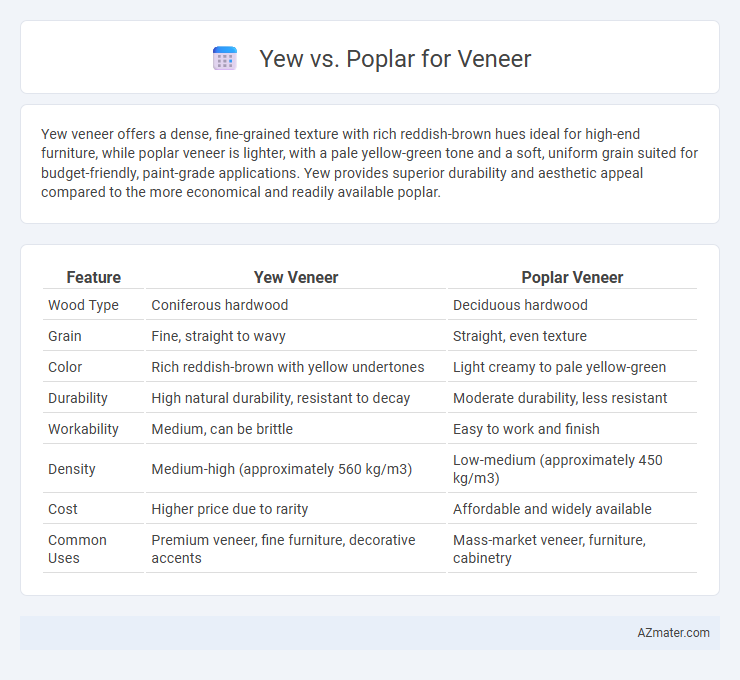
| Feature | Yew Veneer | Poplar Veneer |
|---|---|---|
| Wood Type | Coniferous hardwood | Deciduous hardwood |
| Grain | Fine, straight to wavy | Straight, even texture |
| Color | Rich reddish-brown with yellow undertones | Light creamy to pale yellow-green |
| Durability | High natural durability, resistant to decay | Moderate durability, less resistant |
| Workability | Medium, can be brittle | Easy to work and finish |
| Density | Medium-high (approximately 560 kg/m3) | Low-medium (approximately 450 kg/m3) |
| Cost | Higher price due to rarity | Affordable and widely available |
| Common Uses | Premium veneer, fine furniture, decorative accents | Mass-market veneer, furniture, cabinetry |
Introduction to Yew and Poplar Veneers
Yew veneer offers a warm, fine-grained texture with natural reddish-brown hues, prized for its durability and elegant appearance in high-end woodworking. Poplar veneer is a lightweight, pale wood with a smooth texture, commonly used for cost-effective furniture and cabinetry due to its ease of staining and consistent grain. Both veneers provide versatile options, with yew favored for luxury projects and poplar chosen for practical, budget-conscious applications.
Botanical Overview: Yew vs Poplar
Yew (Taxus spp.) is a coniferous tree known for its dense, fine-grained wood with a rich reddish-brown hue, making it prized for high-quality veneer applications. Poplar (Populus spp.) is a fast-growing deciduous hardwood characterized by a lighter color, soft texture, and uniform grain that facilitates easy machining and cost-effective veneer production. The botanical differences, with Yew's slow-growing evergreen nature versus Poplar's rapid growth as a hardwood, influence their respective wood densities, grain patterns, and suitability for decorative veneer uses.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Yew veneer showcases a rich, warm reddish-brown color with intricate, swirling grain patterns that create a visually striking and unique surface. Poplar veneer typically features a lighter, creamy to pale greenish-brown hue with a straight, uniform grain, offering a cleaner and more subtle aesthetic. Choosing between Yew and Poplar for veneer depends on the desired visual impact, with Yew delivering dramatic character and Poplar providing a smoother, understated look.
Color Variations in Yew and Poplar Veneers
Yew veneer showcases a rich spectrum of colors, ranging from warm golden hues to deep reddish-browns with striking grain patterns, making it highly valued for decorative applications. Poplar veneer, in contrast, typically features a more uniform pale cream to light greenish or brownish tone, offering a subtle and consistent appearance suitable for painted finishes. The pronounced color variation in yew enhances its aesthetic appeal, while poplar's even coloration supports versatile design needs.
Workability and Machining Differences
Yew veneer offers superior workability due to its fine, even grain, allowing for precise cutting and smooth finishes, which makes it ideal for intricate woodworking. Poplar veneer, being softer and more porous, is easier to machine but may require careful handling to avoid splintering and tear-out during cutting. The density and grain consistency of yew contribute to its higher durability in machining processes compared to the more flexible yet less stable poplar.
Durability and Strength Comparisons
Yew veneer offers superior durability and strength compared to poplar, making it ideal for high-stress applications and furniture that requires longevity. The dense grain structure of yew wood provides enhanced resistance to wear, impact, and deformation, whereas poplar is relatively softer and more prone to dents and scratches. For projects demanding a robust and lasting finish, yew veneer outperforms poplar by maintaining structural integrity over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Yew veneer is prized for its density and slow growth, resulting in a more sustainable option due to its long lifecycle and ability to sequester carbon effectively. Poplar veneer, characterized by rapid growth and widespread availability, offers a lower environmental footprint by promoting faster forest regeneration and reducing deforestation pressure. Both species provide eco-friendly choices, but Poplar's faster renewability often aligns better with sustainable forestry practices and carbon management goals.
Common Uses in Furniture and Interiors
Yew veneer is prized for its rich, warm tones and fine grain, making it ideal for high-end furniture, decorative panels, and intricate inlays in interior design. Poplar veneer offers a lighter, more uniform appearance often used in painted furniture, cabinetry, and modern minimalist interiors due to its smooth surface and cost-effectiveness. Both woods provide unique aesthetic qualities that suit specific styles, with yew emphasizing luxury and poplar favoring versatility and economy.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Yew veneer commands a higher price due to its limited availability and slower growth rates compared to poplar, which is more abundant and grows quickly, making it more cost-effective for large-scale projects. Poplar veneer is widely accessible in North America and Europe, offering an economical choice for budget-conscious applications, while yew is primarily sourced in Europe and Asia but remains rare and expensive. The cost disparity is influenced by yew's unique grain patterns and durability, which justify its premium, whereas poplar's widespread availability drives down prices and ensures consistent supply.
Choosing the Right Veneer: Yew or Poplar?
Yew veneer offers a distinctive, rich grain pattern with natural resilience, making it ideal for high-end furniture and decorative applications requiring durability and aesthetic elegance. Poplar veneer presents a smoother, more uniform texture with lighter coloration, suited for projects needing a cost-effective, easy-to-paint surface while maintaining reasonable strength. Selecting between Yew and Poplar veneer depends on balancing aesthetic preferences, budget constraints, and the desired finish for the final wood product.
Infographic: Yew vs Poplar for Veneer
 azmater.com
azmater.com