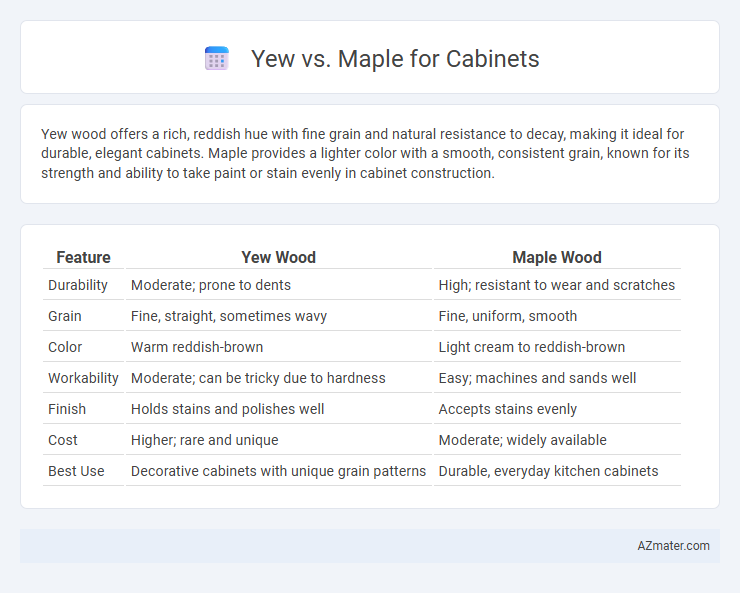
Yew wood offers a rich, reddish hue with fine grain and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for durable, elegant cabinets. Maple provides a lighter color with a smooth, consistent grain, known for its strength and ability to take paint or stain evenly in cabinet construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yew Wood | Maple Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Moderate; prone to dents | High; resistant to wear and scratches |
| Grain | Fine, straight, sometimes wavy | Fine, uniform, smooth |
| Color | Warm reddish-brown | Light cream to reddish-brown |
| Workability | Moderate; can be tricky due to hardness | Easy; machines and sands well |
| Finish | Holds stains and polishes well | Accepts stains evenly |
| Cost | Higher; rare and unique | Moderate; widely available |
| Best Use | Decorative cabinets with unique grain patterns | Durable, everyday kitchen cabinets |
Introduction to Yew and Maple Wood
Yew wood is prized for its fine grain, rich reddish-brown color, and natural resistance to decay, making it a durable choice for cabinetry. Maple wood features a light, creamy color with a smooth, consistent grain pattern that enhances its appeal in modern and traditional cabinet designs. Both woods offer strong hardness and workability, but Yew provides a unique aesthetic with its distinctive grain and warm tones, while Maple is valued for its versatility and ability to accept stains and finishes uniformly.
Botanical Origins and Growth Habits
Yew (Taxus spp.) is a slow-growing, evergreen conifer native to Europe, Asia, and North America, characterized by dense, fine-grained wood with rich reddish-brown hues, making it prized for detailed cabinetry. Maple (Acer spp.), a fast-growing deciduous hardwood primarily found in North America, features pale, creamy to reddish tones with a smooth, uniform grain that offers both durability and aesthetic versatility in cabinet construction. The contrasting growth habits--Yew's compact, slow growth versus Maple's rapid expansion--affect wood density and workability, influencing their respective suitability for fine furniture and cabinetry.
Appearance and Color Differences
Yew wood features a rich, warm reddish-brown color with intricate grain patterns that create a striking, natural aesthetic for cabinets. In contrast, Maple offers a lighter, creamy hue with a smooth, consistent grain, providing a modern and clean look ideal for various design styles. The color stability of Maple allows it to maintain its pale tone over time, while Yew's deeper hues may darken, adding character and depth to cabinetry.
Grain Patterns and Texture
Yew wood features a fine, straight grain with occasional knots, offering a smooth texture ideal for detailed cabinet work and a warm, reddish-brown hue. Maple presents a predominantly uniform, tight grain with a smooth texture that can be enhanced by its light, creamy color, making it highly versatile for cabinetry styles from modern to traditional. The distinct grain patterns of yew lend a rustic, natural appeal, while maple's consistent texture provides a clean, polished finish preferred for sleek cabinet designs.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Yew wood offers moderate strength with a Janka hardness rating around 1,540, making it suitable for cabinetry that requires a balance of durability and aesthetic appeal. Maple, particularly hard maple, boasts a higher Janka hardness of approximately 1,450 to 1,600, providing superior resistance to dents and wear over time. Both woods demonstrate good durability, but maple's denser grain structure typically results in longer-lasting cabinets under heavy use.
Workability and Ease of Machining
Yew wood offers excellent workability with its fine, straight grain, allowing for smooth cutting, shaping, and finishing, making it ideal for detailed cabinetry. Maple, known for its hardness and density, requires sharper tools and more effort to machine but provides a durable, stable surface that resists dents and scratches. Both woods respond well to sanding and finishing, but yew's softness makes it easier for intricate joinery, while maple's robustness ensures long-lasting cabinet performance.
Cost and Availability
Yew wood tends to be more expensive and less readily available compared to Maple, primarily due to its limited regional growth and slower harvesting rates. Maple is widely accessible in North America, resulting in lower prices and consistent supply, making it a cost-effective choice for cabinetry. The durability and fine grain of Maple also contribute to its popularity among cabinet makers seeking both quality and affordability.
Finish Compatibility and Maintenance
Yew wood offers a smooth, fine grain that accepts stains and finishes uniformly, resulting in a sleek, polished cabinet surface. Maple's dense, hard grain resists uneven absorption, requiring pre-treatment for consistent finish application but providing a durable and easy-to-maintain surface. Both woods benefit from regular cleaning and occasional refinishing to preserve their aesthetic appeal, but Maple's hardness typically offers superior resistance to scratches and dents over Yew.
Best Applications: Where Each Wood Excels
Yew wood excels in cabinets requiring intricate detailing and rich, warm tones, making it ideal for traditional or antique-style cabinetry with fine grain patterns that enhance decorative finishes. Maple is best suited for high-traffic areas due to its exceptional hardness and durability, offering a smooth, consistent grain that works well for modern, minimalist designs demanding resilience and easy maintenance. Both woods cater to different design priorities--Yew for aesthetic richness and Maple for structural strength and longevity.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Yew and Maple for Cabinets
Yew offers striking grain patterns and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for durable, decorative cabinets with a warm, reddish hue. Maple provides a smooth, consistent grain and excellent hardness, perfect for cabinetry requiring a clean, versatile appearance and resilience to daily wear. Choosing between yew and maple depends on whether you prioritize aesthetic richness and natural durability or uniformity and robust, long-lasting performance.
Infographic: Yew vs Maple for Cabinet
 azmater.com
azmater.com