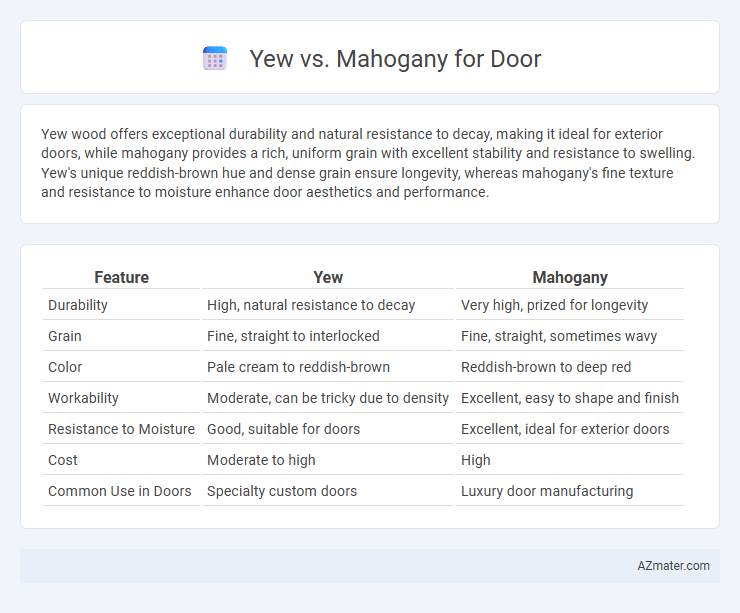
Yew wood offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for exterior doors, while mahogany provides a rich, uniform grain with excellent stability and resistance to swelling. Yew's unique reddish-brown hue and dense grain ensure longevity, whereas mahogany's fine texture and resistance to moisture enhance door aesthetics and performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Yew | Mahogany |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High, natural resistance to decay | Very high, prized for longevity |
| Grain | Fine, straight to interlocked | Fine, straight, sometimes wavy |
| Color | Pale cream to reddish-brown | Reddish-brown to deep red |
| Workability | Moderate, can be tricky due to density | Excellent, easy to shape and finish |
| Resistance to Moisture | Good, suitable for doors | Excellent, ideal for exterior doors |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Common Use in Doors | Specialty custom doors | Luxury door manufacturing |
Introduction to Yew and Mahogany Doors
Yew doors showcase a dense, fine-grained wood known for exceptional durability and distinctive warm tones, making them ideal for traditional or rustic door styles. Mahogany doors are prized for their rich reddish-brown color, smooth grain, and superior resistance to rot, offering a luxurious appearance suited for elegant architectural designs. Both woods provide high stability and longevity, but Yew emphasizes natural resilience while Mahogany highlights refined aesthetics and easy workability.
Botanical Origins and Characteristics
Yew wood, derived from the Taxus genus native to Europe and parts of Asia, is prized for its fine grain, durability, and rich reddish-brown color with subtle yellowish streaks. Mahogany, primarily from the Swietenia genus found in Central and South America, features a deep reddish-brown hue, straight grain, and excellent resistance to decay and insects, making it ideal for high-quality doors. Both woods offer unique botanical characteristics, with yew's dense, tough fibers contrasting mahogany's smooth texture and superior dimensional stability.
Appearance and Grain Patterns
Yew wood showcases a pale yellow to light brown color with subtle reddish hues, featuring fine, straight grains that create a smooth, consistent texture ideal for classic doors. Mahogany exhibits a rich, reddish-brown appearance with deep, flowing grain patterns that bring warmth and luxury to door designs. The contrasting grain complexity and color saturation make Yew suitable for understated elegance, while Mahogany offers a more dramatic and sophisticated aesthetic for high-end doors.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Yew wood exhibits excellent durability, especially in resisting decay and structural weakening, making it suitable for doors exposed to moisture. Mahogany is renowned for its superior strength and dense grain, providing robust resistance against impacts and warping over time. When comparing longevity, Mahogany generally outperforms Yew due to its higher natural oil content that enhances moisture resistance and overall durability in high-traffic door applications.
Resistance to Weather and Pests
Yew wood offers exceptional resistance to weathering and natural decay, making it highly durable for exterior doors exposed to varying climates. Mahogany is naturally resistant to pests like termites due to its dense grain structure, providing long-lasting protection against insect damage. Both woods provide robust defense, but Yew excels in moisture and rot resistance, while Mahogany leads in pest deterrence.
Workability and Ease of Fabrication
Yew wood offers excellent workability due to its fine grain and moderate hardness, making it easier to cut, shape, and sand compared to mahogany. Mahogany, while denser and harder than yew, machines well and holds details effectively but may require sharper tools and more effort during fabrication. Both woods provide quality results for door construction, with yew favoring intricate craftsmanship and mahogany delivering durability alongside smooth finishing.
Maintenance Requirements
Yew doors require minimal maintenance due to their natural resistance to decay and insects, only needing occasional sealing or oiling to preserve their appearance and structural integrity. Mahogany doors demand more frequent maintenance, including regular polishing and sealing, to prevent moisture damage and maintain their rich color and smooth finish. Both woods benefit from protective coatings, but Yew's dense grain structure generally reduces the frequency of upkeep compared to Mahogany.
Cost and Availability
Yew wood is generally more expensive than mahogany due to its limited supply and slower growth rate, making it a rarer choice for doors. Mahogany is widely available in both domestic and imported varieties, offering a more cost-effective option without sacrificing durability or aesthetic appeal. Availability of mahogany ensures lower market prices and easier sourcing for large projects compared to the high cost and scarcity associated with yew.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Yew wood is highly sustainable due to its fast growth and ability to regenerate quickly, making it an eco-friendly choice for doors. Mahogany, while prized for its durability and rich color, often comes from slow-growing trees and is associated with deforestation concerns, posing sustainability challenges. Choosing yew supports responsible forestry practices, whereas mahogany requires careful sourcing from certified, well-managed forests to ensure environmental responsibility.
Best Applications for Yew and Mahogany Doors
Yew wood is best suited for interior doors due to its fine grain, high density, and natural resistance to decay, making it ideal for decorative and traditional panel doors. Mahogany excels in exterior doors because of its exceptional durability, rich reddish-brown color, and excellent resistance to moisture and insect damage, ensuring long-lasting performance in harsh weather conditions. Both woods offer stability and aesthetic appeal, with Yew preferred for intricate carvings and Mahogany favored for grand entryways.
Infographic: Yew vs Mahogany for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com